The Water Fast: How to, Benefits, and Tips for Success
Fasting has been used as a practice to promote health and overall well-being by many cultures for thousands of years.
A water fast is an ancient but newly popularized approach to fasting that entails eliminating all caloric intake and consuming only water for a prescribed period of time.
In the ancient world, prolonged water fasts were associated with religious rituals, providing both spiritual and physical benefits. Fasting was believed to cleanse the body, promote self-discipline, and open the mind to deep insights into the nature of existence.
But even during that time when we were just awakening to physical science, fasting was seen as a way to promote digestion and combat disease. Now, these observations are being confirmed and explained by modern science.
Contemporary research has highlighted many potential health-promoting properties of water fasting, including improved metabolic health, reduced inflammation, protection against various diseases, and cellular repair.
In this article, we’ll dive deeper into what the water fast is, how to do it, what benefits are available, and risks to watch out for.
[TOC]
What is a Water Fast?
A water fast simply means abstaining from any caloric intake for a specific period of time. During this fasting period, you only consume water.
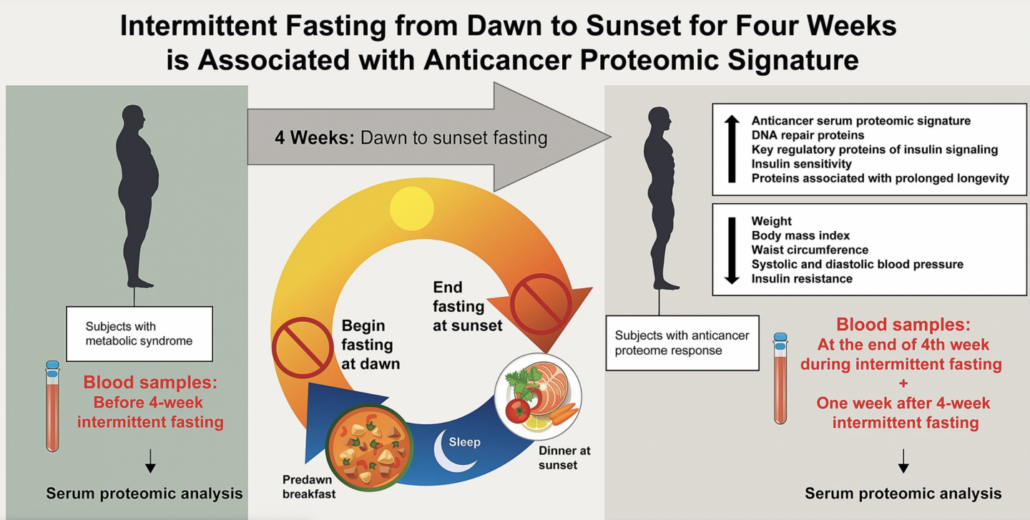
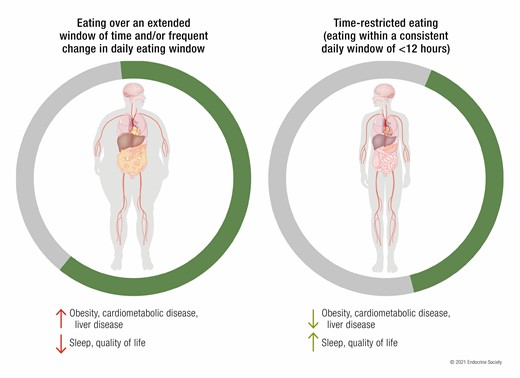
Most water fasts are considered prolonged fasts, lasting 24-72 hours. They are extensions of popular intermittent fasting approaches like 16/8 and OMAD.
Prolonged water fasts have been popularized by nutrition researchers like Dominic d’Agostino, who suggests doing up to 5-day water fasts two to three times per year in order to improve immune function and activate a deep state of cellular repair and renewal.
How to Do A Water Fast
On the surface, a water fast seems pretty simple: don’t eat, drink water. But to reduce the likelihood of uncomfortable side effects and to get the greatest benefits, here are a few helpful guidelines.
