We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Top 6 Whole Foods High in Vitamin D
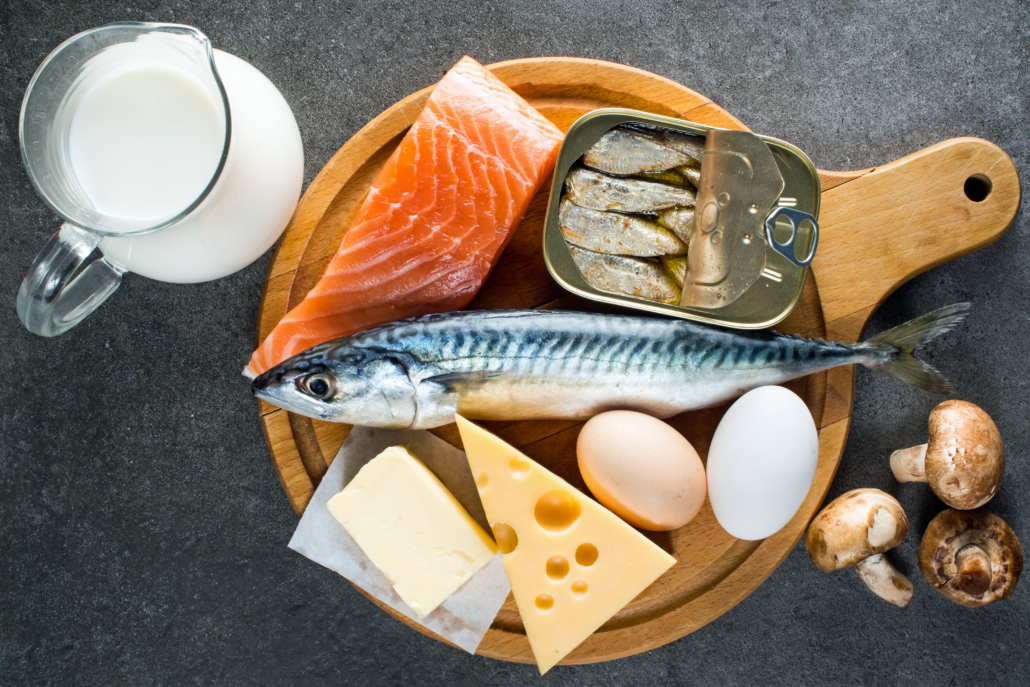

Though we can get most of our vitamin D from sunshine, an estimated 24% of Americans and 40% of Europeans are vitamin D deficient. Depending on the latitude and weather where you live, it may just be impossible to get enough vitamin D from the sun alone. This makes consuming foods high in vitamin D an important supplemental source.1
Vitamin D is a nutrient that is extremely important for the proper functioning of crucial physiological processes, including bone health and immune protection against viruses, infection, cancers, and chronic inflammation. 1
In fact, most organs and body tissues have vitamin D receptors, suggesting many more important roles that scientists are still discovering.2
In this article, we’ll introduce you to the top 6 whole foods high in vitamin D.
Table of Contents
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is both a nutrient we eat and a hormone that our bodies produce when exposed to ultraviolet-B rays from the sun. That’s why it’s often called the “sunshine vitamin.”
It’s also an essential vitamin, meaning that our bodies need to get if from outside sources–in this case, the sun and through our diet.
Roles of Vitamin D in Your Body
Vitamin D plays several other critical roles in the body, including:
- Bone health: Vitamin D helps the body absorb and retain calcium and phosphorus from food necessary for the development and maintenance of healthy bones and teeth.6
- Immune function: Vitamin D helps to regulate the immune system and may play a role in reducing the risk of various autoimmune diseases.5
- Antiviral properties: Studies also show that vitamin D is effective in reducing the severity of viral infections, including COVID-19. 3
- Muscle function: Vitamin D promotes muscle cell growth and reduces inflammation, both of which support strong, healthy muscles.5
- Cardiovascular health: Vitamin D reduces blood pressure and improves blood sugar control.5
- Cancer prevention: vitamin D may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including colon, breast, and prostate cancer.6
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need?
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for vitamin D looks at the necessary amount to maintain only one key role in the body–the maintenance of healthy bones, and protection against rickets, a disease characterized by weakening bones.
However, keep in mind that the RDA of vitamin D assumes very little sun exposure. What this tells us is that the optimal amount of vitamin D from food isn’t well established. And that it can change depending on the climate and the time of year.
