Keto Seafood: Top 5 Choices and Their Health Benefits
Keto seafood options are packed with vital nutrients like zinc, vitamin C, and unique antioxidants. Foods like oysters, shrimp, and crab play a starring role in the pescatarian keto, and Mediterranean keto diets, while providing delicious variety to your standard keto and carnivores diets.
However, some keto seafood like oysters and shrimp do contain some carbs to be aware of.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at a list of the best seafood for a keto diet along with their unique health benefits.
[TOC]
How to Choose The Best Keto Seafood

A ketogenic diet is based on a high-fat, low-carb, and moderate-protein way of eating.
Fortunately, when if comes to keto seafood you don’t have to worry about carbs. But most seafood are surprisingly lean.
This makes selecting the fattiest seafood and adding healthy keto fats like butter, ghee, tallow, and coconut oil a must.
An important rule of thumb is to prepare your keto seafood dishes in ways that fall as close as possible within these macronutrient ranges:
- 70-80% of calories from fat
- 15-30% calories from protein
- 0-10% calories from carbohydrate
It’s worth noting that once your body is adapted to keto after a few weeks to a month or so, you can allow for up to 60 grams of carbs per day depending on your metabolism and activity level. But when just starting out it’s likely that you’ll want to cut carbs to less than 20 grams per day.
Fat to Protein Ratio in Popular Keto Seafoods
Let’s turn to a list of some of the most popular keto seafood with their macronutrient breakdown. As you’ll see most keto seafood, though low in carbs, is also low in fat.
Fish
| TYPE OF FISH | CALORIES | FAT | PROTEIN | CARBS | % CALORIES FROM FAT | % CALORIES FROM PROTEIN | |
| Atlantic Mackerel | 290 | 20.3 | 27 | 0 | 63 | 37 | |
| Farmed Arctic Char | 208 | 12 | 19 | 0 | 58 | 42 | |
| Anchovies | 256 | 15.9 | 28 | 0 | 56 | 44 | |
| Farmed Salmon | 234 | 14 | 25 | 0 | 56 | 44 | |
| Wild King Salmon | 195 | 13 | 22 | 0 | 54 | 46 | |
| Sardines | 139 | 8 | 19 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
Roe and Shellfish
| Type of Seafood | Calories | Fat | Protein | Carbs | % Calories from fat | % Calories from protein | % Calories from carbs |
| Salmon Caviar (Roe) | 260 | 14 | 29 | 2.9 | 45 | 52 | 3% |
| Oysters | 58 | 1.9 | 6.5 | 3.1 | 29 | 33 | 28 |
| Mussels | 97 | 2.8 | 13.5 | 4.5 | 26 | 56 | 19 |
| Shrimp | 135 | 2.0 | 25.8 | 1.7 | 18 | 78 | 4 |
| Dungeness Crab | 107 | 2.0 | 22 | 0 | 17 | 82 | 0 |
| Lobster | 116 | 1.8 | 25 | 0 | 14 | 86 | 0 |
| Clams | 82 | 1.1 | 15 | 3 | 12 | 73 | 15 |
| Scallops | 97 | 1.0 | 19 | 3 | 9 | 78 | 12 |
Top 5 Keto Seafoods
Seafood adds variety to your keto diet both in terms of taste and nutrients.
Take oysters for example–they’re a fantastic source of zinc offering over 600% per serving.
If you’re going full carnivore, Salmon roe is one of the few significant sources of vitamin C in animal foods.
There are also various orange pigmented seafood like lobster, roe, and shrimp that provide an antioxidant called Astaxanthin.
Research has revealed that it may be 6,000 times more powerful than vitamin C. Studies have also shown that it can reduce oxidative stress and protect your liver. [22] [23] [24]
In this list we offer a mix of fish and shellfish. And we provide a more extensive list of keto fish and their benefits here.
Keto Seafood #1: Salmon Roe

Salmon eggs are one of the earth’s most nutrient-dense superfoods. Also known as ikura and salmon caviar, these little morsels are loaded with highly bioavailable vitamins A, B, D, and K2, zinc, iodine.
They’re also prized for their neuroprotective and brain-building omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA. [25]
Some of the many health benefits associated with salmon roe include:
- Neuroprotection against Alzheimer’s and dementia
- Supporting the development of the infant’s brain
- Improves fertility for both men and women
- Elevated cognitive ability
- Anti-depressive properties
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Improved heart health
- Antioxidant properties
- Boosted immune system
You can explore salmon roe’s superfood benefits in-depth here.
