We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Top 5 Keto Superfoods To Help You Thrive

Table of Contents
Keto is a low-carb way of eating, so people tend to focus on what they have to remove, but just as important are these 5 keto superfoods that you can enjoy in abundance.
These 5 keto superfoods will help you achieve your macro and micronutrient needs without sacrificing your culinary pleasure.
What is keto?
A ketogenic (keto) diet means eating high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-to-no carbohydrates. This macronutrient ratio switches the body from using carbohydrates for fuel, to turning fat into energy molecules called ketones. When ketone levels become elevated, you are in the metabolic state called ketosis, hence the name “keto diet”.
The macronutrient profile of a ketogenic diet looks like this:
- 70-80% of calories from fat
- 15-30% calories from protein
- 0-10% calories from carbohydrates
Many people think of the ketogenic diet as a way to lose weight. But most people are unaware that a keto diet can be used to treat many other chronic and serious health issues.
Ketogenic diets have been in use for over 100 years to treat epilepsy. And research over the last couple of decades has shown ketogenic diets are also effective for the treatment of cancer , neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s , type 1 and type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease among many others.
What are superfoods?
The term “superfood” might seem impressive, but in reality it’s just clever marketing. It was invented by marketing teams trying to sell specific types of food, not by food scientists trying to help educate people!
If bananas and muffins were among the first so-called superfoods, this type of marketing isn’t especially scientific — but it works.
A brief history of superfoods
The term superfood was coined as early as 1915. In 1917 it was used by the United Fruit Company to champion the humble banana’s nutritional status. According to this source, bananas were a cheap, easily digestible superfood protected from mold by their thick outer skin.
The term superfood began being used more prominently in 1949 when a Canadian newspaper described a special type of muffin as “a superfood that contained all the known vitamins and some that had not been discovered.”
Since that time, marketers have had it easy — to promote a certain food, all they have to do is rebrand it as a superfood!
Medical journals and governments have endorsed the superfood concept, too. In 1999 the USDA inadvertently boosted blueberry sales by declaring them among the most powerful superfood antioxidants.
Over the years foods as diverse as kale, seaweed, and ginger have also enjoyed the popularity that comes with promising initial research and superfood labeling. While some experts say the term superfood is imprecise and/or misleading, others say it’s a functional way to describe above-average foods.
How to Define Superfoods
If clever marketers came up with the term, how do we objectively decide which foods make the cut?
Miriam Webster offers a somewhat helpful definition for superfoods:
“A food (such as salmon, broccoli, or blueberries) that is rich in compounds (such as antioxidants, fiber, or fatty acids) considered beneficial to a person’s health.”
To be a little more specific, superfoods are believed to be unusually rich in antioxidants, fiber, fatty acids, or other health-promoting compounds. The thinking goes that superfoods are nutrient-dense and that this allows them to directly impact your health. People buy and eat superfoods for therapeutic reasons like fighting inflammation, warding off aging, losing weight, sleeping better, and more.
Animal vs. plant superfoods
Most foods marketed as superfoods are plant-based, not animal-derived: kale, blueberries, maca root powder, are some recent examples.
But when you look at the head-to-head comparisons, the superiority of plant foods quickly gets called into question.
In addition to being higher in nutrients than most plant-based superfoods, animal-derived superfoods are lower in plant toxins and antinutrients. Many of the most popular plant-based superfoods contain hidden antinutrients like phytic acid that lockout and deplete important nutrients like zinc and calcium. This means plant many superfoods are much lower in net nutrients than originally thought.
If you’re trying to up your fat-soluble vitamin intake, animal-derived superfoods offer a clear advantage over plant-based alternatives.
What makes a keto superfood?
The major ingredients in superfoods can be divided into two primary categories: micronutrients and macronutrients.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are nutrients that confer metabolic benefits without providing calories. When we talk about the micronutrient profile of superfoods, we’re referring to their vitamin, mineral, enzyme, and antioxidant content.
These types of nutrients aren’t used for fuel as much as they’re used as cofactors and catalysts for biological processes.
These complex processes take place on the chemical level and contribute to every important system in the body including brain and bone health, vision, fertility, sleep, mood, and immunity among others.
