Top 6 Best Cuts of Steak: Ranked by Taste and Nutrition
A thick juicy steak is the highlight of most respectable restaurant menus, and the centerpiece of backyard bbqs alike. Steak is as American as, well, apple pie, just a whole lot healthier! But what are the best cuts of steak?
In this article we’ll rate the best cuts of steak based on their nutritional benefits. Surprisingly to some, the most delicious and healthiest are also the fattiest.
[TOC]
Fatty Steak is Not Bad For You
News flash, fatty steak is not bad for you!
But how can that be? you might be asking. Isn’t saturated fat bad for you? Isn’t that why we’re supposed to eat lean steak?
Nope. The guidelines for choosing lean meats and limiting saturated fat are based on outdated observational studies dating back to the 1950s. They are simply wrong. But how do we know this?
We follow the science. Numerous high-quality modern studies looking at over 1 million combined participants and published in the world’s most prestigious medical journals all tell us the same thing:
For the average person, saturated fat has NO significant association with heart disease, stroke, diabetes, death from heart attacks, and cancer. 1 2 3 4 5
Take for example this 2020 review study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, and authored by over a dozen researchers from the world’s most renowned medical schools. The researcher team found that:
“Although intake of processed meat has been associated with increased risk of CHD, intake of unprocessed red meat is not, which indicates that the SFA content of meat is unlikely to be responsible for this association.” 6
They conclude, “Whole-fat dairy, unprocessed meat, and dark chocolate are SFA-rich foods with a complex matrix that are not associated with increased risk of CVD. The totality of available evidence does not support further limiting the intake of such foods.” 7
So, with the anti-fat nonsense in our rearview mirror, let’s take an honest, science-based look at the best cuts of steak, ranked by their nutritional benefits.
Ribeye Steak (Tomahawk)
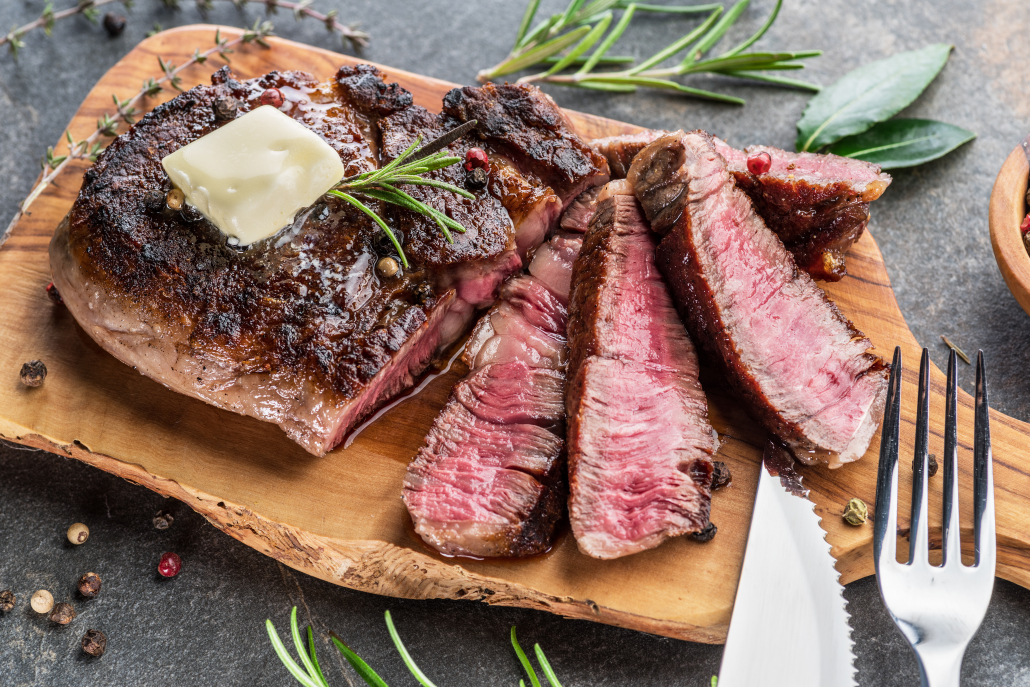

Ribeye steaks are the best cuts of steak when it comes to both nutrients and taste. They routinely win contests of flavor thanks to their abundant fat marbling, which also gives it an iconic tender and juicy texture.