In any case, here are the official RDAs
- Adults 19 years and older: 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults 70 years and older: 800 IU (20 mcg)
Keep in mind that people with darker skin are more likely to have lower levels of vitamin D, and may need to get more vitamin D from food and supplements.
This is because melanin–the pigment that makes skin dark–effectively shades the skin from UVB rays. Studies show that 20% of white adults and 75%-80% of black adults have low vitamin D levels in their blood.7 8
While an estimated 1 billion people worldwide are deficient in vitamin D. These deficiencies span all ethnicities and age groups.5
A word of warning: Sitting near a window while working or soaking up rays while driving won’t contribute to your vitamin D levels. Window glass blocks UVB ultraviolet light.
Can I Get Enough Vitamin D from Food?
The short answer is, yes, you can get plenty of vitamin D from foods high in vitamin D.
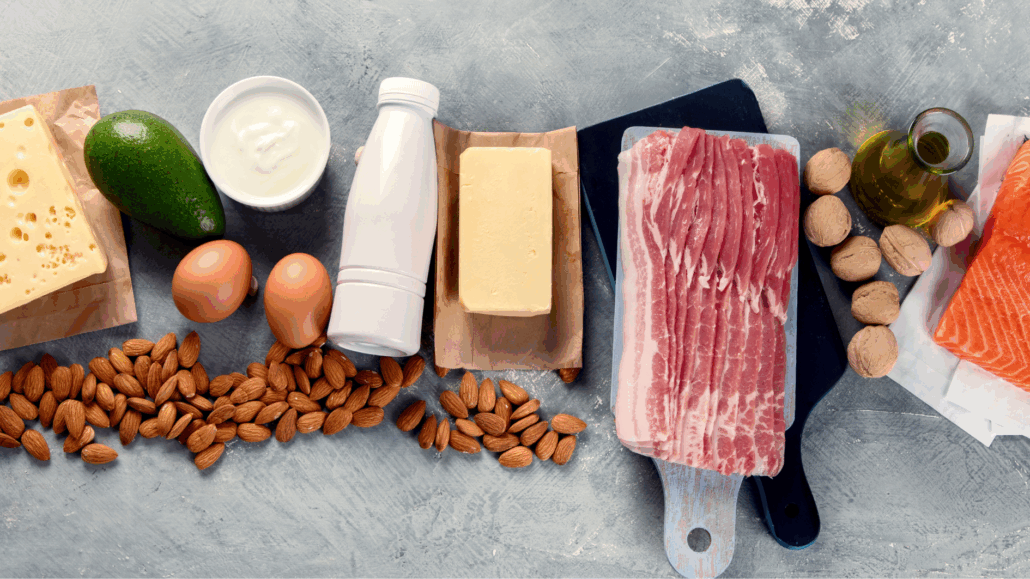
Since vitamin D is found mostly in animal products like fatty fish, egg yolks, cheese, pasture-raised pork products, and beef liver, people on meat-based diets like carnivore and keto have an easy time getting enough vitamin D from food.
For vegans and vegetarians, it’s more of a challenge. And across the board, many people rely on vitamin D supplements for their dietary RDA.
Top 6 Foods High in Vitamin D
These fatty whole foods will boost your vitamin D intake along with various other essential macro and micronutrients.
1. Pasture-Raised Lard

Pork, in general, is a decent source of vitamin D. While pasture-raised pork that gets to hang out in the sunshine can offer significantly higher concentrations.
Surprisingly, pastured lard is one of the best vitamin D sources on the planet, offering 1,000 IU of Vitamin D per tablespoon.[6] This makes lard nearly as high as cod liver oil.
Popular pork spareribs contain lower but still significant, 138 IU per 4-ounce serving.
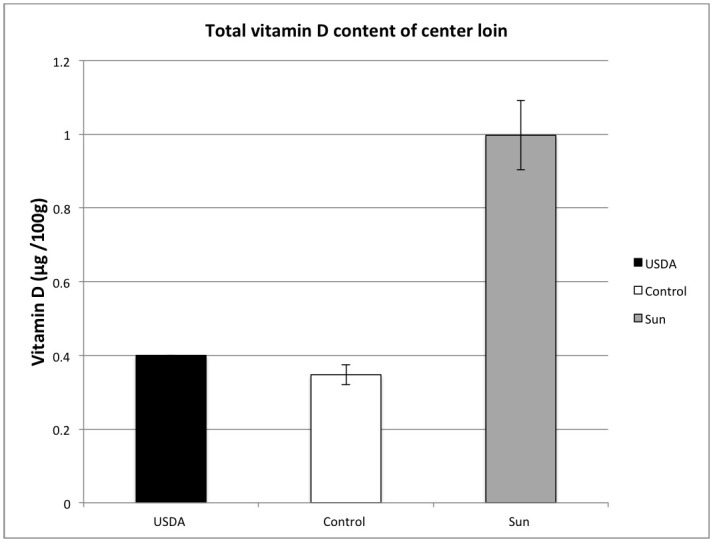
Source: Larson-Meyer DE, Ingold BC, Fensterseifer SR, Austin KJ, Wechsler PJ, Hollis BW, Makowski AJ, Alexander BM. Sun exposure in pigs increases the vitamin D nutritional quality of pork. PLoS One. 2017
2. Salmon

Salmon is loaded with healthy fats, including omega-3s. Stored amidst this fat is an abundance of vitamin D.