For example, vitamin A is a prominent micronutrient found in many superfoods. Vitamin A benefits the skin and is essential for properly functioning vision. In terms of bioavailability, the best source of vitamin A is preformed vitamin A from animal foods — as opposed to the carotenoid forms of the vitamin found in plant foods.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are nutrients that provide calories. (In many cases they also confer metabolic benefits, just like micronutrients do.) The three main types of macronutrients are fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Your body needs much larger amounts of macronutrients than it does micronutrients.
While superfoods are by definition rich in micronutrients, their macronutrient content can vary widely. Beef liver is rich in all three macros, for example, while much-touted plant superfoods like kale are low in all three and don’t contain many calories.
Keto Superfood #1: Rib Eye

Ribeye is delicious and nutritious. It’s rich in calories, healthy fats, proteins, and a wide variety of important fat and water-soluble vitamins. There are few foods as satiating and satisfying as rib eye!
Is rib eye keto-friendly?
Yes — ribeye is completely keto-friendly. It contains no carbohydrates whatsoever. As an added plus, most types of ribeye have close to the ideal 2:1 fat to protein ratio that keeps your body from convert protein into carbs via gluconeogenesis.
Note here that even though the gram weight of fat to protein is about equal, fat has twice as many calories per gram as protein.
| Nutrient | 225g Rib Eye | Recommended Daily Value (RDV) | % RDV |
| Calories | 655 cal | 2500 | 18.6% |
| Protein | 54g | 60g (Standard Diet, not Keto) | 90% |
| Fat | 50g | 30g (Standard Diet, not Keto) | 166% |
| Saturated Fat | 23g | 20g (Standard Diet, not Keto) | 115% |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 25g | ||
| Carbohydrates | 0g | 1200g (Standard Diet, not Keto) | 0% |
| Niacin (B-3) | 13.5mg | 16mg | 30% |
| B 6 | 1.4mg | 2mg | 70% |
| Selinium | 56.25 mcg | 67mcg | 84% |
| Iron | 3.24mg | 20mg | 16% |
| Magnesium | 144mg | 420mg | 34% |
| Zinc | 9.45mg | 11mg | 86% |
| Potassium | 666mg | 4000mg | 17% |
| Phospherus | 400mg | 700mg | 57% |
Ribeye: top highlights
Ribeye is an excellent source of heme iron, B vitamins, zinc, and more. Grass-fed ribeye is also rich in beneficial fats like conjugated linoleic acid and stearic acid. It even contains some omega 3’s.
Another benefit: ribeye is rich enough in creatine to be mildly anabolic, or muscle-building. These anabolic properties benefit more than just bodybuilders — studies have correlated muscle mass with increased longevity and healthspan in all people.
If you need more convincing about the healthiness of red meat, you can learn more here
Keto Superfood #2: Beef Liver

Beef liver may very well be nature’s original superfood. It’s incredibly high in hard-to-get B vitamins and contains every vitamin and mineral you need to survive and thrive. Traditional cultures regarded beef liver as sacred — you might want to, as well!
Is beef liver keto-friendly?
Liver does contain some carbs (especially if it’s fresh), but it’s still compatible with a low-carb, high-fat diet. One only needs small amounts of liver to hit all their RDA’s, which means that its trace carbohydrate content doesn’t get the chance to really add up.
We also recommend slathering protein-rich liver with healthy fats like tallow and butter in order to reach your keto macronutrient ratio goals.
Nutrition *per 100g
| Nutrient | Amount | % of Recommended Daily Value (RDV) |
| Calories | 135 | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 3.9g | 1% |
| Total Protein | 20.4g | 41% |
| Total Fat | 3.6 | 6% |
| Vitamin A | 16899 IU/ 5096.4 mcg | 338% |
| Vitamin C | 1.3 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 16.0 IU/ 0.4 mcg | 4% |
| Vitamin E (Alpha Tocopherol) | 0.4 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 3.1 mcg | 4% |
| Thiamin | 0.2 mg | 14% |
| Riboflavin | 2.8 mg | 162% |
| Niacin | 13.2 mg | 66% |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.1 mg | 54% |
| Folate | 290 mcg | 72% |
| Vitamin B12 | 59.3 mcg | 988% |
| Pantothenic Acid | 7.2 mg | 72% |
| Choline | 333 mg | |
| Betaine | 4.4 mg | |
| Calcium | 5.0 mg | 1% |
| Iron | 4.9 mg | 27% |
| Magnesium | 18.0 mg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 387 mg | 39% |
| Potassium | 313 mg | 9% |
| Sodium | 69.0 mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 4.0 mg | 27% |
| Manganese | 0.3 mg | 16% |
| Selenium | 39.7 mcg | 57% |
Nutrition Table
Liver: top highlights
Liver is an incredible source of folate, vitamin B12, pantothenic acid, riboflavin, niacin, and vitamin A. It might as well be renamed the energy organ.