When roasted the ribeye is referred to as Prime Rib. It becomes a rib eye when cut into steaks.
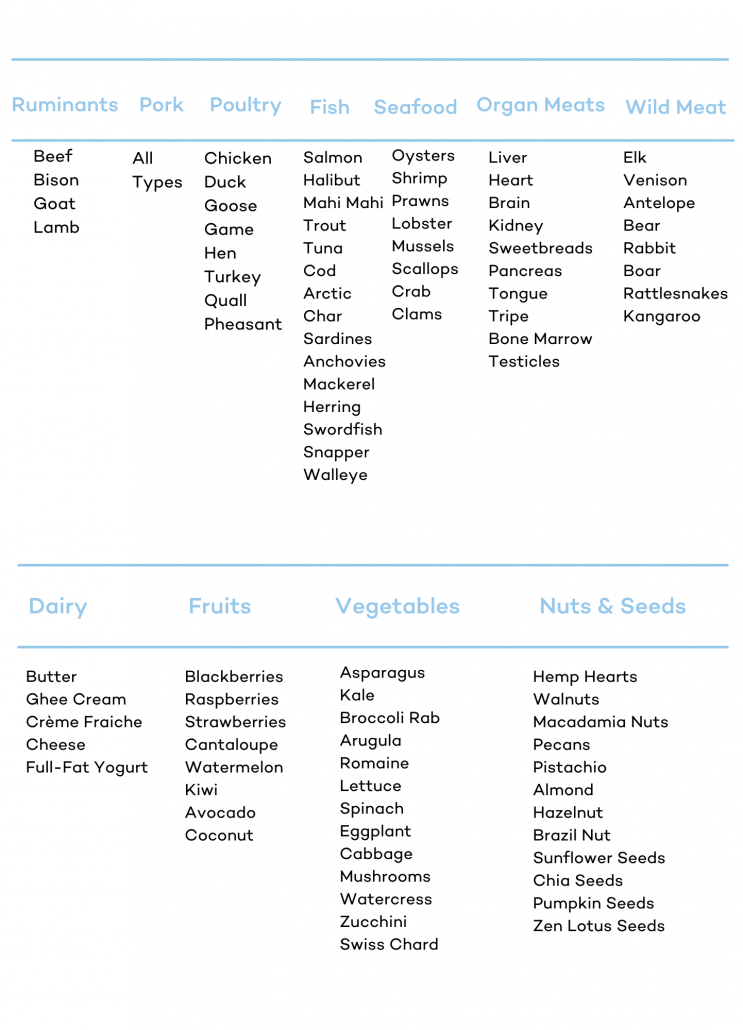
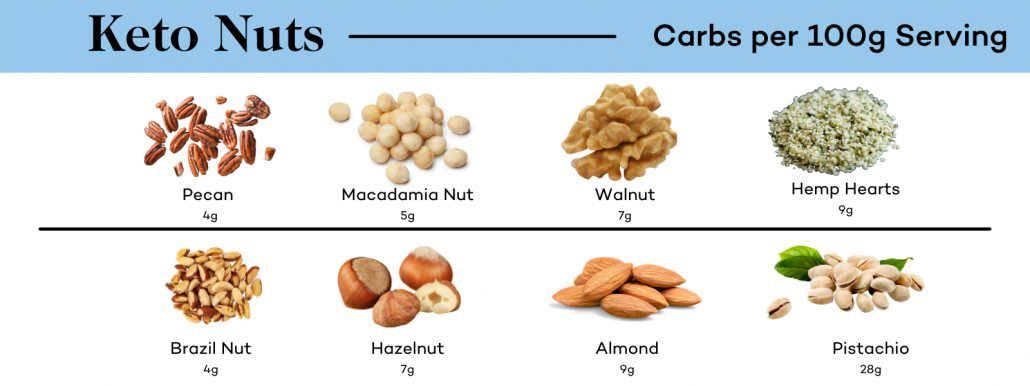
But even with all that luscious marbling, rib eye is only the 4th fattiest cut of steak. If you’re eating a keto diet you can learn more about the fattiest cuts of keto meats here.