Eat Nutrient-Dense Foods
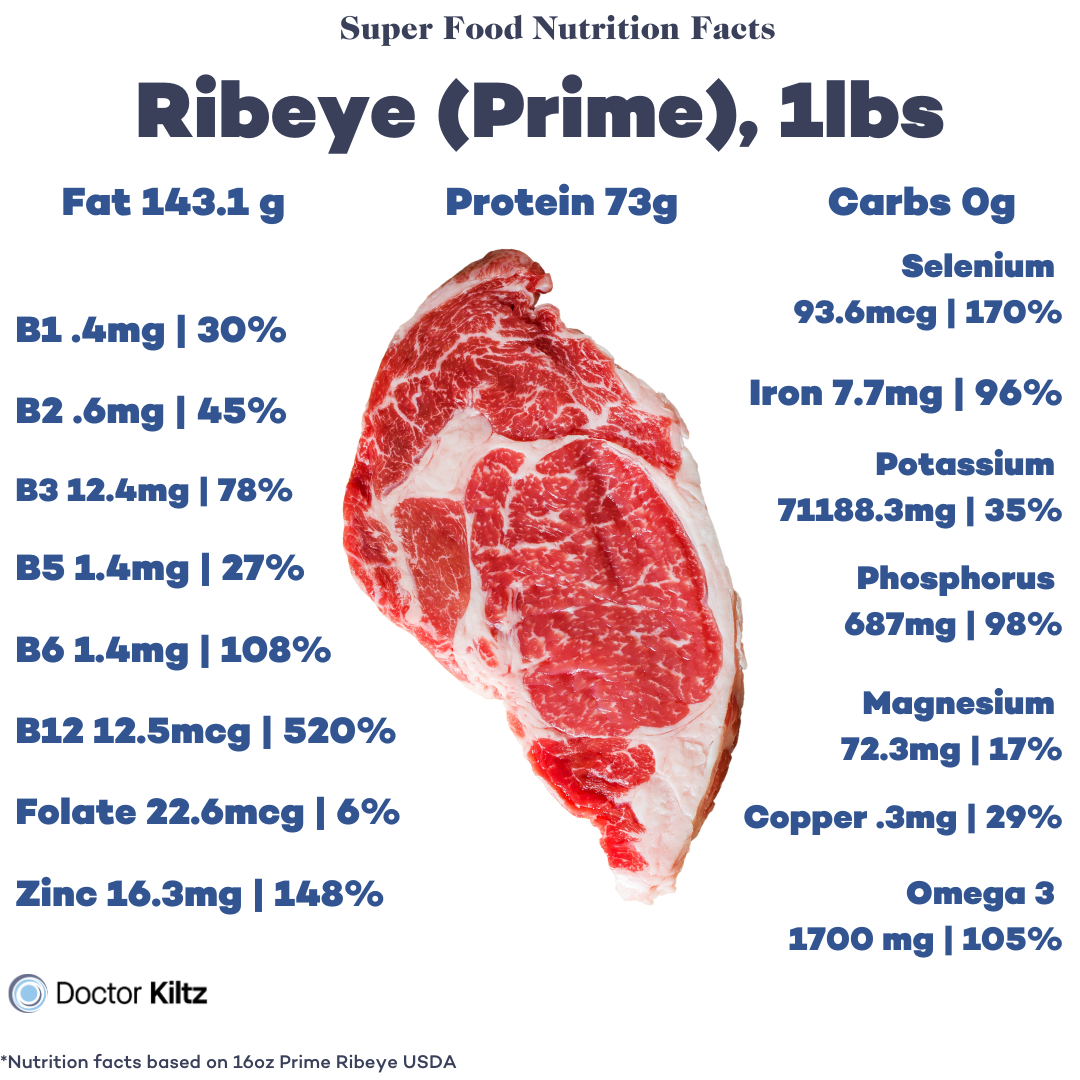
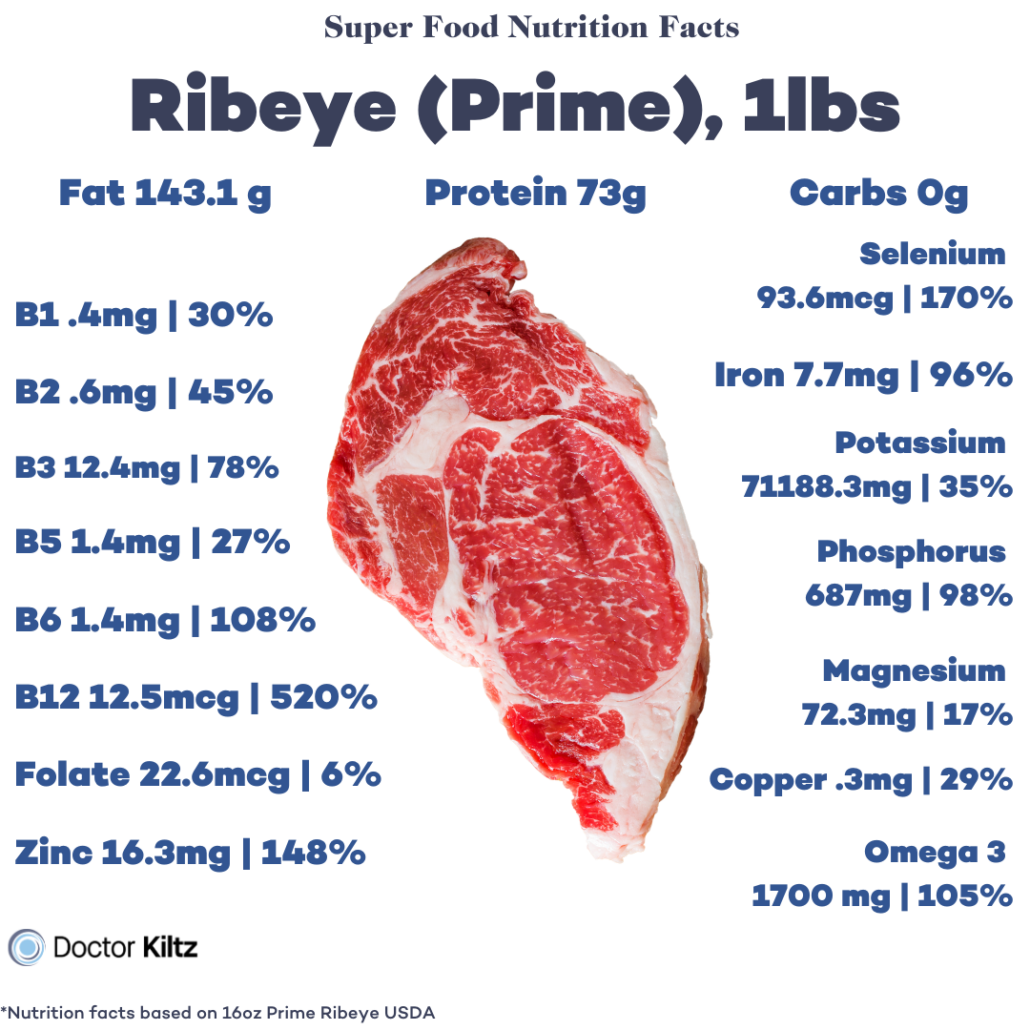
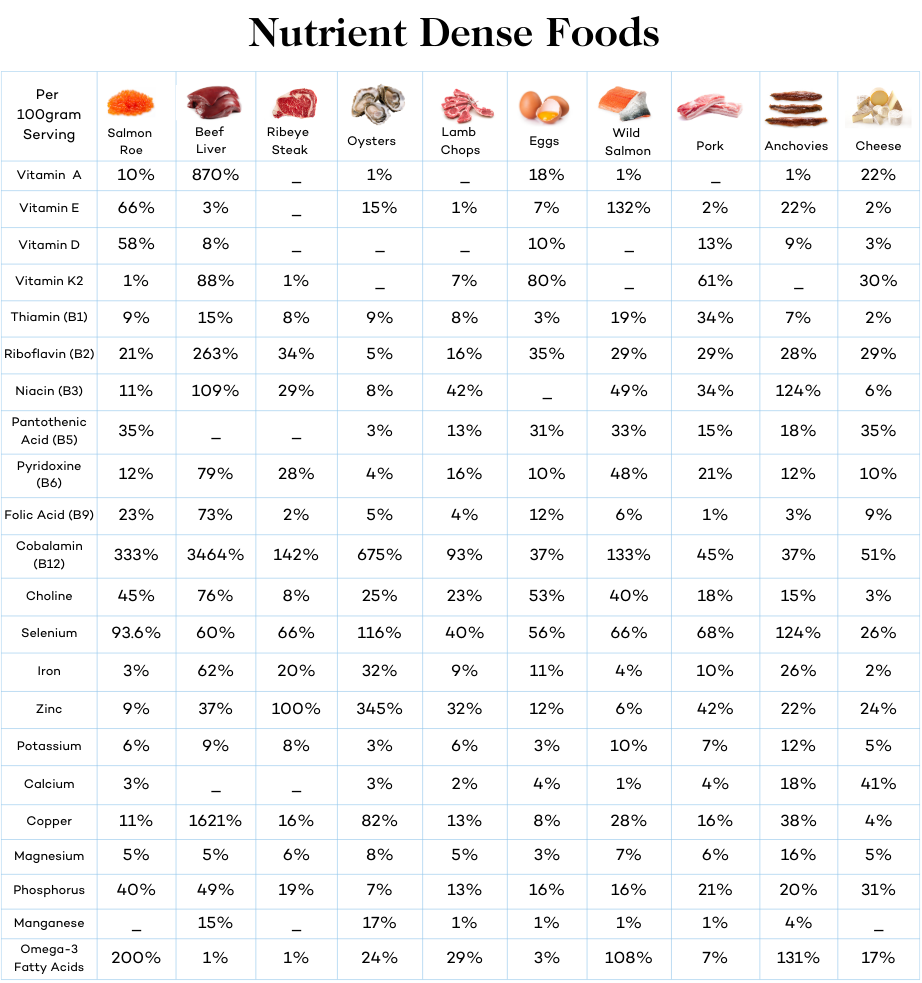
For at least two to three days before your fast cut all processed (if you’re serious about your health and wellness, it’s imperative to cut processed foods altogether) foods. Get all of your calories from nutrient-dense whole food, including:
- Red meat–steak, lamb, bison, pork
- Organ meats–liver, kidney, heart
- Fish and shellfish–wild salmon, oysters, mussels
- Animal fats–butter, ghee, tallow
- Full-fat dairy–blue cheese, cream, yogurt
By consuming these foods, you’re supplying your body with the ideal nutrients to sustain its physiological functions and nourish fasting-induced stem cells. At the same time, eating fattier foods and reducing carbs prepares your body for a fasted state, reducing side effects of the metabolic transition.
Intermittent Fasting
Fasting intermittently before a prolonged water fast trains your body to seamlessly enter a deep, prolonged fasted state.
This is especially helpful when preparing for a 48-72-hour fast.
You can even ease into the intermittent fasting protocol and gradually increase the intensity before entering a full water fast. Here’s an example of a graduated approach
- Time Restricted Eating: Eat only within an 8-hour window during daylight hours
- 18/6: Eat only within a 6-hour window during daylight
- OMAD: Eat only one large meal a day–usually within a 1-2 hour window.