- 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of farmed salmon contains around 526 IU or 66% of the RDV. 4
- 3.5-ounce (100-gram) wild salmon can contain up to 160% of the RDV 5
2. Atlantic Mackerel
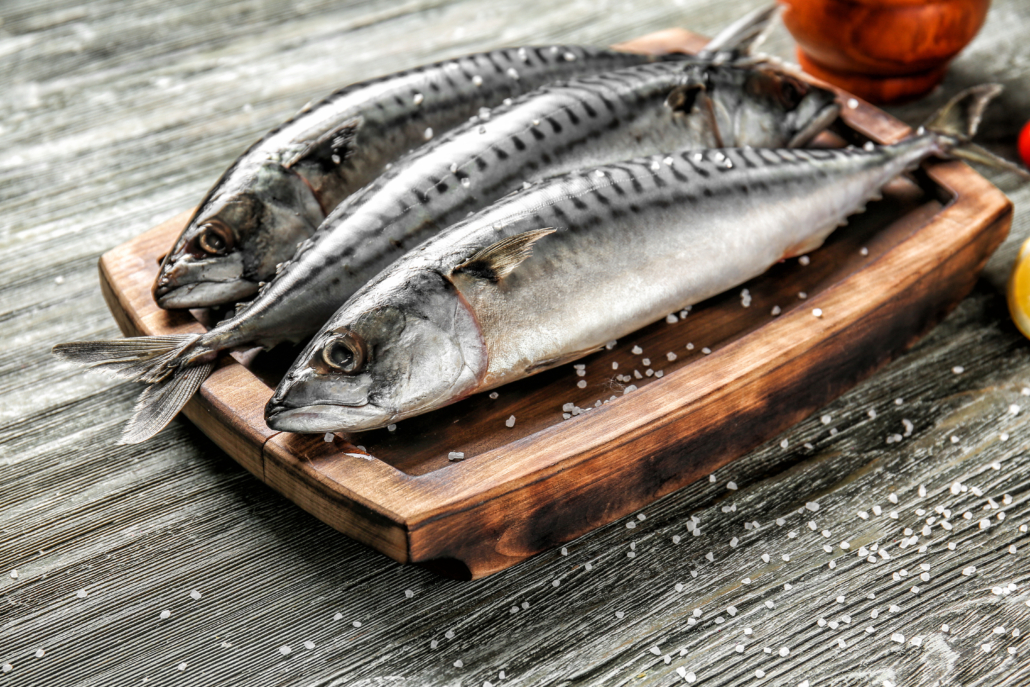

Atlantic mackerel is one of the most nutrient-dense foods out there, and most people it flys (er, swims) under the radar.
- 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of Atlantic mackerel provides 643 IU, or 91% of vitamin D 10
In addition to vitamin D, mackerel also offers a whopping 2990 mg of omega-3 per serving.