Aside from complete proteins and nurturing fats, ribeye is also a fantastic source of various B vitamins, zinc, selenium, and numerous meat-specific compounds. These include:
- Carnitine: improves male fertility, reduces anemia, supports mitochondrial function, and cardiac ischemia. [7] [8] [9] [10]
- Carnosine: Heart and muscle protective. Prevents glycation, protects against telomere damage to prevent agings. [5] [2] [3] [4]
- Creatine: Associated with improved cognition and protection against Alzheimer’s. Boost athletic performance, and heart health. [10] [11] [12] [13]
- Taurine: Antioxidant that reduces glycation, oxidative stress, and may reduce depression.
- Heme Iron: Found only in beef and other red meats, vital to healthy immune function, cognition, and energy metabolism. [16]
| NUTRIENT | 200G (7 oz) | |
| Calories | 582 cal | |
| Fat | 55g | |
| Saturated Fat | 20g | |
| Monounsaturated Fat | ||
| Carbohydrates | 0 | |
| Protein | 48g | |
| Vitamins | ||
| B1 (Thiamin) | 14% | |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | 35% | |
| B3 (Niacin) | 44% | |
| B6 | 60% | |
| B12 | 245% | |
| Minerals | ||
| Magnesium | 12% | |
| Potassium | 18% | |
| Iron | 31% | |
| Copper | 33% | |
| Phosphorus | 42% | |
| Selenium | 93% | |
| Zinc | 113% |
New York Strip
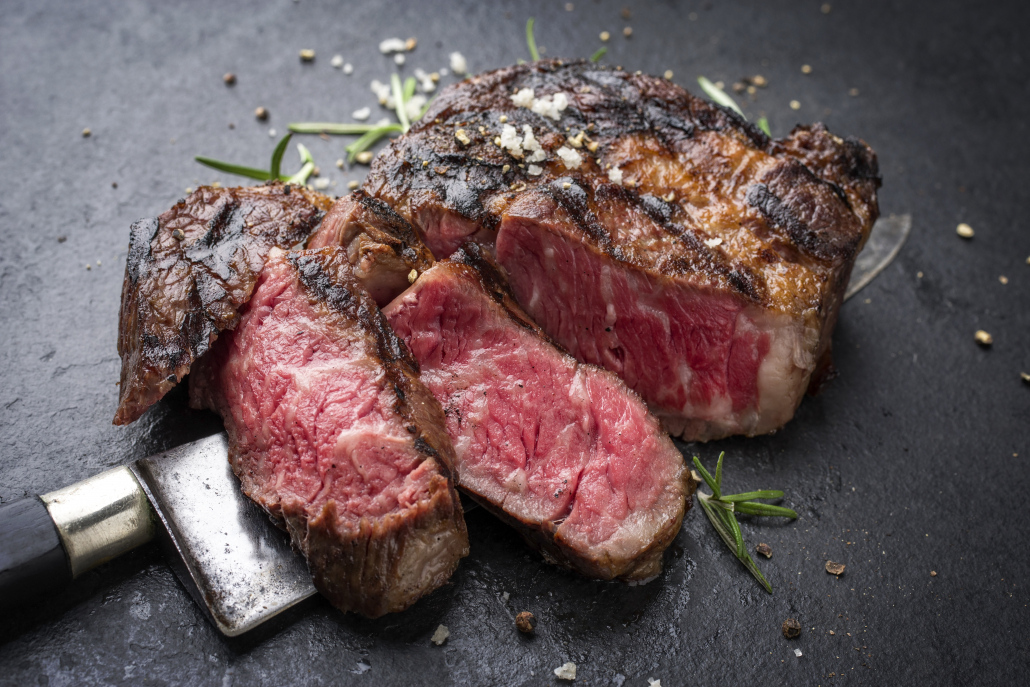

The New York strip is a steakhouse staple that does equally well on the grill as it does in the pan. That’s due in large part to succulent fat marbling.