Post Water Fast Refeeding
Consume much smaller than normal meals and chew your food completely.
Giving into your instinct to feast after a prolonged fast can trigger a dangerous condition called refeeding syndrome that can cause heart, blood, and brain issues do to acute metabolic and electrolyte changes.
For a 24-hour water fast, you only need to gradually re-introduce food for the following day. But after longer fasts, a gradual refeeding period can be good to maintain for up to three days.
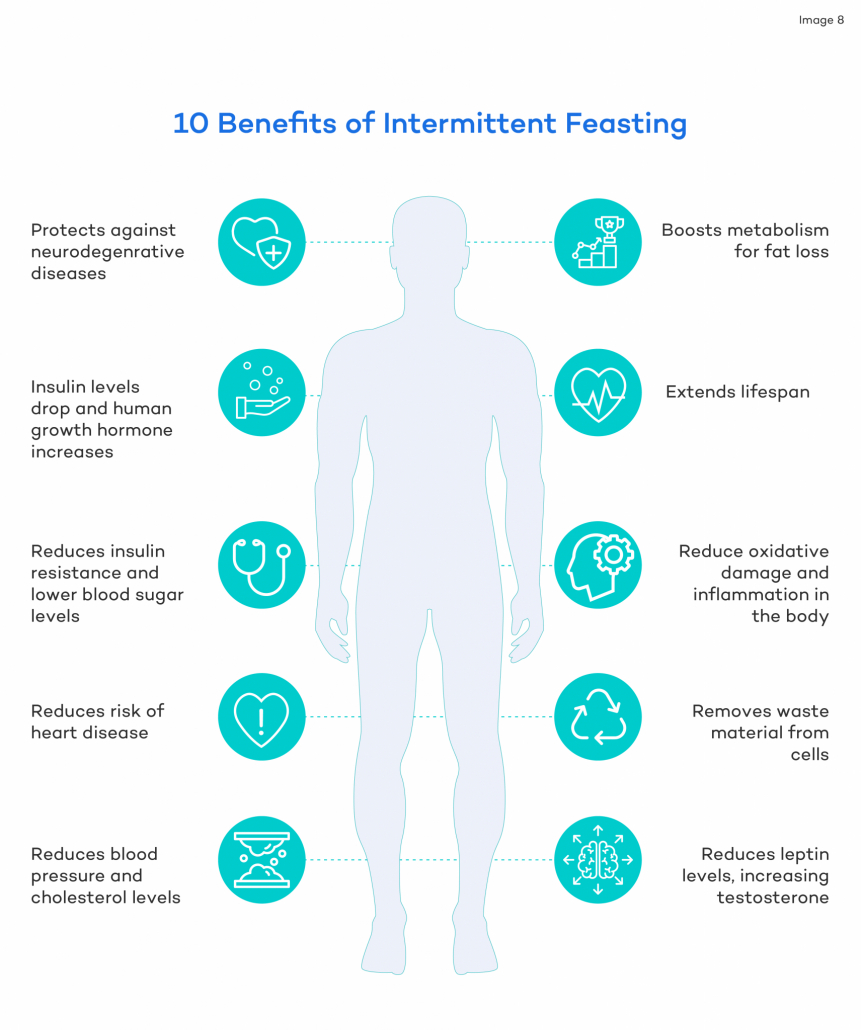
Potential water Fast Benefits
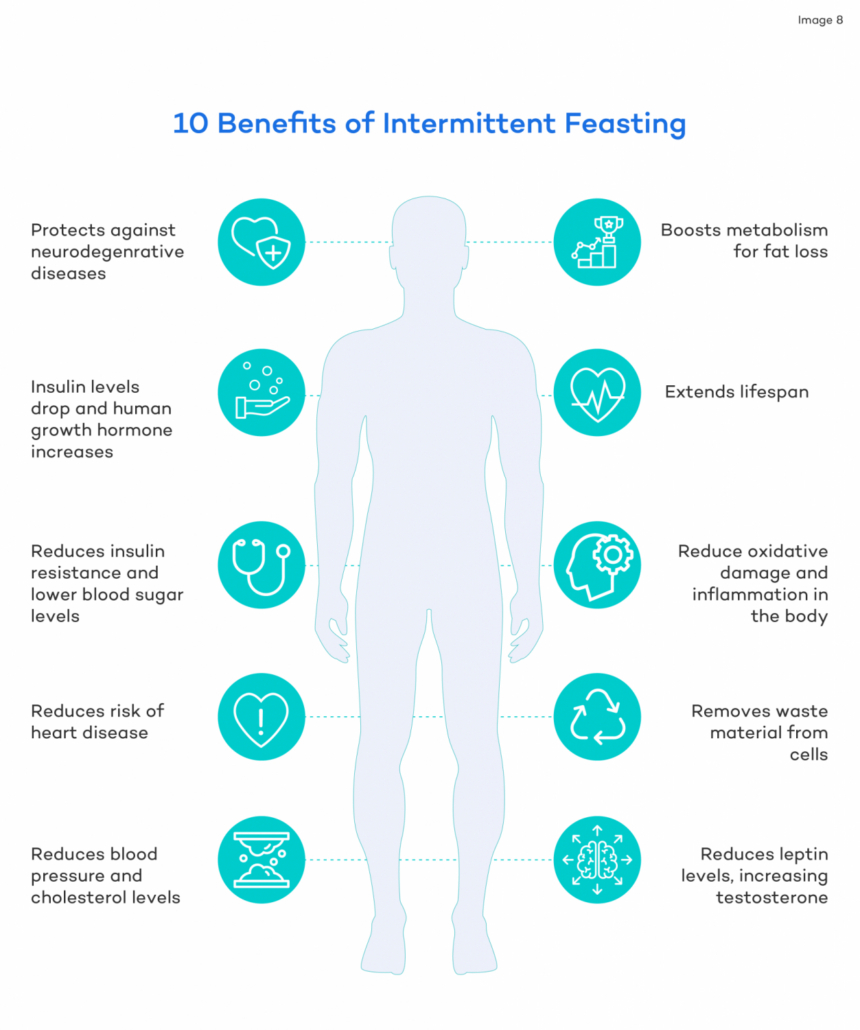
