Time Restricted Eating vs. Intermittent Fasting: What’s the Difference?
Time-restricted eating (TRE) and intermittent fasting are closely related strategies for cycling between periods of eating and not eating in order to improve numerous health factors. In simple terms, time-restricted eating is a specific type of intermittent fasting.
There are a couple of key factors when differentiating time-restricted eating vs. intermittent fasting. These include
- The time of day that you are restricting your eating
- The length of time during which you are restricting your eating
In this article, we’ll look at how these factors distinguish time-restricted eating vs. intermittent fasting, along with their benefits and drawbacks.
[TOC]
Why Time Restricted Eating and Intermittent Fasting?
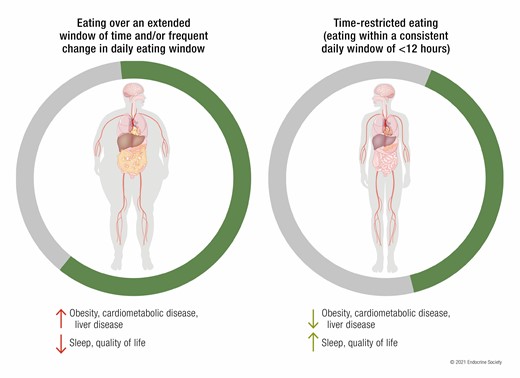
Source: Emily N C Manoogian, Lisa S Chow, Pam R Taub, Blandine Laferrère, Satchidananda Panda, Time-restricted Eating for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Diseases, Endocrine Reviews, Volume 43, Issue 2, April 2022
The Standard American diet calls for eating at least three meals a day with snacks in between–most of it high in inflammatory ingredients, including
For many people, this means eating from the moment they wake up until the moment they fall asleep.
Research shows that the constant consumption of high-carb modern foods wreaks havoc on our metabolic health. Modern eating patterns result in
- chronically elevated levels of insulin, dysregulate other important hormones, and trigger the body to store calories as fat
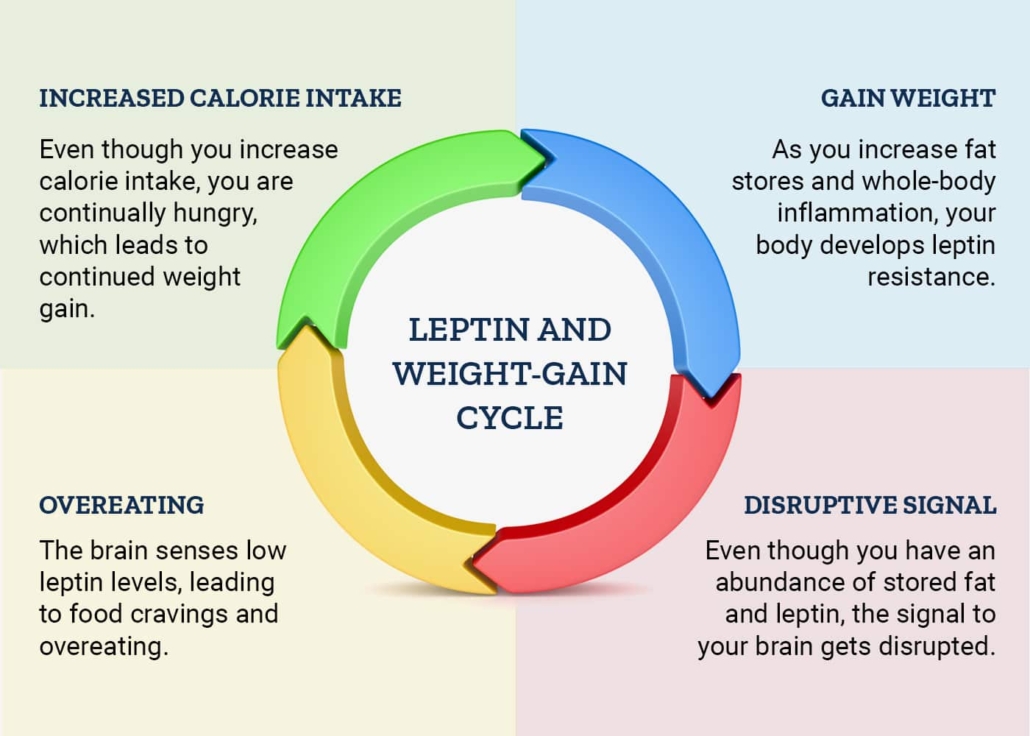
- chronically elevated leptin levels lead to leptin resistance. When you’re leptin resistant, your brain loses the ability to “hear” the chemical messages that tell your body to stop eating. Instead, your body is stuck in “starvation mode.” You crave fattening, high-carb foods, move less to conserve energy and keep eating.