Salmon Roe nutrition per 100g
| NUTRIENTS | AMOUNT | |
| CALORIES | 250 kcal | |
| CARBOHYDRATE | 2.90 g | |
| FIBER | 0 g | |
| SUGARS | 0 g | |
| FAT | 14.0 g | |
| SATURATED FAT | 2.04 g | |
| MONOUNSATURATED FAT | 4.13 g | |
| POLYUNSATURATED FAT | 4.12 g | |
| OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS | 3.50 g | |
| OMEGA-6 FATTY ACIDS | 0.31 g | |
| PROTEIN | 29.20 g | |
| VITAMINS | ||
| COBALAMIN (B12) | 20.0 mcg | 333 % |
| VITAMIN E | 10mg | 66% |
| VITAMIN D | 232 IU | 58 % |
| CHOLINE | 247.5 mg | 45 % |
| PANTOTHENIC ACID (B5) | 3.50 mg | 35 % |
| VITAMIN C | 16 mg | 26 % |
| RIBOFLAVIN (B2) | 0.36 mg | 21.2 % |
| PYRIDOXINE (B6) | 0.32 mg | 16.0 % |
| VITAMIN E | 2.68 mg | 13.3 % |
| FOLATE | 50.0 mcg | 12.5 % |
| VITAMIN A | 91 mcg RAE | 10.1 % |
| THIAMIN (B1) | 0.14 mg | 9.3 % |
| NIACIN (B3) | 0.40 mg | 2.0 % |
| VITAMIN K | 0.73 mcg | 0.9 % |
| Selenium | 65.5 mcg | 93.6% |
| Magnesium | 300 mg | 75% |
| Iron | 11.88 mg | 66% |
| Sodium | 1500 mg | 62.5% |
| Phosphorus | 390 mg | 39% |
| Calcium | 275 mg | 27.5% |
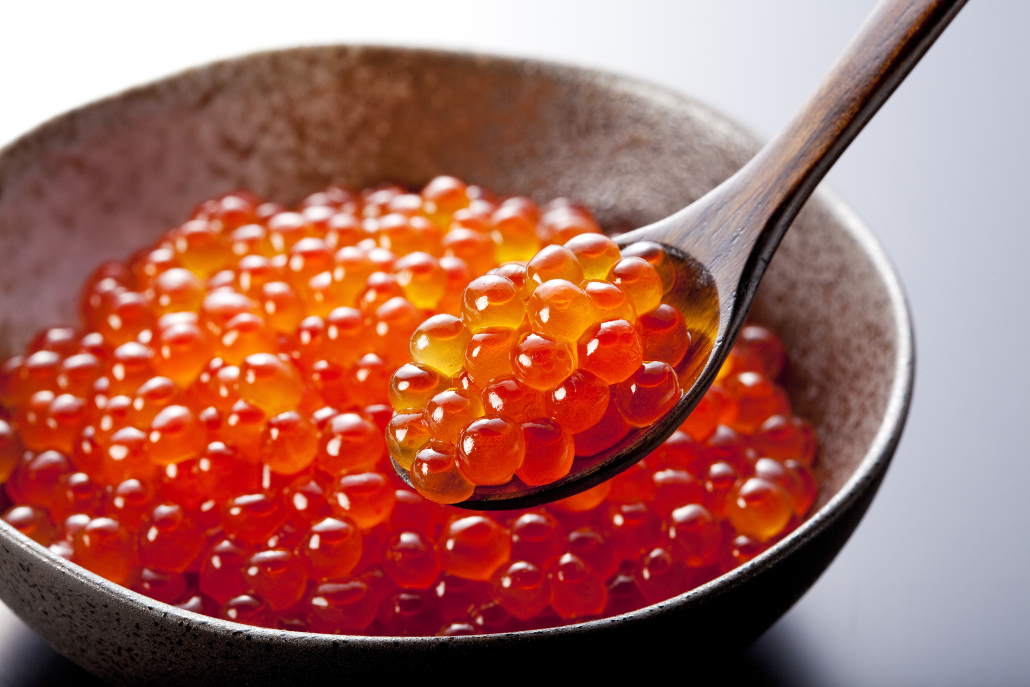
Keto Seafood #2: Oysters

Keto dieters devour oysters for their unique textures, subtle flavors, and even for their purported aphrodisiac effects. But most people aren’t aware of the nutrients packed into these little bivalves.
Let’s take a look at some oyster nutrition highlights.