Studies show that water fasting activates various beneficial physiological processes that promote health benefits, including
- Protection against neurodegenerative disease
- Increased fat burning
- Reduced oxidative stress and inflammation
- Cellular repair and renewal (autophagy)
- Increases testosterone
- Reduced blood pressure and improved cholesterol levels
- Improves heart health
- Reduces insulin resistance and improves blood sugar control
- Increases beneficial hormones BDNF and HGH
Let’s take a closer look at a few of these key benefits.
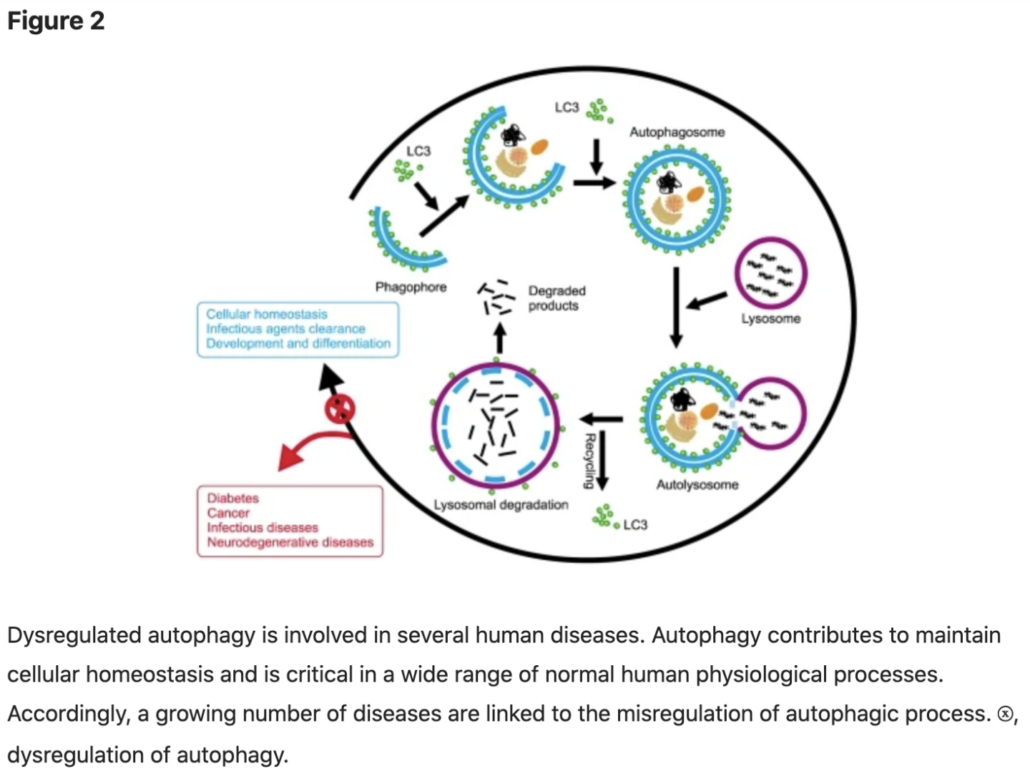
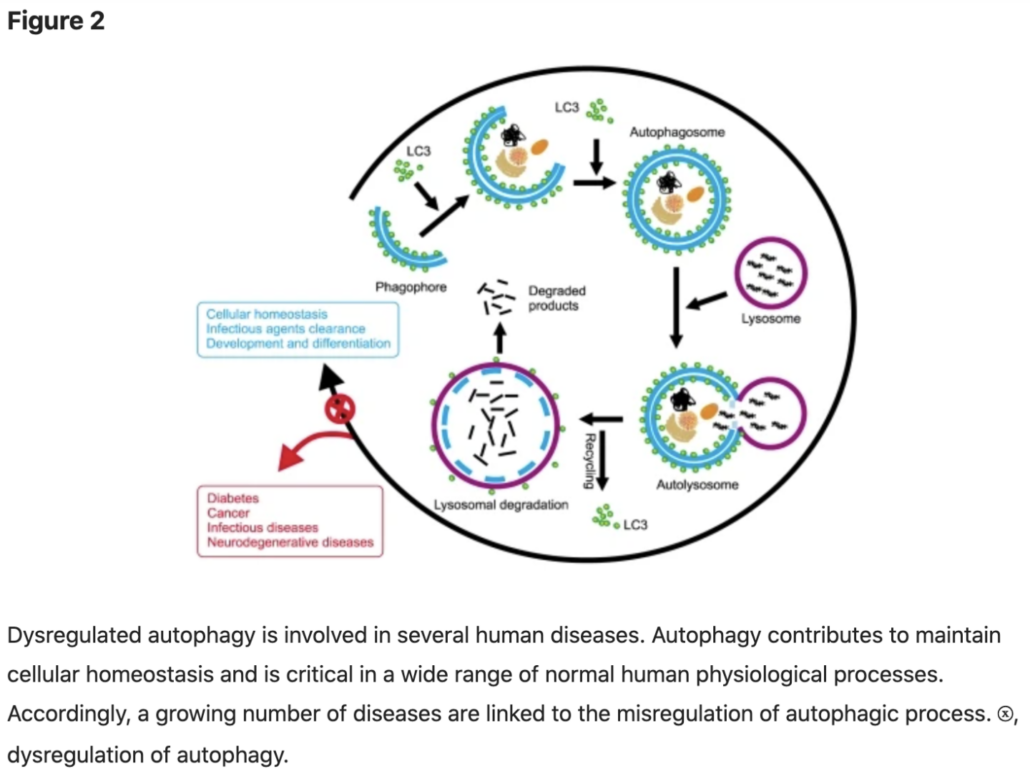
