What is The 5/2 Diet Plan: Review and Benefits
Fasting has experienced a resurgence in recent years, and for good reason: it’s an ancient practice that can offer powerful health benefits like cellular regeneration and weight loss. One of the simplest types of fasting out there is known as the 5:2 diet plan. Adherents of the 5:2 diet say it makes losing weight and boosting energy easy— and even hunger-free. In this review of the 5:2 diet plan we’ll take a balanced look at just how effective it may be.
[TOC]
How to Do The 5:2 Diet
The 5:2 Diet is one of the most popular forms of intermittent fasting today. Also known as the Eat Stop Eat Diet, this diet was brought into the mainstream by a journalist named Michael Mosley.
As stated above, one of the upsides of 5:2 dieting is its simplicity. The diet’s concept is all in the name: it calls for eating normally five days a week and fasting for two days per week.
Technically speaking, the 5:2 diet isn’t a diet so much as a meal timing strategy. Some people eat whatever they want during those five ‘normal’ days. These same people attest that this dietary freedom is what makes 5:2 eating truly sustainable in the long run. [1]
5:2 Diet Plan: the Specifics
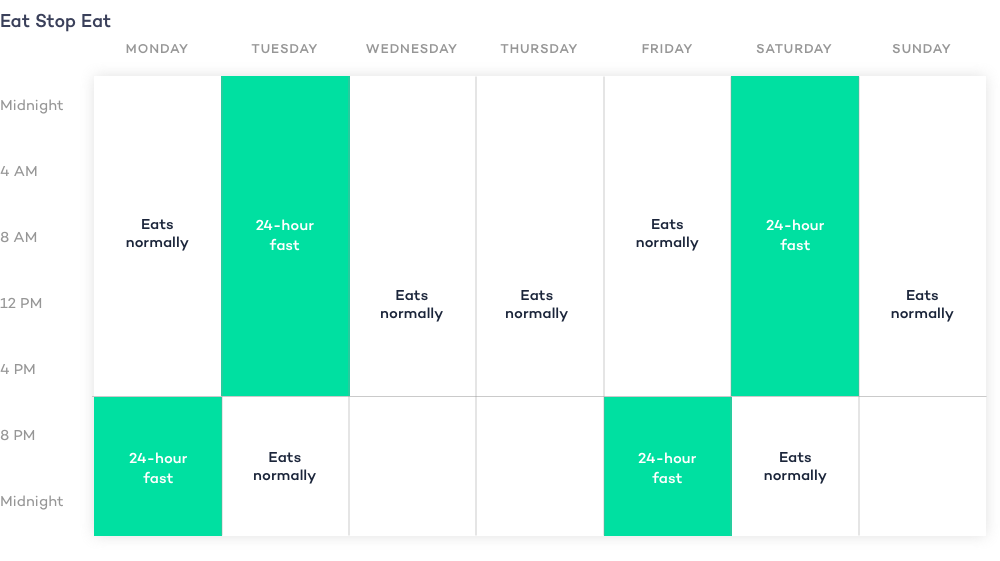
There are many ways to interpret the 5:2 diet. Some people fast on two consecutive days each week, while others prefer to space the fasting days out:
- Monday: fast
- Tuesday: fast
- Thursday: feast
- Friday: feast
- Saturday: feast
- Sunday: feast
Even the 5:2 diet’s fasting days are up for interpretation. While many people fast from food completely and stick with calorie-free liquids, others make allowance for 500-600 calories on fasting days.
5:2 Diet Benefits
Not many studies have been done on the benefits of 5:2 intermittent fasting specifically. That being said, study after study has illustrated the many benefits of fasting and intermittent fasting in general. It’s likely that the 5:2 diet makes available most if not all the benefits of other types of fasting. Here are some of the highlights. [2][3]
- Metabolic flexibility
- Satiation (i.e. sustainability)
- Hormone-driven weight loss
- Reduced cancer cell development
Metabolic flexibility
The 5:2 diet’s variable eating windows may force your body to become more metabolically flexible. In layman’s terms, this metabolic flexibility refers to the ease with which your body can shift between using different types of fuel.
Most Americans on the standard American diet are stuck in perpetual carb-craving mode, which can lead to hyperinsulinemia and excess glycation.
On the other hand, most health-conscious people on the keto diet are confined to complete fat-burning mode, which can produce its own form of “physiological” hyperinsulinemia in the long run.
5:2 intermittent fasting teaches the body to alternate between fat-burning and carb-burning with ease.
With time the 5:2 diet should make it easy for your body to go in and out of ketosis — a metabolic state that has many benefits but some potential drawbacks in the long run. In other words, 5:2 dieting may give you access to the metabolic best of both worlds. [4]
Periodically going without eating in this way might be better for weight loss than traditional calorie restriction alone.
Some studies suggest that the increased energy variance seen with 5:2 dieting may result in faster weight loss. Other studies suggest that intermittent fasting may allow you to lose fat while retaining your muscle mass. This type of body recomposition is basically the gold standard when it comes to quantifying any diet’s effectiveness.
Satiation (i.e. Sustainability)
The 5:2 diet is simple and sustainable. Many adherents say that the diet keeps them satiated and free from hunger. For some people, following the 5:2 diet is far easier than staying in a slight calorie deficit every single day. [5]
The low serum insulin levels seen on fasting days mean these days stay surprisingly hunger-free. [6] And then, when you do eat, your body should be insulin sensitive enough to know where to apportion the extra fuel. [7]
In this way, the 5:2 diet is an effective strategy for kicking your carb addiction
Hormone-Driven Weight Loss
While not many studies have put 5:2 fasting under the microscope, several studies have investigated the benefits of one of its closest relatives, 4:3 fasting.
