We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Carnivore Diet for Autoimmune Issues? How it Works
According to a 2021 study on the carnivore diet conducted by Harvard, 56% percent of the 2,029 participants cited autoimmune disorders as a reason for going carnivore.
And how did that turn out for them?
After at least six months on the carnivore diet, 89% of study participants reported improving or resolving their autoimmune disorders.
So, why is the carnivore diet so effective for treating autoimmune disorders?
Because it eliminates numerous substances and compounds that harm your body and trigger immune responses.
These immune-stimulating substances include:
- High carbs foods and added sugars
- plant toxins
- Plant antinutrients
- FODMAP foods
- industrial vegetable oils
- Toxic plant molds (mycotoxins)
- additives in processed foods
By eliminating these substances and replacing them with nourishing and nutrient-dense animal products, you are dramatically reducing your body’s overall inflammation load.
Table of Contents
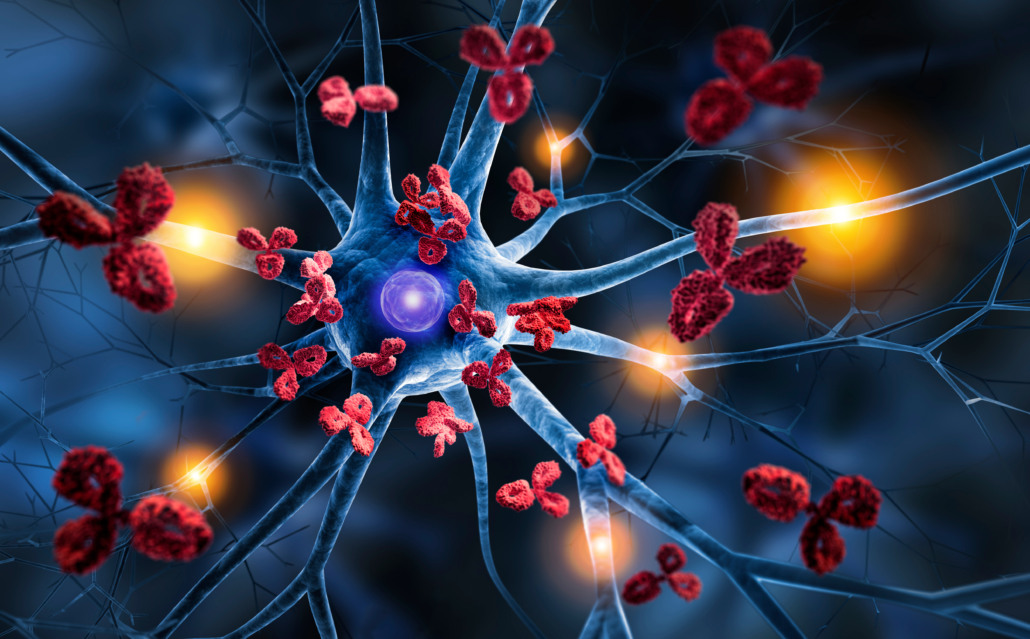
Autoimmunity and Inflammation
Inflammatory disease and chronic inflammation are general terms for autoimmune diseases.
When inflammation occurs in your body, your immune system is attacking your own bodily tissues.
Inflammation is an important and natural process that humans evolved as a way to combat infection and heal wounds. But our inflammatory response system evolved over eons as hyper-carnivorous hunter-gatherers.
Inflammation becomes a problem in the context of our modern diets loaded with foods that our bodies were not designed for.
The standard American diet is loaded with high-carb grains and fruits, added sugars, industrial seed oils (marketed as healthy “vegetable oils), and plant foods that have thousands of naturally occurring pesticides and antinutrients.
Though most of these substances are not acutely toxic, repeated exposure over time damages tissues, triggering inflammatory responses that never get the chance to turn off.
Common Autoimmune Disorders Targeted by the Carnivore Diet
Common autoimmune disorders addressed by the carnivore diet include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- inflammatory bowel disease
- Chron’s disease
- multiple sclerosis
- Heart disease
- PCOS
These chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorders affect nearly every organ in the body.
Common signs of autoimmune diseases include:
- Inflammation
- Joint stiffness
- Pain
- Rashes
- Fatigue
- Low mood/depression
- Anxiety
- Digestive problems–bloating, diarrhea, bloody stool, etc.
How common are these autoimmune diseases?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and research conducted by the Rand Corporation :
- Diseases related to chronic inflammation are the most significant cause of death worldwide
- Diseases related to chronic inflammation will increase persistently for the next 30 years
- 60% of Americans have at least one chronic inflammatory condition
- 42% of Americans have more than 1 chronic inflammatory condition
- 12% of American adults have 5 or more chronic inflammatory conditions
- Worldwide 3 out of 5 people die from chronic inflammatory diseases, including stroke, respiratory diseases, heart disorders, cancer, obesity, and diabetes
Carnivore Diet and Discordance Theory
The view that modern autoimmune diseases are caused by a misalignment between the modern foods we eat and our evolutionary physiology is called the discordance theory.