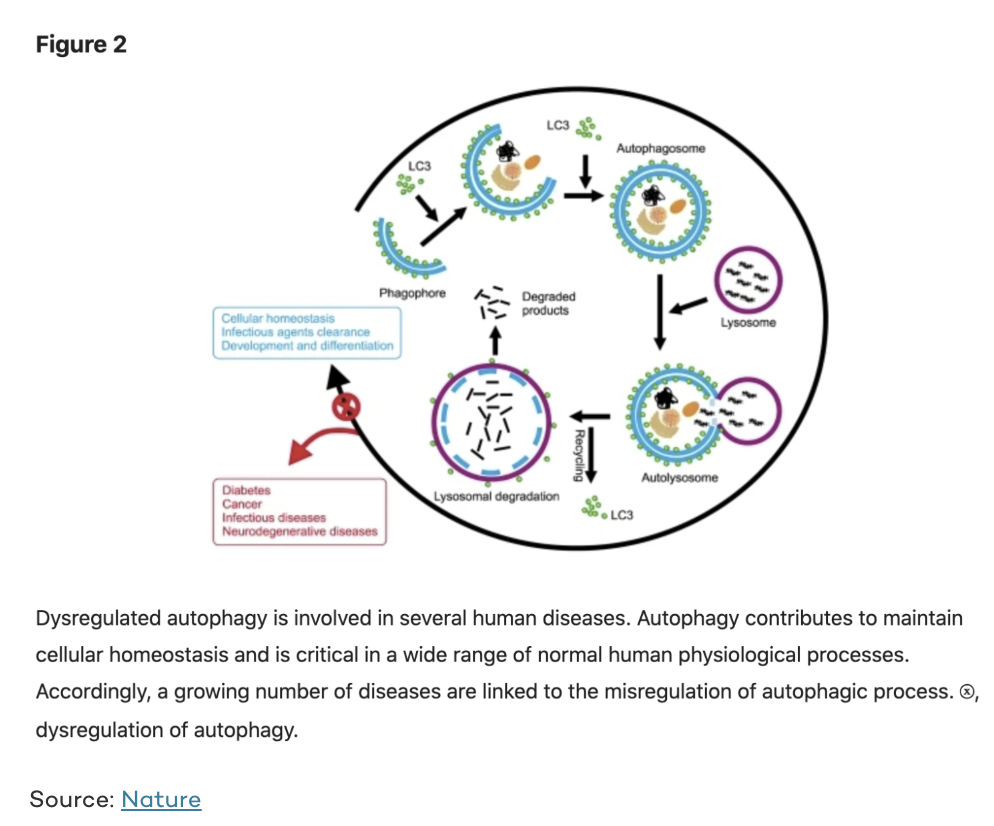
Autophagy (Cellular Repair and Renewal)
Autophagy is a process of cellular recycling and repair. The word means “self-eating,” which is an appropriate way to describe a process where old and worn out intracellular parts are cleared out and refashioned into fresh and functional cell parts.
Though a fairly recent discovery, autophagy is an incredibly important process that has been shown to offer protection from viruses, bacterial infection, and numerous diseases..
Though autophagy can be activated by shorter 16-18 hours fasts, prolonged water fasts can increase the autophagic action.