As one of the best cuts of steak, the New York Strip has a very similar nutrition profile with the ribeye. It’s loaded in B vitamins, zinc, and selenium.
| NUTRIENT | 200G (7 oz.) |
| Calories | 616 cal |
| Fat | 44g |
| Saturated Fat | 17.7g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | |
| Carbohydrates | 0 |
| Protein | 51g |
| Vitamins | |
| B1 (Thiamin) | 8.5% |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | 21% |
| Choline | 25% |
| B5 (Pantothenic acid) | 30% |
| B3 (Niacin) | 90% |
| B6 | 108% |
| B12 | 113% |
| Minerals | |
| Magnesium | 11% |
| Potassium | 19% |
| Iron | 21% |
| Copper | 18% |
| Phosphorus | 45% |
| Selenium | 80% |
| Zinc | 55% |
T-Bone
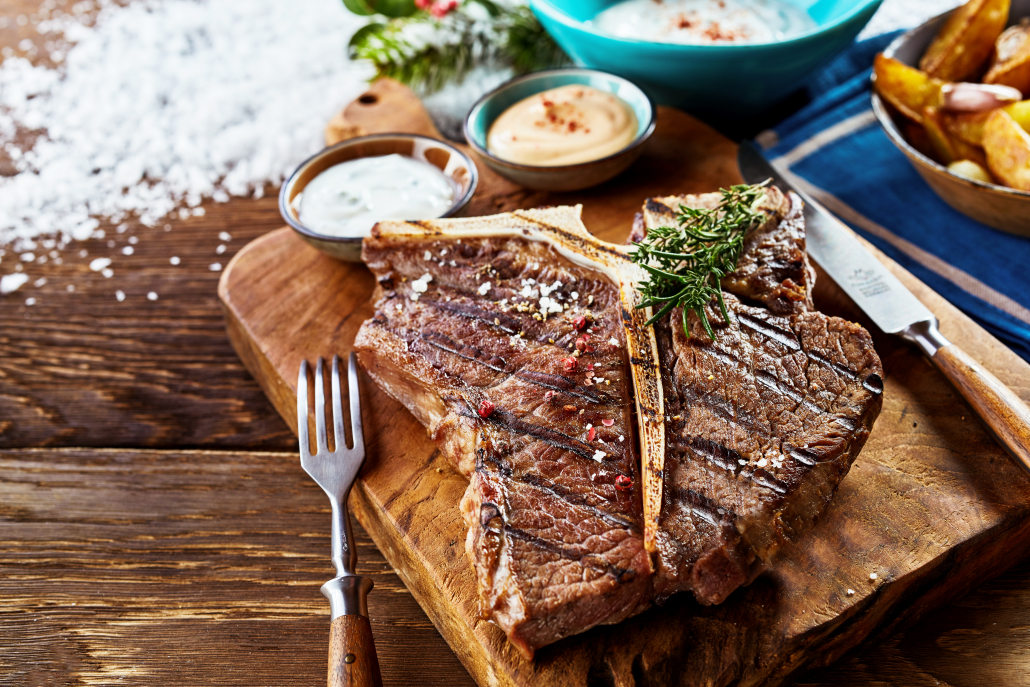

If we asked you to think of steak, you’d probably see a picture of T-Bone in your mind’s eye.
But did you know the T-bone steak is actually two different steaks in one?
The T-bone itself divides a tenderloin filet (filet mignon) and a New York strip steak. For this reason, it can be a little tricky to cook. T-bones are best grilled and enjoyed medium-rare at most since the meat near the bone will remain less done than the rest of the steak.
The porterhouse steak is also a T-bone, it’s just cut in a way that makes the tenderloin part larger.