It’s worth noting that liver is so high in vitamin A that you may want to treat it more like a supplement than a dietary mainstay. Excess vitamin A can be very difficult for your body to clear out.
Liver & fertility
The folate and preformed vitamin A found in beef liver are critical nutrients when it comes to fertility. A deficiency of both nutrients are associated with higher rates of birth defects, including palate malformation and neural tube defects.
Thankfully, preventing these types of defects is as easy as ensuring adequate intake before and during pregnancy — which is exactly what ancient cultures did.
Folate is so important for gestational health that it’s now present in all fortified cereal products. However, the natural folate in liver is easier for your body to process and utilize than its synthetic equivalent.
On another note, liver isn’t the only organ meat that should be viewed as a keto superfood. Many other organ meats deserve superfood status, too!
Keto Superfood #3: Salmon Roe
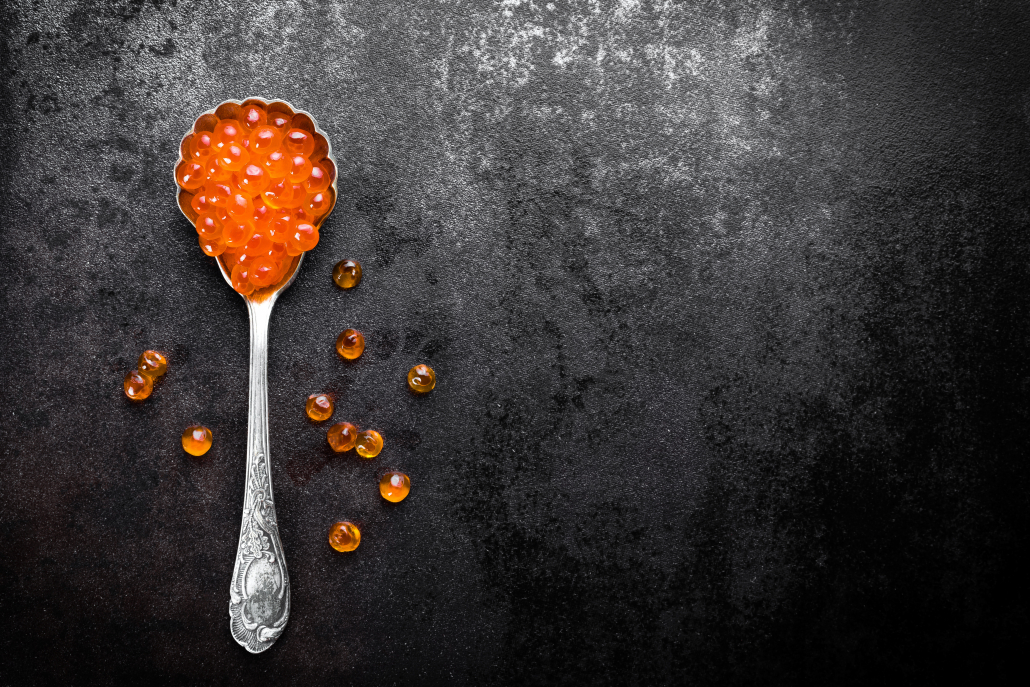

Salmon roe is another incredibly nutrient-dense, keto-friendly food. Also known as fish eggs, roe is rich in omega 3 fatty acids (DHA and EPA), vitamin D, vitamin B12, and many trace minerals.
Just as impressive as these nutrients is their quality. The omega 3’s present in salmon roe are found in a phospholipid form that allows them to easily enter the brain.
Is salmon roe keto-friendly?