Many researchers refer to modern autoimmune diseases as “‘the diseases of civilization.”
These diseases are associated with modernity because they only became common after the agricultural revolution around 10,000 years ago.
In societies that still consume mostly pre-agricultural hunter-gatherer diets low in sugars, and high in animal-based fats and protein, these inflammatory diseases are virtually non-existent.
Autoimmunity Begins in the Gut
Since the modern foods we eat are implicated in autoimmune diseases, it makes sense that they’re the first wave of inflammatory damage that takes place in the gut.
Your body experiences abrasive fibers, plant toxins, pesticides, toxic molds, and antinutrients as “antigens.” Antigens are toxic foreign substances that elicit an immune (inflammatory) response from your body.
Over time, this inflammatory response weakens the gut lining, resulting in a syndrome called intestinal permeability, or “leaky gut.”
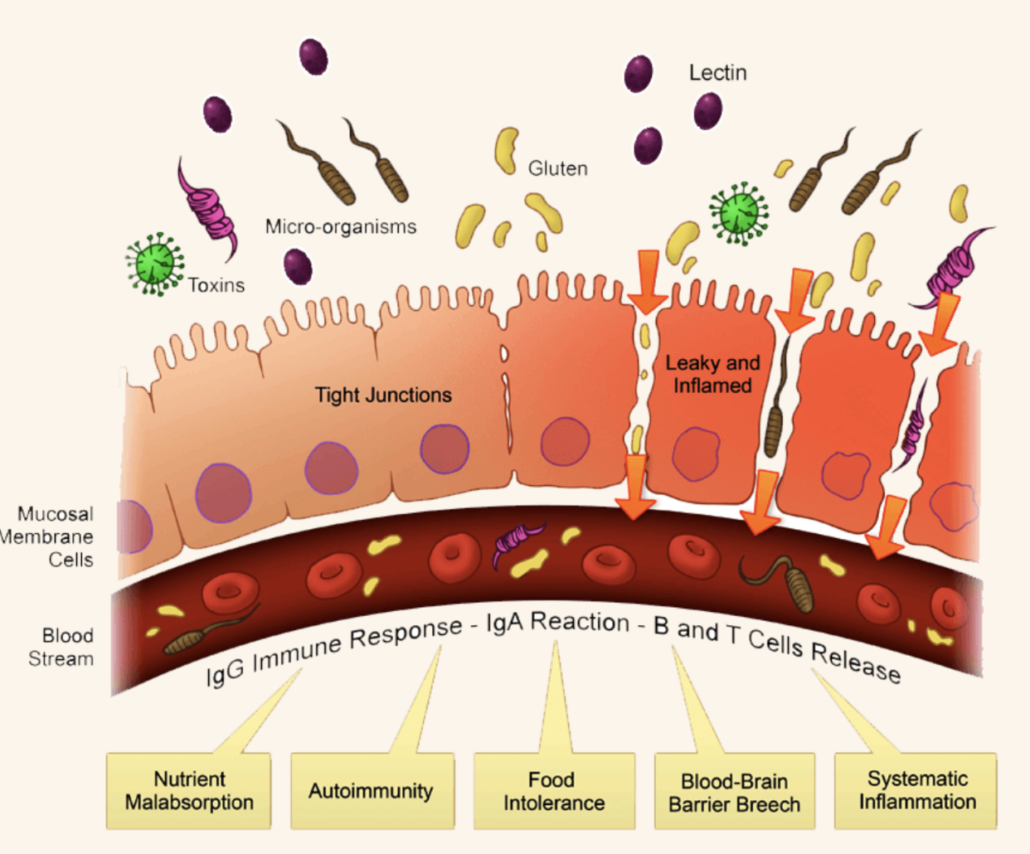
Intestinal permeability allows sugars, toxins, and harmful pathogens to cross into the bloodstream where they’re carried to every other part of the body, spreading antigenic sites and accompanying inflammation.
This process has led to many researchers viewing gut permeability as a probable root cause of various autoimmune diseases.