3. Oysters
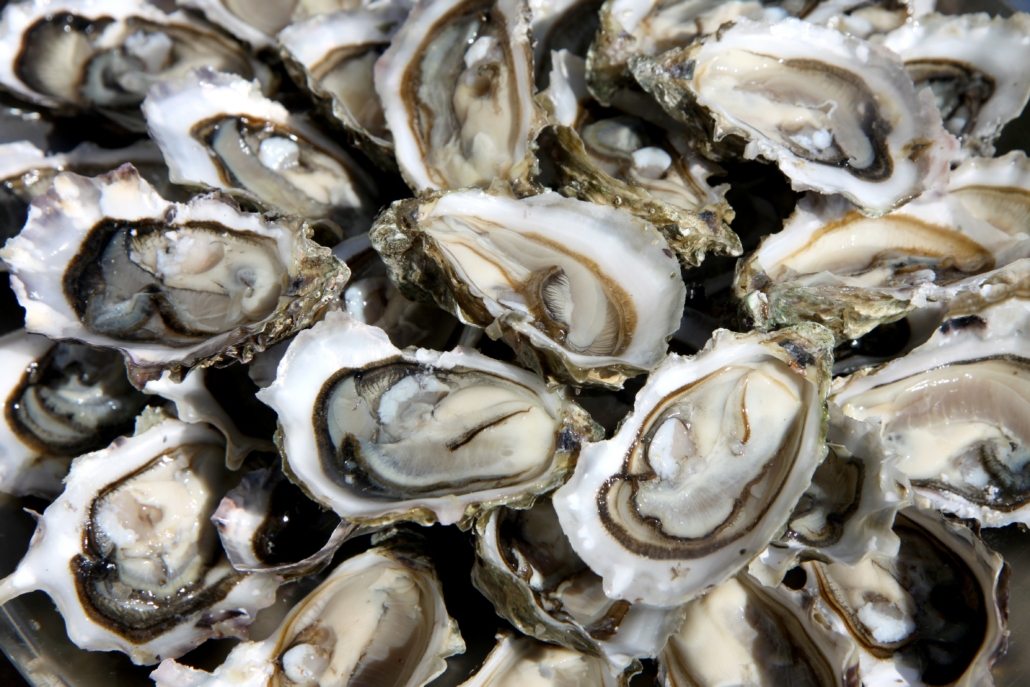

Oysters are a bonafide superfood with high levels of various essential nutrients.
In fact, the combination of zinc, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and selenium act as antioxidants in the body, combatting oxidative stress and reducing inflammation. [11] [12]
- 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of oysters provides 320 IU, or 80% RDV of vitamin D.
5. Egg yolks
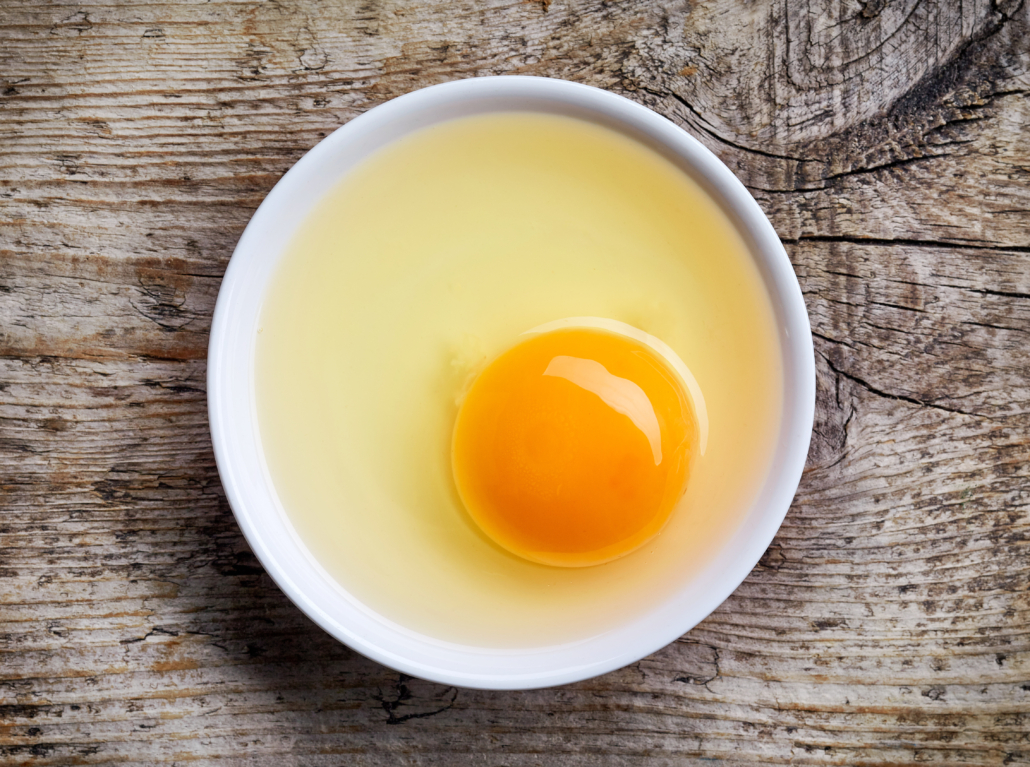

Eggs are another superfood loaded with nutrients. And this makes sense when considering that eggs need to contain all the essential ingredients for building an entire creature.