Salmon roe is perfectly keto-friendly. It’s about 3% carbohydrates by weight, which doesn’t amount to much given that only small amounts of roe need to be eaten.
| Nutrient | 100g of Salmon Roe | Recommended Daily Value (RDV) | % RDV |
| Calories | 250 calories | 2,500 calories | 10% |
| Protein | 29 grams | 50 g (standard diet, not keto) | 58% |
| Fat | 14 grams | 30 g (standard diet, not keto) | 47% |
| Carbohydrates | 2.9 grams | 120 g (standard diet, not keto) | 2.4% |
| Niacin | 1.8 milligrams | 16 mg | 20% |
| Selenium | 40 micrograms | 70 mcg | 73% |
| Iron | 0.6 milligrams | 20 mg | 3.3% |
| Magnesium | 20 milligrams | 420 mg | 4.8% |
| Zinc | 1 milligram | 11 mg | 9% |
| Potassium | 221 milligrams | 4000 mg | 4.7% |
| Phosphorus | 402 milligrams | 700 mg | 32% |
Salmon roe & fertility
Salmon roe’s nutrient profile may have special value for pregnant women. Its omega 3:6 ratio is off the charts, and research has shown that restoring this ratio back to more even levels reduces obesity and relieves inflammation.
The phospholipid omega 3’s in roe provide easily-absorbed DHA to the brains of growing babies and their mothers alike.
Ancient cultures understood that salmon roe could benefit the growing baby, even though they didn’t understand what particular ingredients gave it that ability. Weston Price found that landlocked peoples stopped at almost nothing to provide fish roe to their childbearing women.
Salmon roe is good for male fertility, too. Studies have found that low omega 3 levels in men are associated with lower fertility rates. Thankfully, this condition appears reversible: other studies have shown that DHA supplementation can restore fertility to infertile mice. Salmon roe’s 10:1 ratio of omega 3:6 can help rebalance this important ratio.
Salmon roe: top highlights
Salmon roe is nature’s best source of omega 3 fatty acids, solidifying its place among keto superfoods.
Salmon roe is also unusually rich in antioxidants for animal food. Its primary antioxidant is called astaxanthin. Research has found that this antioxidant may protect against UV rays and other types of oxidative stress.
All in all, there’s probably no better food to eat if you want to invest in the future health of you and your children.
Keto Superfood #4: Eggs

Within their delicate shell, eggs contain everything needed to form a new animal–they’re essentially a nose-to-tail superfood.
With a full-spectrum blend of healthy fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, eggs contain almost everything needed to sustain our body’s most important biological functions.
Are eggs keto-friendly?
Yes: eggs are virtually carb-free. They’re rich in complete proteins and keto fats, too. One can eat dozens of eggs a day and still stay in ketosis. (In fact, if you’re trying to improve your body composition, this might be a great idea!).
| Nutrient | 100g of Eggs | Recommended Daily Value (RDV) | %RDV |
| Calories | 63 calories | 2,500 calories | 2.5% |
| Protein | 12.6 grams | 50 g (standard diet, not keto) | 25% |
| Fat | 5.6 grams | 30 g (standard diet, not keto) | 19% |
| Carbohydrates | 0.7 grams | 120 g (standard diet, not keto) | 0.06% |
| Niacin | 0.34 mg | 16 mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 20 mcg | 70 mcg | 36% |
| Iron | 1.75 mg | 20 mg | 8.75% |
| Magnesium | 6 mg | 420 mg | 1.4% |
| zinc | 1.29 mg | 11 mg | 12% |
| Potassium | 83 mg | 4000 mg | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 113 mg | 700 mg | 16% |
Eggs & fertility
Eggs are a great fertility food, largely for the same reasons as salmon roe: essential fatty acids.
Research hints that consuming the right blend of omega 3, omega 6, and omega 9 fatty acids may improve fertility in women. Free-range eggs from chickens fed their natural diet have a great omega 3:6 ratio.
Male fertility may also improve from egg consumption. Up to 80% of male infertility is due to oxidative stress, and eggs contain powerful antioxidants that directly address this problem.
Eggs are a rich source of the B vitamin choline, too. A single egg contains ~ 140 milligrams of choline — 25% of one’s RDV. Given that 90-95% of pregnant women don’t consume the recommended amount of choline, pregnant mothers would do well to include some eggs in their diet. The egg’s yolk contains pretty much all its choline, so don’t just eat the whites!
Eggs: top highlights
All in all, eggs are a recipe for better heart health, more anabolism, and improved fertility.
You can learn more about the goodness of pastured eggs, here.