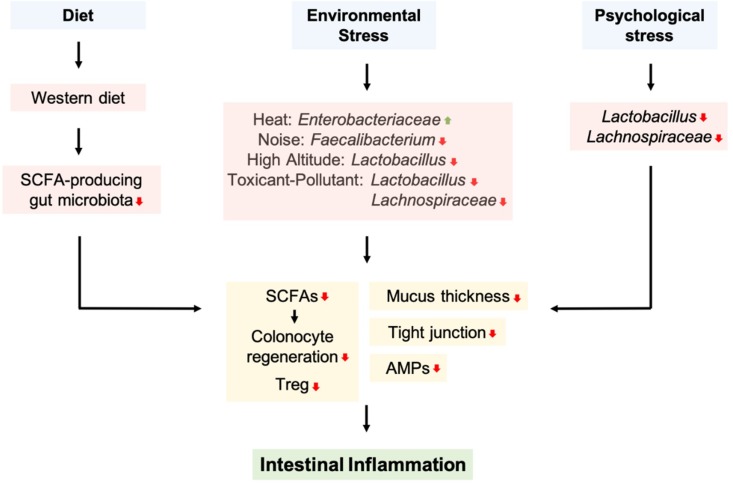
Source: Lobionda S, Sittipo P, Kwon HY, Lee YK. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Intestinal Inflammation with Respect to Diet and Extrinsic Stressors. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(8):271
Autoimmune stimulating agents eliminated on a carnivore diet
Let’s take a closer look at each of the autoimmune-stimulating substances that a carnivore diet eliminates.
Carbohydrates and Added Sugars
Most carnivore diet foods are extremely low in carbs.
Numerous studies show that high-carb diets promote inflammation while low-carb diets decrease inflammation.
Sugar and excess carbs cause inflammation due to the following mechanisms:
- Binding to tissues, DNA, RNA, and proteins in the process called glycation
- Damage to the glycocalyx–a protective membrane coating every cell in the body. The glycocalyx regulates vital functions, including cardiovascular health and immune system response
- Promoting harmful bacteria, and reducing protective bacteria in the gut leads to intestinal permeability 5
- Increasing “bad” LDL cholesterol 6 14
One of the studied ways that sugar directly contributes to chronic inflammation is through the process of glycation.
Glycation takes place when sugar molecules bind to proteins, fats, RNA, and DNA.
Seed “Vegetable” Oils
While animal fats are majority saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids, seed oils are mostly Omega-6 linoleic polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
Linoleic acid is a precursor of arachidonic acid– a highly inflammatory compound.
Arachidonic acid itself is involved in the creation of over twenty pro-inflammatory eicosanoids.
Studies show that these compounds may be the root of numerous chronic inflammatory diseases.
In a 2018 study looking at the role of vegetable oils in heart disease (accurately understood as an autoimmune disorder), researchers concluded, “In summary, numerous lines of evidence show that the omega-6 polyunsaturated fat linoleic acid promotes oxidative stress, oxidized LDL, chronic low-grade inflammation and atherosclerosis, and is likely a major dietary culprit for causing CHD [congenital heart disease], especially when consumed in the form of industrial seed oils commonly referred to as ‘vegetable oils.”
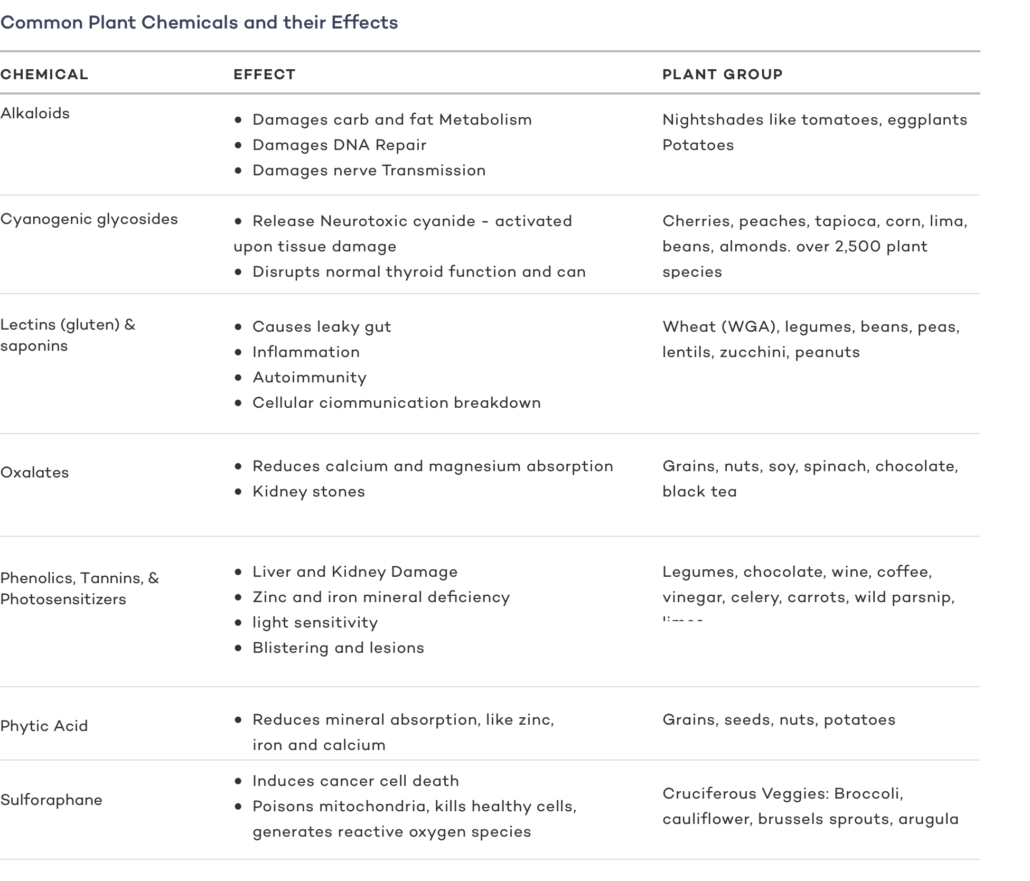
Plant Toxins and Antinutrients
Every plant produces its own blend of toxins and antinutrients. These compounds protect the plants from predators while facilitating internal processes, but they’re harmful to humans.