Selenium is one of the many nutrients that stand out in a T-bone steak, at 96% of your RDV per serving. Selenium acts as a powerful antioxidant that protects against numerous cancers, and heart disease. 17
| NUTRIENT | 200G (7 oz.) |
| Calories | 574 cal |
| Fat | 42g |
| Saturated Fat | 18g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | |
| Carbohydrates | 0 |
| Protein | 48g |
| Vitamins | |
| B1 (Thiamin) | 8% |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | 36% |
| Choline | 22% |
| B3 (Niacin) | 70% |
| B6 | 102% |
| B12 | 150% |
| Minerals | |
| Magnesium | 8% |
| Potassium | 12% |
| Iron | 36% |
| Copper | 16% |
| Phosphorus | 38% |
| Selenium | 96% |
| Zinc | 58% |
Beef Short Ribs
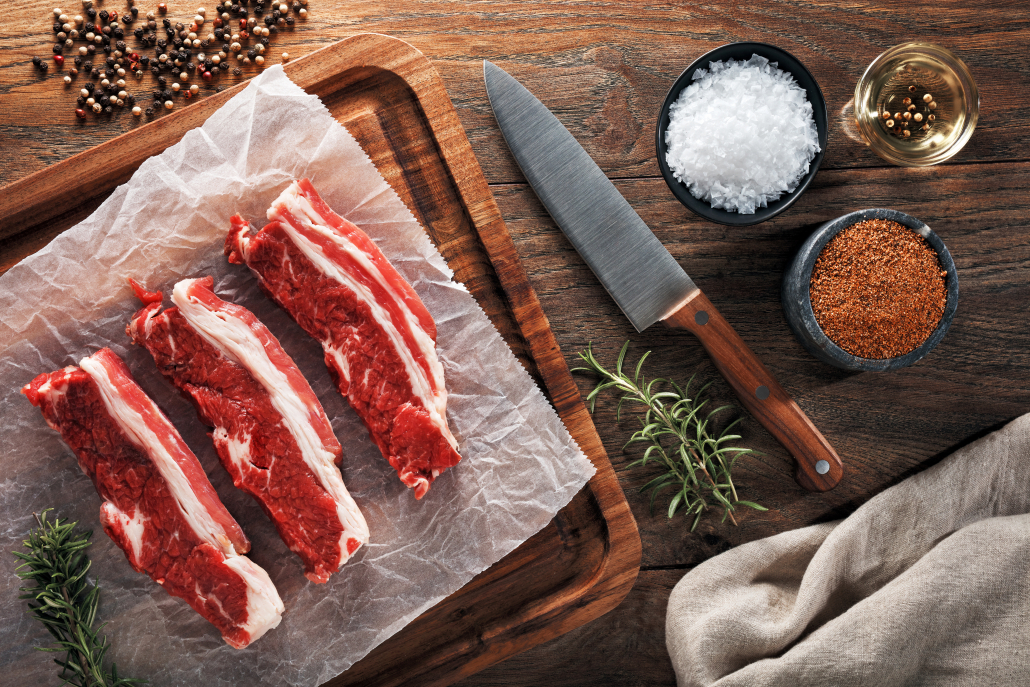

Beef short ribs are another favorite, and no surprise, deeply marbled with delicious fats. This cut is a staple in many Asian cuisines. When done right beef short ribs can melt off the bone.