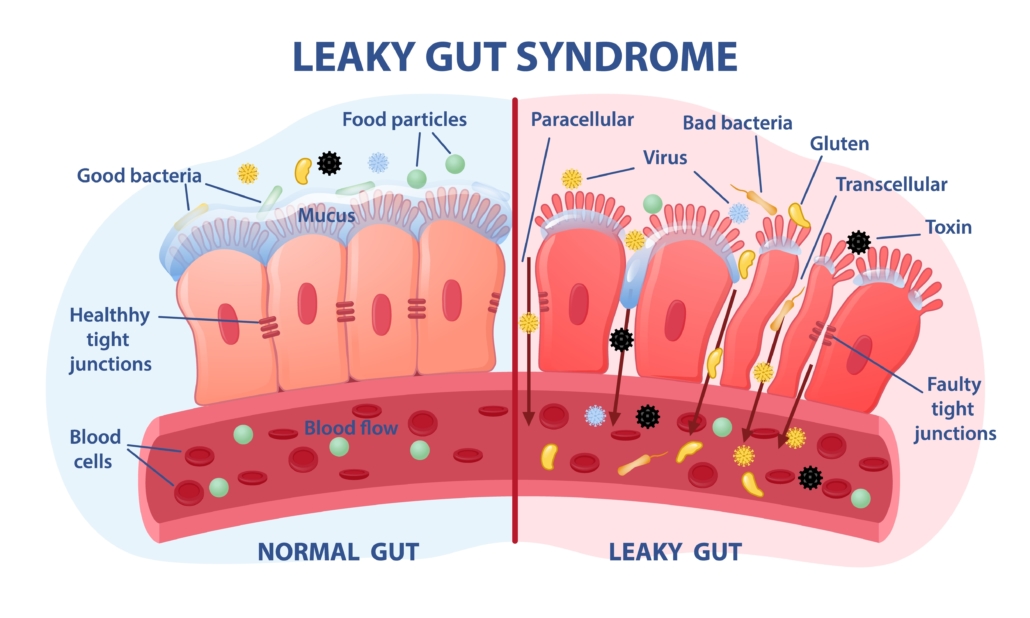
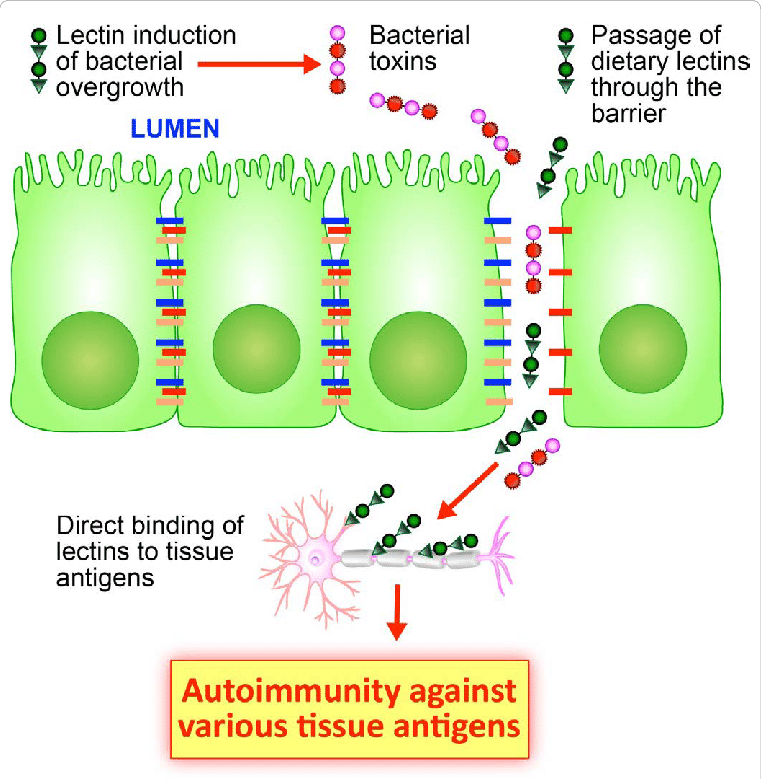
- chronic exposure to plant toxins and antinutrients that damage your intestinal barrier allowing pathogens into the bloodstream. From there, they circulate to every tissue in the body, causing chronic inflammation.