Researchers believe that autophagy is a central mechanism in many of the studied potential benefits of water fasting, including
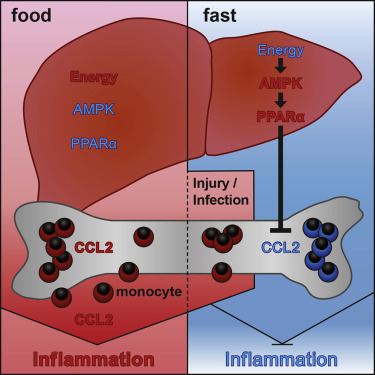
Reduce Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a deadly epidemic responsible for heart disease, stroke, respiratory diseases, cancer, obesity, autoimmune disorders, and diabetes.
These diseases are account for 3 out of 5 deaths worldwide. And 60% of Americans have one or more inflammatory conditions.
A water fast can reduce inflammation in three key ways
- Stimulates intestinal stem cells that heal gut permeability– when the gut leaks, pathogens enter the blood and travel throughout the body, causing inflammation.
- Activates the removal of inflammatory antigens, bacteria, and viruses via autophagy
- Reducing circulating monocytes–inflammatory white blood cells.
Studies have found that fasting reduces inflammation associated with
- rheumatoid arthritis
- Sjogren’s
- Multiple sclerosis
- diabetes
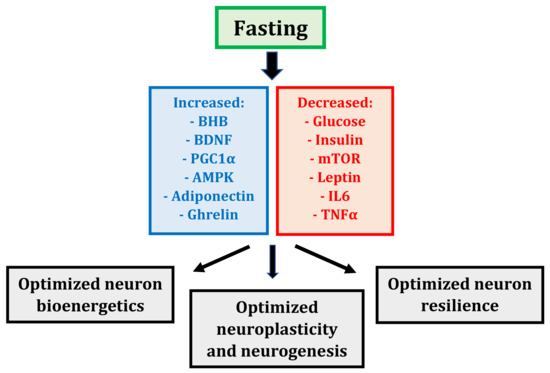
Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Studies have found that fasting can protect the brain from age-related degradation and improve cognitive function.
A study on men with mild cognitive impairment found that “Overall, the MCI-afflicted older adults who practiced IF regularly had better cognitive scores and reverted to better cognitive function at 36 months follow-up.”
A 2021 animal study found that fasting activated a gene linked to longevity and promoted brain growth and long-term memory consolidation.
Water fasts also support brain health by activating the production of powerful energy molecules made from fat called ketones, while simultaneously activating glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Each of these metabolic processes protects against neurodegenerative disorders.
Improved Insulin and Leptin Sensitivity
Insulin and leptin are important hormones associated with fat storage, hunger/satiety, and motivation (or lack thereof) for physical movement.
The high-carb standard American diet leads to both insulin resistance and leptin resistance. In both cases, this means that your body’s ability to receive and/or respond to the presence of these hormones becomes impaired.
In the case of insulin resistance, your body struggles to clear sugar from your blood, leading to a host of downstream diseases and disorders like fatty liver disease, type-2 diabetes, PCOS, and various chronic inflammatory conditions.
When your body is not responding properly to leptin, your brain thinks you’re starving even when you’ve had more than enough to eat. Instead of feeling full, you feel a need to keep eating, you have cravings for fattening, high-carb foods, and your body sends signals to conserve energy by making you less motivated to move.
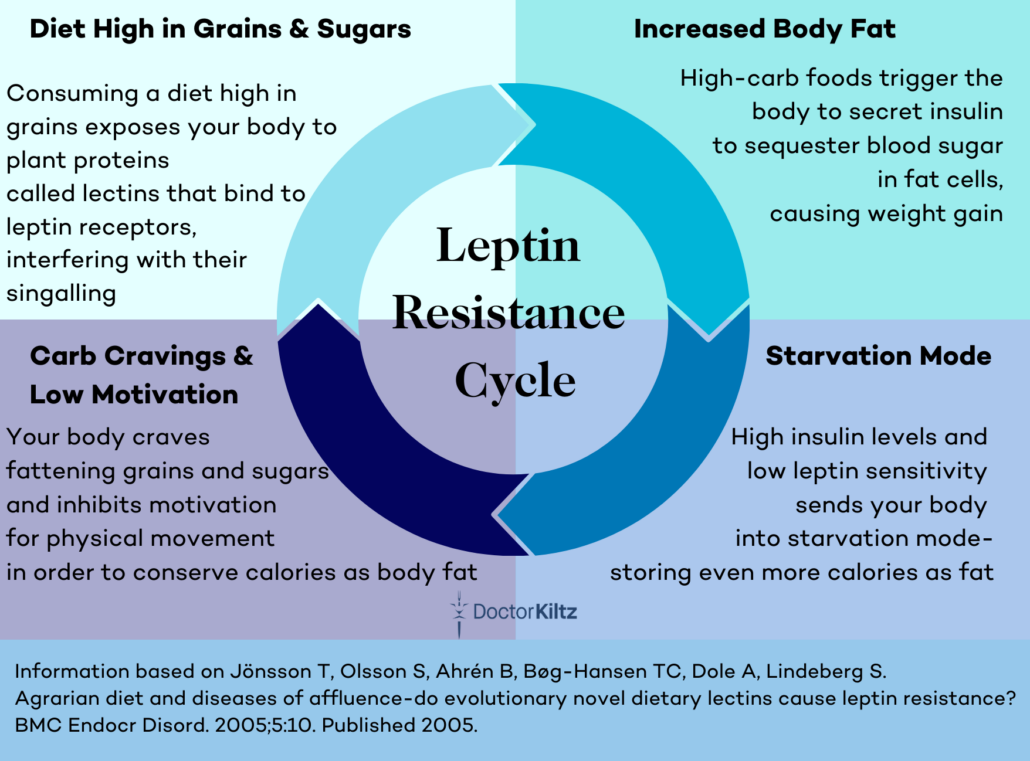
The good news is that water fasting has been shown to increase leptin and insulin sensitivity.