The combination of 250% RDV of vitamin B12 and 102% of zinc makes short ribs one of the best cuts of steak. Your body relies on these molecules to accomplish more than 300 essential functions from immune response, DNA synthesis, metabolism, and much more. 18 19 20
| NUTRIENT | 200G (7 oz.) |
| Calories | 470 cal |
| Fat | 36g |
| Saturated Fat | 16g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | |
| Carbohydrates | 0 |
| Protein | 34g |
| Vitamins | |
| B1 (Thiamin) | 14% |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | 26% |
| Choline | 22% |
| B3 (Niacin) | 42% |
| B6 | 46% |
| B12 | 250% |
| MInerals | |
| Magnesium | 8% |
| Potassium | 14% |
| Iron | 24% |
| Copper | 16% |
| Phosphorus | 34% |
| Selenium | 68% |
| Zinc | 102% |
Tri-Tip Roast
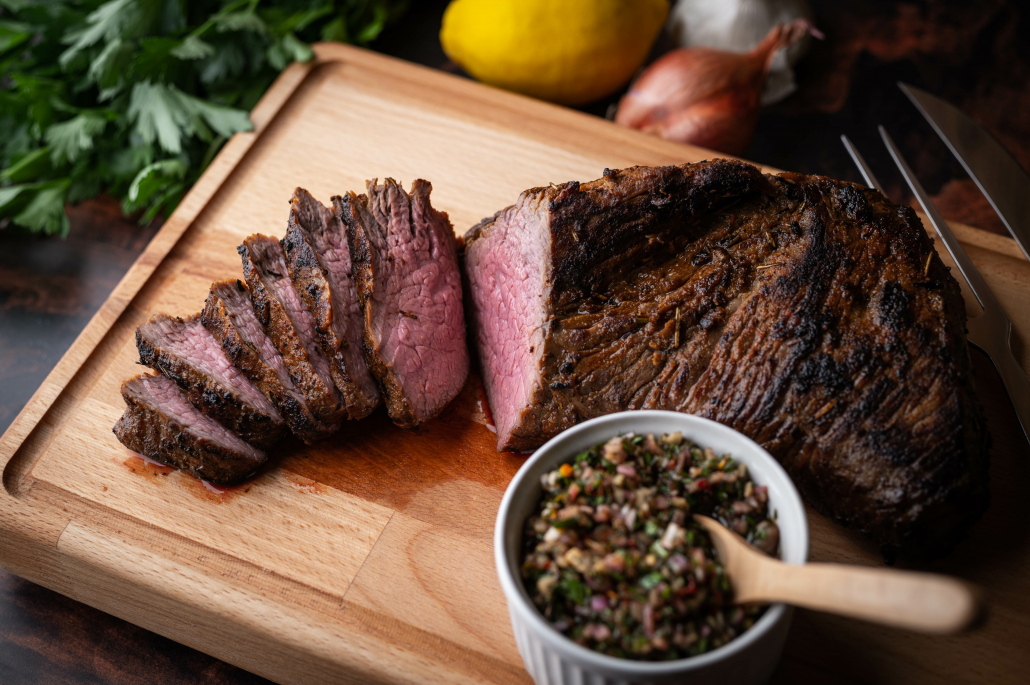

Cut from the bottom sirloin, the tri-tip roast is somewhat leaner. It gets its name from its boneless triangular shape.
Some steak masters say it’s best marinated and cooked whole in the oven. But it’s also great grilled with low to medium indirect heat. When sliced into strips, it makes a great stir fry.
Like our other best cuts of steak on the list, Tri-tip is loaded with protein, healthy fats, B vitamins, zinc, and copper.
Copper is one of the underrated nutrients in our diet. Sufficient copper intake is associated with numerous health benefits including increased bone mineral density, protection against infectious disease, cardiovascular health, and collagen formation in the skin. 21 22 23
| NUTRIENT | 200G (7 oz.) |
| Calories | 514 cal |
| Fat | 30g |
| Saturated Fat | 12g |
| Carbohydrates | 0 |
| Protein | 34g |
| Vitamins | |
| B1 (Thiamin) | 22% |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | 44% |
| Choline | 42% |
| B3 (Niacin) | 52% |
| B6 | 68% |
| B12 | 236% |
| MInerals | |
| Magnesium | 12% |
| Potassium | 24% |
| Iron | 36% |
| Copper | 38% |
| Phosphorus | 54% |
| Selenium | 38% |
| Zinc | 100% |
Beef Liver
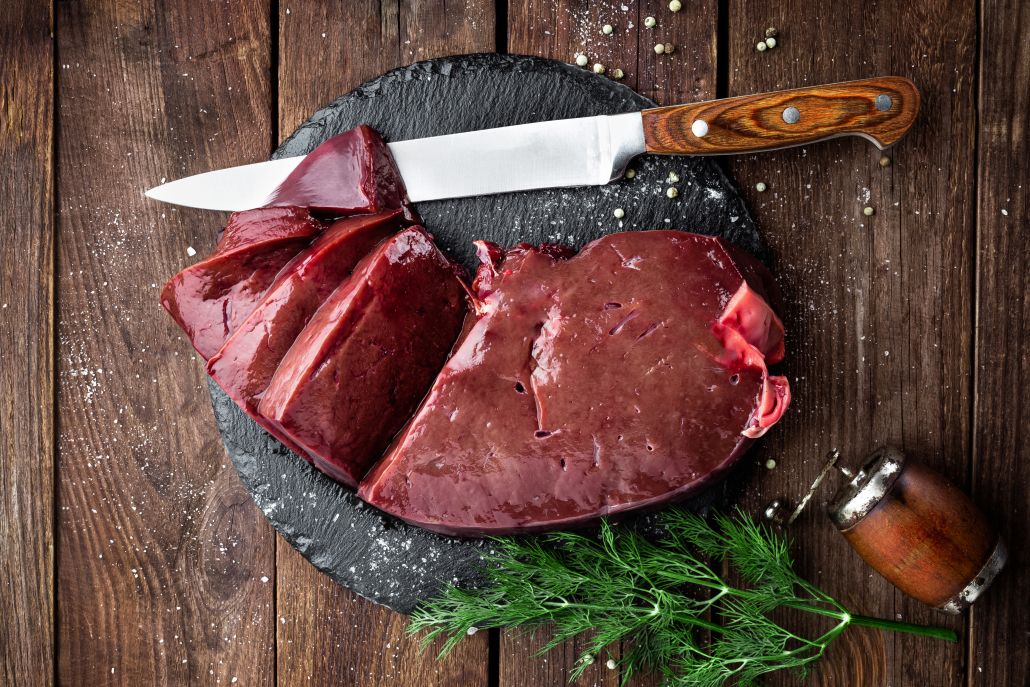

Steak means cow meat, and this includes organ meats–the most nutrient-dense superfoods on earth. A former mainstay on dinner tables across America, beef liver is making a comeback thanks to the rise of nose-to-tail eating.
If we were ranking this list based only on nutrition benefits, liver would be far and away #1.