The impact of this metabolic damage is reflected in the fact that worldwide, 3 out of 5 people die from modern, chronic inflammatory diseases, including
- Stroke
- cardiovascular disease
- respiratory diseases
- heart disorders
- Cancer
- Obesity
- type 2 diabetes,
- various autoimmune disorders.
Because these diseases are virtually nonexistent in traditional hunter-gatherer societies, they are often called “diseases of civilization.”
Numerous studies on time-restricted eating and intermittent fasting have shown benefits that directly address the roots of these diseases, including
- Restores insulin sensitivity
- Restores leptin sensitivity
- Reduces inflammation
- stimulates autophagy–a process of cellular repair and renewal
- stimulates stem cell production, helps heal intestinal permeability
- improves insulin sensitivity
- increases BDNF–miracle grow for your brain
- supports weight loss
- reduced risk of cancer
- supports mindful eating
Which is Better, Time Restricted Eating vs. Intermittent Fasting?
When exploring time-restricted eating vs. intermittent fasting, let’s define their similarities and differences.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting simply means cycling between specific periods of eating and not eating. The fasting time can be of nearly any length, and take place at any time during a 24-48 hour cycle.
For instance, the largest intermittent fasting studies on humans have looked at the month-long Muslim religious practice of fasting between sunrise and dusk during Ramadan.
At the same time, intermittent fasting refers to popular methods like
- OMAD (one meal a day)
- 24-hour fast
- 20 hour fast
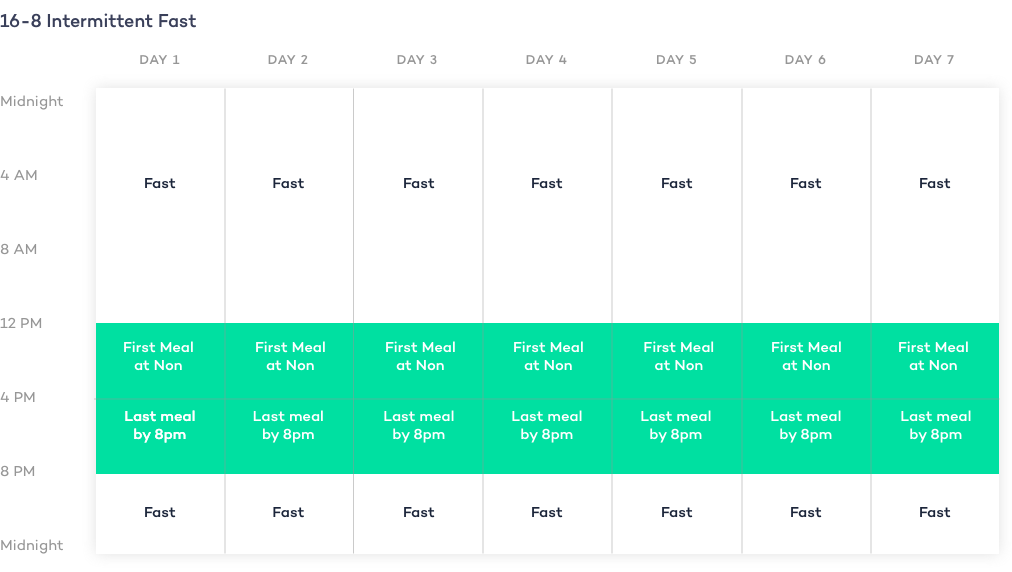
- 16/8 fast
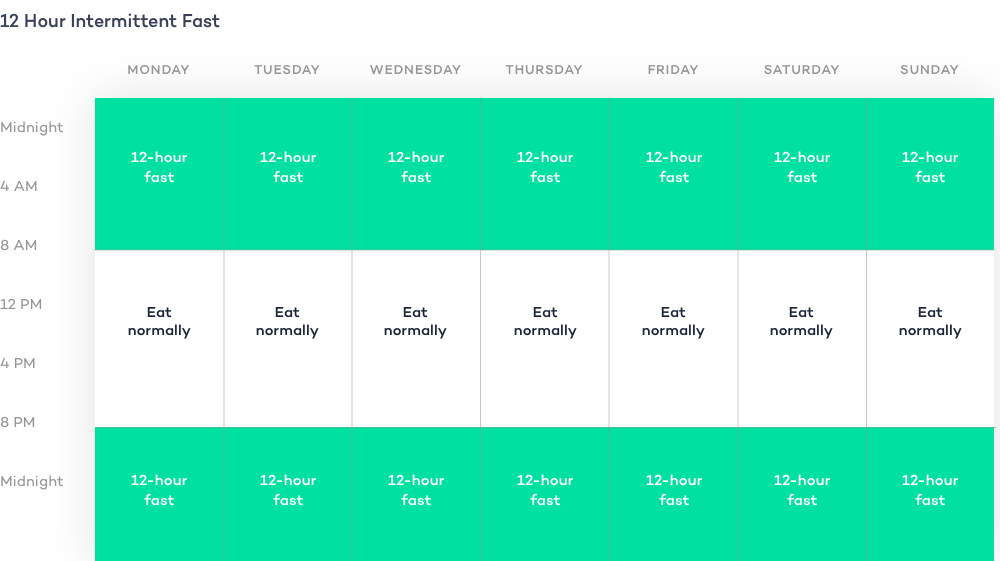
- 12 hour fast
What Sets Time Restricted Eating Apart from Intermittent Fasting?
Ttime-restricted eating is a type of intermittent fasting.
The key difference between time-restricted eating vs. intermittent fasting is that TRE specifically calls for eating within a limited number of hours during daylight.
In other words, time-restricted is aimed at aligning your eating with your circadian rhythm. While intermittent fasting includes all intentional fasting patterns and doesn’t distinguish between fasting during day or night. 4
This approach to eating in alignment with natural light and dark cycles is also called chrononutrition.6
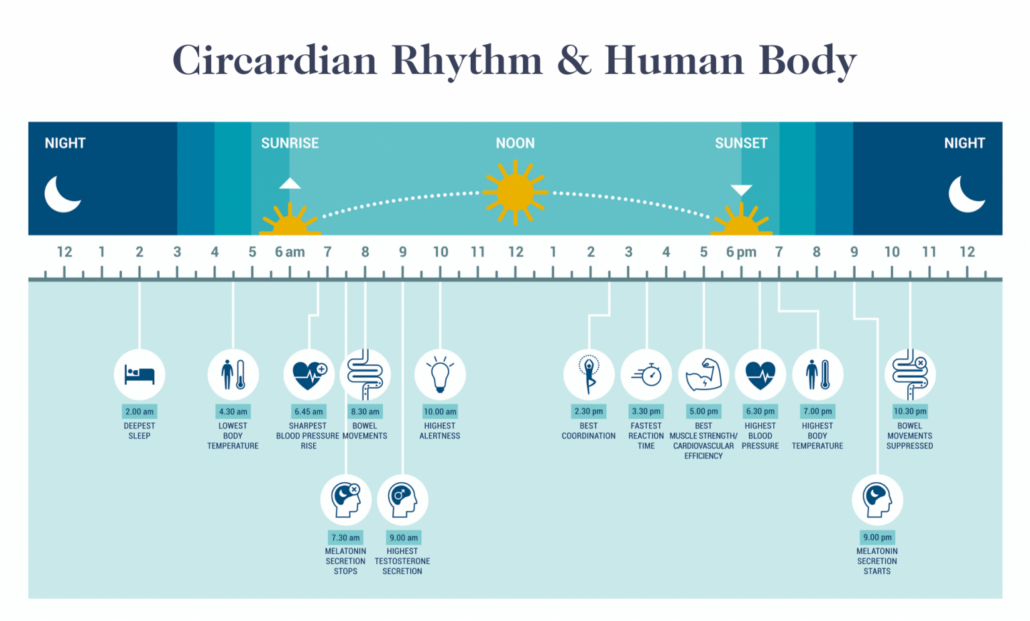
Why Does the Time of Day You Eat Matter?