Keto Superfood #5: Bone Marrow
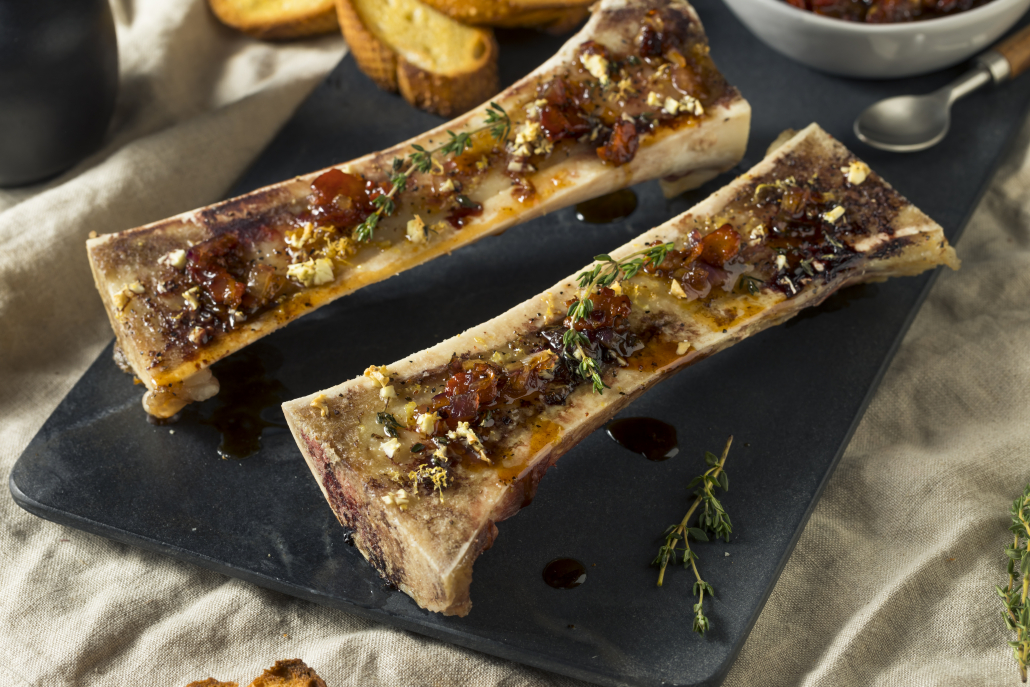

Bone marrow is a spongy substance found in the center of bones. Marrow has a rich, subtly sweet flavor that makes it a great base for sauces and soups.
Is bone marrow keto-friendly?
Bone marrow is very keto-friendly. It contains no carbs and is loaded with healthy fats. If you’re struggling to get in enough fat calories on your keto diet, bone marrow is a perfect addition.
| Nutrient | 100g of Bone Marrow | Recommended Daily Value (RDV) | %RDV |
| Calories | 770 calories | 2,500 calories | 30% |
| Protein | 7 grams | 50 g (standard diet, not keto) | 14% |
| Fat | 80 grams | 30 g (standard diet, not keto) | 266% |
| Carbohydrates | 0 mg | 120 g (standard diet, not keto) | 0% |
| Niacin | 0.4 mg | 16 mg | 3% |
| Selenium | 20 mcg | 70 mcg | 36% |
| Iron | 0.8 mg | 20 mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 1.8 mg | 420 mg | 0.4% |
| Zinc | 0.1 mg | 11 mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 137 mg | 4000 mg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 7 mg | 700 mg | 1% |
Bone marrow for skin health
Bone marrow is an excellent source of collagen, which means it can support healthy skin and bones. Research has found that supplementing your diet with collagen may improve skin health and reduce aches and pains. Bone marrow’s conjugated linoleic acid content may also be responsible for its inflammation-relieving effects.
Bone marrow: top highlights
Bone marrow is an ultra-nourishing source of easily absorbable calories and fats. As is the case with many traditional animal foods, bone marrow’s full nutritional profile has not been very well studied. That means it could also contain yet-to-be-discovered nutrients, so this keto superfood is likely more super than we even know.
The Takeaway
Keto superfoods provide an abundance of easily absorbed nutrients without the downsides of conventional plant-based superfoods.
Here’s a recap of 5 great keto superfood choices:
- Ribeye: Ideal for anyone who wants to build lean muscle mass.
- Beef Liver: Ideal for athletes, children, and pregnant women.
- Salmon roe: Ideal for children, pregnant women, and anyone who needs a natural brain boost.
- Eggs: Ideal for anyone who wants to keep their hormonal profile intact.
- Bone Marrow: Ideal for skin, joint, and overall health.
These 5 superfoods are just the start. The truth is that many animal products are rich enough in micronutrients, macronutrients, to be truly super for your health.