Zinc in Oysters
Just 3.5 ounces of oysters contains over 600% of your RDV. Zinc works in tandem with vital fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, to regulate immunity, metabolism, and bone health among other critical functions.
The pioneering diet researcher Weston A. Price discovered that the presence of these nutrients together was a feature of traditional cultures that were essentially free from “diseases of civilization” including heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and osteoporosis .5
Reduced Oxidation
Oysters provide vitamins that double as antioxidants, including zinc along with vitamin D, vitamin B12, and selenium. 7 8
Oysters are also a source of a recently discovered antioxidant known as 3,5-Dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl alcohol or DHMBA. Researchers have found that DHMBA has offers 15 times more antioxidant power than synthetic vitamin E. 9
Nutrients per 100 grams
| RAW OYSTER | % RDV | |
| CALORIES | 68 | |
| PROTEIN | 7 grams | |
| FAT | 2.5 grams | |
| CARBS | 3.9 grams | |
| VITAMIN D | 320 IU | 80% |
| VITAMIN B12 | 19.5 mcg | 324% |
| IRON | 6.7 mg | 37% |
| MAGNESIUM | 47 mg | 12% |
| PHOSPHORUS | 135 mg | 14% |
| ZINC | 90.8 mg | 605% |
| COPPER | 4.5 mg | 223% |
| MANGANESE | 0.4 mg | 18% |
| SELENIUM | 63.7 mcg | 91% |
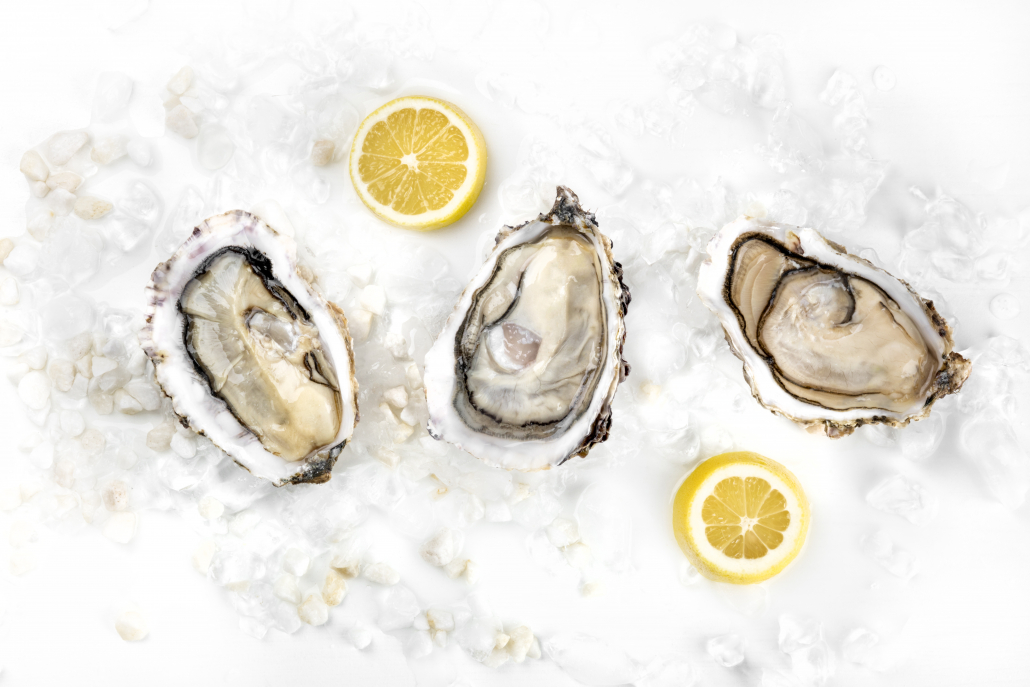
Keto Seafood #3: Dungeness Crab

Dungeness crab is a great source of selenium. This mineral reduces inflammation and may protect against prostate cancer. 10 11
It’s also loaded with B12 and omega-3 fatty acids including DHA and EPA. Promising research has shown that the combination of these compounds can increase each other’s brain health promoting activities. 12
Nutrients per 100 grams
| Dungeness Crab | 81 CALORIES | % RDV |
| PROTEIN | 17 grams | |
| FAT | 1 gram | |
| DHA (fatty acid) | .009g | 44% |
| EPA (fatty acid) | .22g | 73% |
| CARBS | 1 gram | |
| VITAMIN B3 (Niacin) | 3.1 mg | 20% |
| VITAMIN B12 | 19.5 mcg | 324% |
| MAGNESIUM | 47 mg | 12% |
| PHOSPHORUS | 182 mg | 18% |
| ZINC | 4.3 mg | 31% |
| COPPER | .7 mg | 75% |
| SELENIUM | 37.1 mcg | 67% |
Keto Seafood #4: Atlantic Mackeral
Atlantic mackerel is fatty, nutrient-packed, low in mercury, and affordable.