But for many people, beef liver is an acquired taste. What liver lacks in succulence, it more than makes up for in bioavailable nutrients. It’s loaded in protein, and its B vitamins, vitamin A, and copper are literally off the charts.
In fact, it’s so abundant in vitamin A that liver should be enjoyed only occasionally in order to reduce the risk of vitamin A toxicity.
Thanks to liver’s complex matrix of nutrients, eating liver gives most people a tangible energy boost, while supporting numerous physical functions including:
- Protection against skin aging
- Improved fertility
- Healthy fetal development
- Strong bones
- Heart health
- Cognitive performance
- Strength and endurance
- Elevated mood
- Eye health
- Strong immune system
If the idea of cooking and eating liver just isn’t palatable to you, you can still get these benefits in the form of beef liver supplements. Tasteless and scentless,desiccated liver supplements but the benefits grass-fed New Zealand cattle organs in the palm of your hand,
Liver is so nutrient-rich that we’re showing you the nutrition values for only 100 grams (3.5 oz), which is half the serving size of the other best cuts of steak on the list.
| NUTRIENT | 100G (7 oz.) |
| Calories | 169 cal |
| Fat | 5.1g |
| Saturated Fat | 3g |
| Carbohydrates | 0 |
| Protein | 27g |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin D | 8% |
| B1 (Thiamin) | 15% |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | 263% |
| Choline | 77% |
| B3 (Niacin) | 109% |
| B6 | 79% |
| Vitamin A | 870% |
| B12 | 3464% |
| MInerals | |
| Potassium | 9% |
| Iron | 35% |
| Copper | 1621% |
| Phosphorus | 49% |
| Selenium | 60% |
| Zinc | 37% |
The Best Cuts of Steak: The Takeaway
For many people, steak is the gold standard of the American diet, and for good reason. The best cuts of steak are loaded with healthy fats, complete proteins, and abundant vitamins and minerals.
However, most people view steak as unhealthy due to faulty research from the 1950s-1990 that demonized red meat and saturated fat. Fortunately, numerous more recent and higher-quality studies have found that fresh red meat and whole food saturated fats do not cause cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
The new science allows us to give red meat the appreciation (and place at our tables) that it deserves. These top 6 best cuts of steak provide your body with nearly everything it needs to thrive!
Bon appetite!