Its benefits include improved insulin sensitivity, reduced body fat, and improved leptin levels. Yet the benefits of 4:3 fasting also include some less intuitive changes, including allergy relief, improved cardiac rhythm, and reduced menopausal symptoms. [8]
One of the most thorough 4:3 studies–a randomized controlled study involving both obese and healthy-weight participants–showed that the 4:3 group showed significant improvements over the control group for many health markers, including [9]
- Reduced fat mass
- Reduced body weight
- Normalized leptin levels
- No change in muscle mass
- Reduced triglyceride levels
- Healthier cholesterol levels
- Reduced inflammation levels
Other studies confirm intermittent fasting’s hormone-driven ability to promote weight loss. One recent review found that modified IF caused a 3-8% reduction in weight and a 4-7% reduction in visceral fat after as little as three weeks. Once again, intermittent fasting seems to melt off fat while sparing important muscle tissue. [10]
Reduced Cancer Cell Development
Fasting exerts a series of changes within the body that then make it harder for cancer cells to thrive.
One study found that fasting could reduce cancer cell proliferation by restoring healthy circadian rhythm (circadian rhythm refers to the rhythmic biochemical changes caused by day/night cycles).
This finding is especially significant given many of us have a ‘broken’ internal clock, courtesy of staying up too late and staring at blue-lit devices. Here’s what the study’s authors said: [11]
“Time-restricted feeding can reset the disrupted clock rhythm, protect against cancer and metabolic syndrome. Based on these observations, we hypothesized that intermittent fasting for several consecutive days without calorie restriction in humans would induce an anticarcinogenic proteome and the key regulatory proteins of glucose and lipid metabolism.”
Intermittent fasting’s ability to restore proper circadian rhythm may be protective against cancer, DNA damage, immune system compromise, and metabolic syndrome. Circadian rhythm really is that important — and fasting really is that restorative.
How to Make the 5:2 diet Even More Effective
5:2 dieters have found ways to make the diet even more effective over time. Here are some proven tactics that could help you get your very best results out of this form of IF:
- Focus on healthy fats
- Add in ketone-boosters
- Partake in gentle exercise (especially at first)
- Stay nourished with organ meats and organ supplements
Focus on Healthy Fats
The traditional 5:2 diet allows you to eat normally on ‘fasting’ days. Yet you can do even better by swapping out junk foods and empty calories for nourishing animal products like the best cuts of steak, eggs, and bone broth and plenty of health fats. Making this change will allow you to feel even more satiated and energized.
Add in Ketone-Boosters
Some research suggests that adding exogenous/dietary ketones to a ketogenic diet can amplify its effects. [12]
The easiest way to do this is by upping your medium-chain triglyceride consumption. No need to get too fancy here — coconut oil is a great source of MCTs. so cooking with it or adding it into your coffee should suffice.
Partake in Gentle Exercise (especially at first)
Occasionally exercising in a fasted state can supercharge fat-burning and speed up your body’s journey towards metabolic flexibility.
And if you’re brand new to the 5:2 diet, doing some gentle exercise may help you get into ketosis quickly, resulting in fewer cravings. Some of our favorite modes of exercise include walking and swimming, though you really can’t go wrong if you’re doing something you enjoy.
Stay Nourished with Organ Meats and Organ Supplements
Taking premium beef organ supplements can make your fasting routine even more effective. These supplements contain energizing B vitamins that prevent your metabolic rate from dipping too low on fasting days. [13] If nothing else, supplementing with beef organs can help you avoid developing nutrient deficiencies.
Is the 5:2 Diet Right for you?
Thousands of real-life experiences and dozens of studies all attest that 5:2 intermittent fasting is simple, sustainable, and effective. Yet it’s not for everybody. 5:2 fasting isn’t right for certain groups.
Groups who shouldn’t try the 5:2 diet
- Those who are underweight
- Those who struggle with eating disorders
- Those who don’t have excess visceral fat to lose
- Those who are experiencing thyroid dysfunction
- Women who are nursing, pregnant, or trying to boost their fertility
This last category deserves some extra attention. Intermittent fasting seems to affect women more intensely than it does men. This is due to the hormonal differences between the genders. [14]
Some women report that they stop menstruating on the 5:2 diet. If this happens to you, stop the diet immediately and simply stick with three nourishing meals per day and eventually try a gentler approach. Check out our article on IF for women to learn more about these potential pitfalls and solutions.
5:2 Diet Plan: The Takeaway
The 5:2 diet is a modern version of an eating pattern humans evolved to thrive on. So perhaps it’s not surprising that 5:2 fasting offers a variety of evolutionarily-primed benefits, including:
- Fat loss
- Muscle gain
- Improved immunity
- Improved gut health
- Reduced cancer risks
- Reduced DNA damage
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Reduced diabetic/prediabetic symptoms
Just be aware that the 5:2 diet isn’t for everyone. If you try it for yourself, we encourage you to take the journey with care by listening closely to your body. If you feel great on 5:2 fasting, wonderful! If you don’t feel great after a few weeks, consider trying a different fasting strategy supported with the new knowledge you’ve learned about how your body responds.





































 Nearly all keto fruits and
Nearly all keto fruits and 