Highlights include 91% of your RDA in vitamin D per serving, making Atlantic mackerel one of the richest vitamin D food sources on the planet.
Vitamin D plays an important role in immune function and regulating inflammation. 2 Not surprisingly, vitamin D has been shown effective in reducing the severity of COVID-19. 3
Atlantic mackerel is also loaded with 2990 mg of omega-3 per 3.5 oz serving. This can go a long way in rebalancing our over-abundance of omega-6’s that we get from vegetable and nut oils. The Standard American Diet has an alarming 1:16 omega 3 to 6 ratio. The human diet evolved with a 1:1 ratio.
Quality mackeral can come in canned form, making it a great keto snack.
Best of all, 3 lbs of canned mackerel come in at around $20.
Nutrients in Atlantic Mackerel Per 3 oz.
| Atlantic Mackerel | Amount per 3 oz. | % RDA |
| Fat | 12g | |
| Saturated Fat | 2.6g | |
| Cholesterol | 60mg | |
| Protein | 16.2g | |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin D | 546.6IU | 91% |
| Vitamin B12 | 7.4µg | 309% |
| B3 | 7.7mg | 48% |
| B2 | .3 | 26% |
| B6 | .3mg | 26% |
| B5 | .8gm | 14% |
| Vitamin A | 453.0IU | 15% |
| Significant Minerals | ||
| Selenium | 37µg | 68% |
| Magnesium | 65mg | 15% |
| Potassium | 267mg | 6.8% |
Keto Seafood #5: Mussels
Of all the top keto seafood, mussels take the prize for providing the most vitamin B12 at 500% of your RDA per serving.
Mussels are also one of the best dietary sources of omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA.
Studies have shown that these fatty acids are crucial for fetal development, including brain and immune function.
They also play a major role in cardiovascular health, acting as anticoagulants while reducing inflammation to provide protection against artery disease and heart attacks. EPA and DHA have also been linked to preventing Alzheimer’s disease, managing body weight, and cognitive function. 13
| Mussels | Amount per 3 oz. | % RDA |
| Fat | 2g | |
| DHA (fatty acid) | .25g | 127% |
| EPA (fatty acid) | .19g | 63% |
| Cholesterol | 28mg | |
| Protein | 12g | |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin B12 | 12µg | 500% |
| B3 | 1.6mg | 10% |
| B2 | .2 | 16% |
| B5 | .5gm | 10% |
| Significant Minerals | ||
| Selenium | 44.8µg | 81% |
| Iron | 4mg | 22% |
| Manganese | 3.4mg | 148% |
Possible Downsides to Seafood on Keto
Nearly all fish and shellfish contain some heavy metals and mercury from industrial waste in our oceans. Shellfish generally have less mercury than other fish.14 15
Low Mercury Keto Seafood
All the keto seafood options on this list are low in Mercury. These along with other low mercury keto seafood Include:
- Anchovies
- Atlantic croaker
- Atlantic and Pacific chub mackerels
- Black sea bass
- Butterfish
- Catfish
- Clams
- Cod
- Crab
- Crawfish
- Flounder
- Freshwater trout
- Haddock
- Hake
- Herring
- American spiny lobster
- Mullet
- Oyster
- Perch
- Pickerel
- Plaice
- Pollock
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Scallops
- Shad
- Shrimp
- Skate
- Smelt
- Sole
- Squid (calamari)
- Tilapia
- Tuna (canned light, skipjack)
- Whitefish
- Whiting
Keto Seafood: The Takeaway
The best keto seafood provide an extensive list of crucial vitamins and minerals including robust amounts of vitamin B and D, zinc, selenium, copper, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Though most keto seafood are excellent sources of protein, most of them are fairly lean. This means you’ll have to boost the fat of your seafood with whole food fats like tallow, and butter. But that’s no reason not to add them to your everyday keto grocery list.
Pescatarian keto dieters have the pleasure of making this keto seafood the center of their culinary universe. While carnivore dieters and nose-to-tail aficionados will enjoy the diverse nutrients and gastronomic varieties of these fruits of the ocean.