The drop in leptin has the added benefit of increasing testosterone.
Increased BDNF and HGH
A water fasts stimulates the production of two beneficial hormones called BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) and HGH (Human Growth Hormone).
BDNF has been called “miracle grow for the brain,” due to its ability to generate brain cell growth.
In animal studies, increased BDNF is associated with reduced depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases.
While in humans, studies have found that low levels of BDNF are associated with various neurodegenerative disorders.
HGH (Human Growth Hormone)
Water fasting for at least 24 hours can induce the production of HGH.
In one study with 200 participants, a 24-hour water fast increased HGH by a factor of 20 in men and 13 in women.
Higher circulating HGH (human growth hormone) is associated with better memory, more muscle mass, and reduced cortisol.
Weight Loss
During a water fast, insulin levels drop and norephedrine increases. This combination triggers your body to break down fatty acids into ketones.
Your body is essentially turning fat into fuel to maintain your muscle mass.
Water fasting for 24 hours has been shown to increase the rate at which your body converts nutrients and fat into energy by 14%.
Digestion Reset and Intestinal Healing
Our intestines are the first line of defense against food-borne pathogens and toxins. The standard American diet is loaded with substances that damage your intestines, including
- excess fiber
- Sugar
- naturally occurring plant toxins and antinutrients.
Chronis consumption of these substances can lead to intestinal permeability, which is associated with various chronic inflammatory disorders.
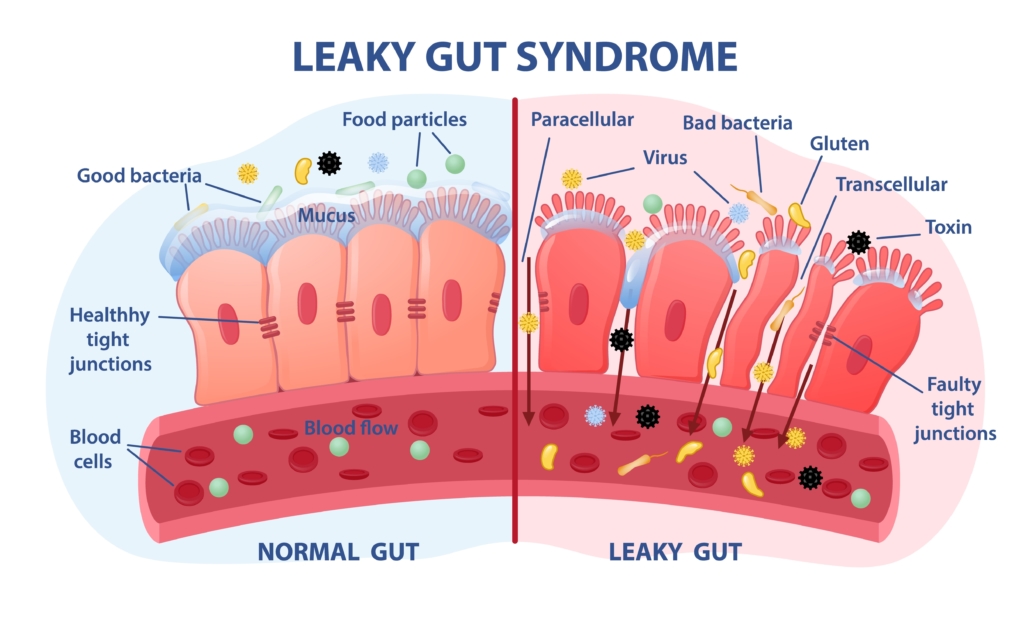
Researchers at MIT found that a 24-hour water fast “provided evidence that fasting induces a metabolic switch in the intestinal stem cells, from utilizing carbohydrates to burning fat.” And that this switch “enhanced [cell] function significantly.”
Who Should Not do a Water Fast?
Water fasting is safe and accessible for most people. However, there are a few groups that are better served by other dietary and lifestyle interventions. These include :
- People with gout
- People with type 1 diabetes
- Pregnant people
- Children
- People with eating disorders
Water Fast: The Bottom Line
Water fasting entails consuming only water for an extended period of time–usually 24-72 hours.
Both human and animal studies have linked water fasting to a variety of health benefits, including reduced inflammation, neuroprotection, insulin and leptin sensitivity, and weight loss.
Though more challenging than intermittent fasting protocols, water fasting has the potential to increase many of the benefits associated with fasting.
If you’re considering a water fast, it is important to prepare appropriately by consuming only nutrient-dense whole foods before and after your fast, easing into the fast by practicing intermittent fasting leading up to the water fast, and slowly re-introducing food afterward in order to avoid refeeding compilations.