Keep in mind that the vitamin D in eggs is stored in the yolk–egg whites are a waste of nutrients. And if you haven’t heard, there is no longer an upper limit cholesterol. Our science has gotten better and we’ve finally admitted that dietary cholesterol is not associated with heart disease.
- One large conventional egg contains 37 IU of vitamin D, or 5% of the DV 18
- Eggs from hens fed a diet vitamin D-enriched diet may provide 250% of your RDV in vitamin D per egg.21
As with pork, pasture-raised chicken eggs have up to 6 times more vitamin D than conventional eggs. 19, 20
Two scrambled pastured eggs can provide over 200 IU of vitamin D. 6
6. Various Other Fish
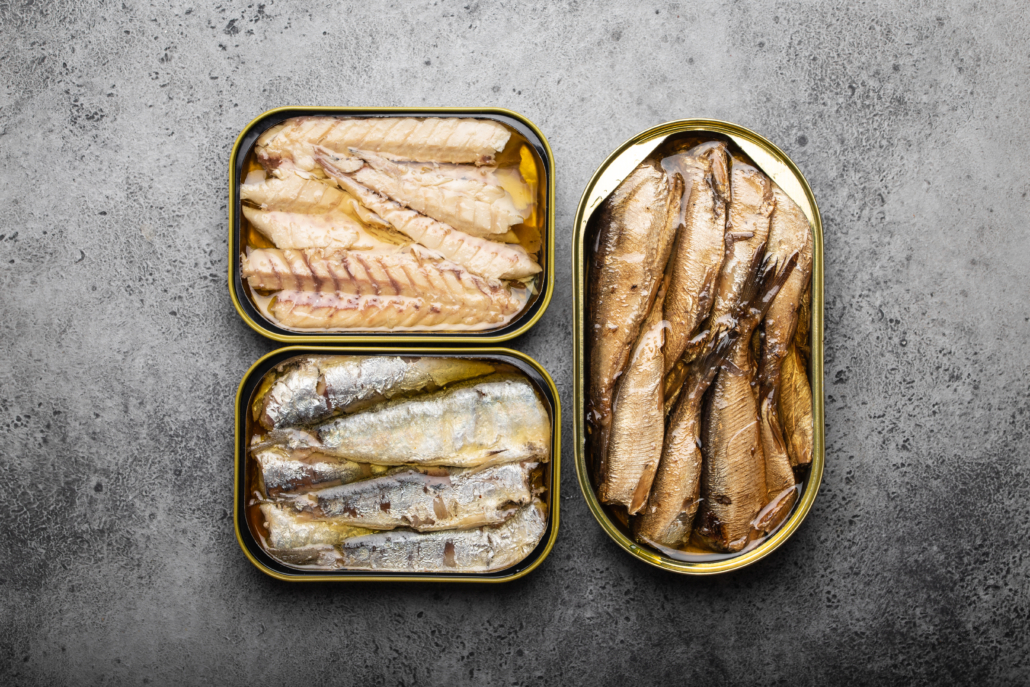

Noticing a trend? Fatty fish provide excellent to good amounts of vitamin D.
- Canned light tuna packs up to 269 IU of vitamin D in a 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving, which is 34% of the DV (15
- Fresh Atlantic herring provides 214 IU per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving or 27% of the DV. 6
- Halibut and mackerel provide 190 IU and 643 IU per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving
- Pickled herring is also a good source of vitamin D, providing 113 IU per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving, or 14% of the DV
- A 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of canned sardines provides 193 IU or 24% of the DV 8
Beware that most fish is contaminated with pollution. And the bigger the fish, the greater the likelihood of mercury contamination. 16
Foods High In Vitamin D: The Bottom line
Our bodies can make most of the vitamin D we need from sunshine. However, depending on your lifestyle and the climate and latitude of where you live, getting sufficient vitamin D from sunshine isn’t always possible.
This is where foods high in vitamin D become important dietary sources.
The top sources of vitamin D include
- Pasture-raised lard (and pork products to a lesser extent)
- Salmon
- Atlantic mackerel
- Oysters
- Egg yolks–especially from pasture-raised hens
- Various fatty fish, including sardines, anchovies, and herring
In addition to vitamin D, these whole animal products provide a dense matrix of other essential nutrients.
Though it is possible to get vitamin D from supplements, and from foods fortified with vitamin D (milk and organ juice), sticking with whole food sources is a smart way to increase your intake of all your macronutrient and micronutrient needs.