Naturally occurring plant chemicals make up a whopping 99.99% of all pesticides people consume as part of a regular diet.

Source: Ames BN, Profet M, Gold LS. Dietary pesticides (99.99% all natural). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(19):7777-7781.
Common autoimmune-stimulating plant toxins include:
 Lectins
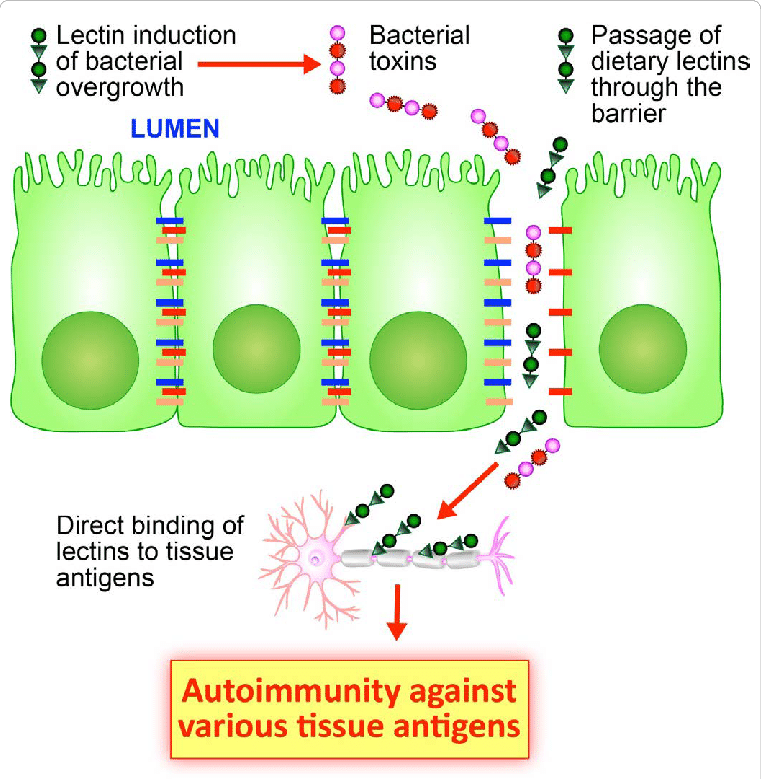
Lectins
Lectins are sticky proteins found in most plants. They are an active compound in many inflammatory plant foods.
Studies show that lectins exacerbate inflammation associated with IBS and autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis [9].
A 2017 study looking at the role of lectins found that
- Plant-derived dietary lectins are involved in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and celiac disease
- Plant lectins can activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and promote the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, which may contribute to food-associated chronic inflammation and inflammatory diseases.
Mycotoxins
Mycotoxins are toxic compounds formed by mold and fungi on grains, fruits, and coffee.
Mycotoxin contamination is a growing problem as global climate change leads to grains being stored in wetter and warmer conditions. [37]
One study on grains grown in Zimbabwe found that 13%-25% of small grains and 50% of maize were contaminated by mycotoxins. [40]
The body responds to mycotoxins as an antigenic threat and releases inflammatory cytokines. These substances bind to cell receptors resulting in autoimmune issues leading to blocked arteries, various cancers, and neurological disorders. [38] [39]
FODMAPS
FODMAPS stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols.
All grains and many other vegetables contain FODMAPS. These substances lead to intestinal overgrowth associated with chronic inflammation of the gut mucosal lining. [31] [32]
Carnivore Diet for Autoimmune Disorders
The carnivore diet is commonly used to resolve numerous autoimmune disorders.
The effectiveness of the carnivore diet against autoimmune disorders is likely due to the elimination of various inflammatory compounds found in plant foods.
Plant toxins, antinutrients, carbs, added sugars, fiber, FODMAPS, and vegetable oils all promote chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is the booth a root cause general term for autoimmune disease.