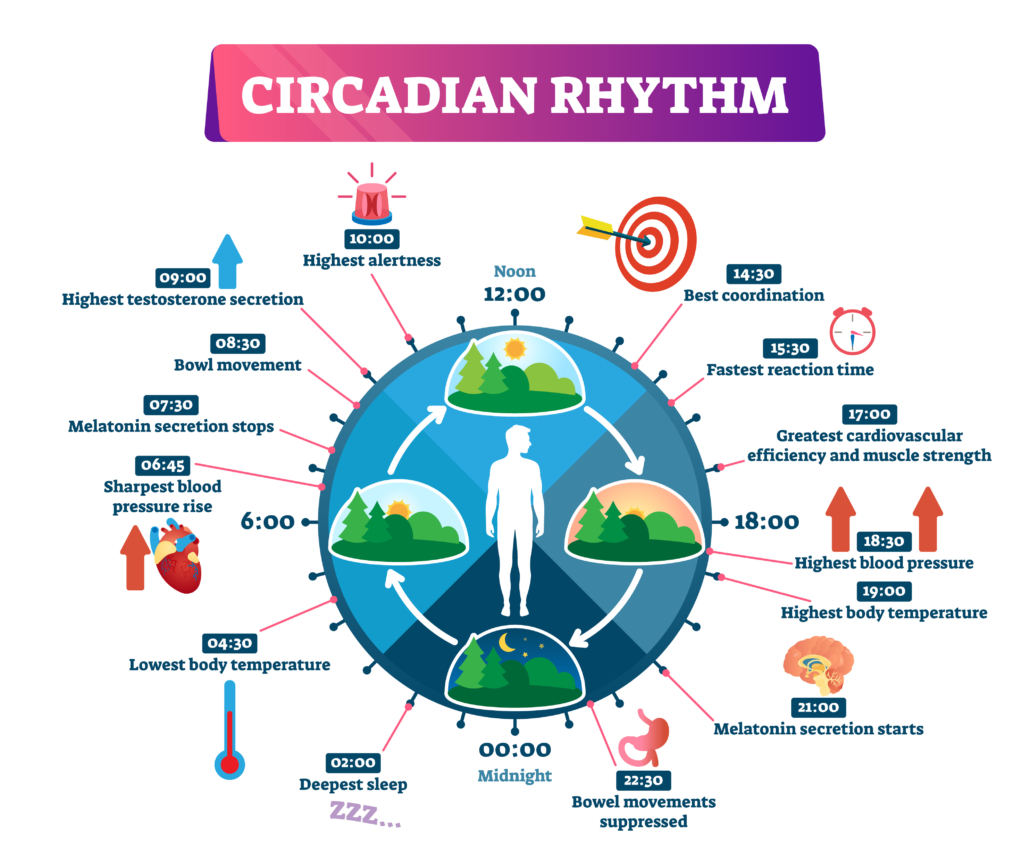
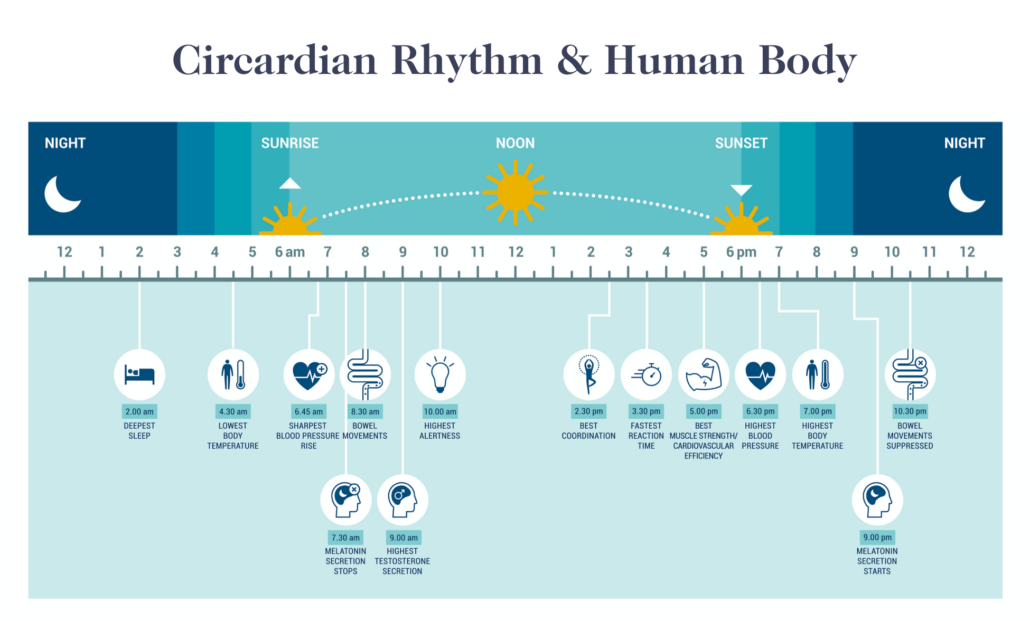
For millions of years before electricity and even fire, our physiology evolved in relation to natural light an dark cycles that governed our physical behavior, eating habits, and metabolism.
The result of evolving with the natural light and dark cycle is our internal biological clock, known as our circadian rhythm. Our circadian rhythm regulates many important bodily functions, including[1]
- sleep
- metabolism
- digestion
- hormone secretion
- immunity
- cognition
- neurobehavior
Accordingly, studies looking at the effects of eating in alignment with our circadian rhythm by taking our meals during daylight and abstaining from food after the sun goes down reveal numerous benefits, including
- weight loss [13]
- better sleep[14]
- relief from digestive symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation. [16]
- lower risk of intestinal dysbiosis (overgrowth of harmful bacteria)[17]
- Better immune function[18]
A 2014 review of numerous studies on time-restricted eating found that TRE can result in similar benefits, including 4
- decreased body weight
- lower triglycerides
- lower fasting glucose (blood sugar) levels
- lower levels of “bad” low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- higher levels of “good” high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
Time Restricted Eating vs. Intermittent Fasting for Autophagy

One of the most important features of time-restricted eating is that it supports autophagy.
Autophagy means “self-devouring.” It refers to the process where your body breaks down old and damaged cells and cell components and recycles them into new parts and cells.
Studies show that time-restricted eating patterns that restrict caloric intake for at least 16-18 hours overnight stimulate autophagy.[1] [2] 6 [3]
Autophagy supports numerous important pysioligical functions, including
- Slows aging and promotes longevity
- Supports teh health of every organ in the body
- supports cardiovascular health 5
- reduces inflammation 6
- protects against infection from bacteria and viruses 6
- protects against neurodegenerative diseases
- protects against cancer 6
Time Restricted Eating vs Intermittent Fasting: The Bottom Line
Time-restricted eating vs. Intermittent fasting is a bit of a false comparison. This is because time-restricted eating is a version of intermittent fasting.
The differentiating feature between intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating is that the TRE eating window takes place during daylight hours.
Eating during daylight hours and fasting during dark aligns eating with your circadian rhythm. Doing so improves sleep, supports healthy blood lipid levels, reduces insulin resistance, controls blood sugar, reduces blood pressure, and stimulates autophagy.