Top 20 High Oxlate Foods to Reduce or Eliminate
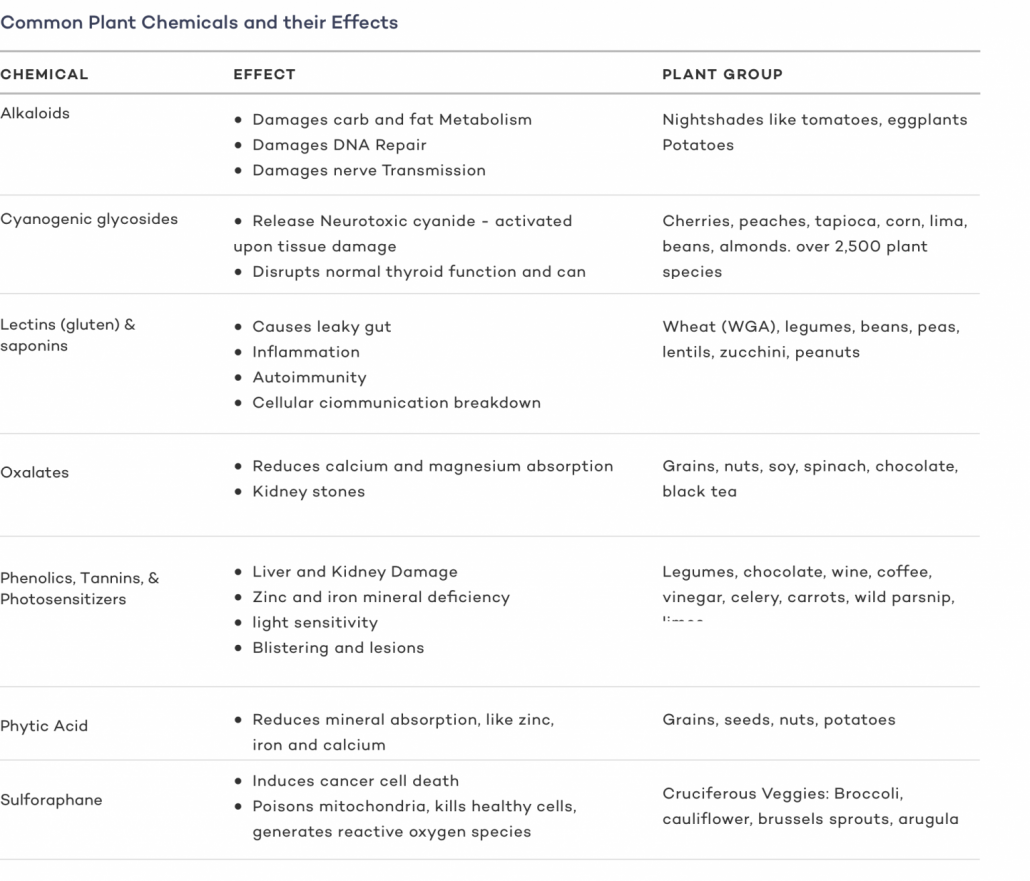
Oxalates are one of the many natural chemical defense mechanisms common in plant foods. In small doses, oxalates aren’t acutely harmful. However, repeated exposure to high oxalate foods can contribute to serious issues, including mineral deficiencies, fungal infections in the intestines, kidney stones, and increased risk of renal failure.
In this article, we’ll explore what you need to know about oxalate in your food, the risks of oxalate exposure, and a list of high-oxalate foods to eliminate or avoid.
[TOC]
What You Need to Know About Oxalates
Oxalates are naturally occurring organic compounds in plants. They play a key role in regulating a plant’s internal mineral content and help defend against predation. [1]
But as with other natural plant toxins and antinutrients, what’s good for plants is often bad for humans.
It’s important to remember that from the perspective of a plant, humans are predators. Though we’ve been told that vegetables are our friends, they are equipped with sophisticated chemical defenses. In small doses, these chemicals don’t do much harm. But consuming an abundance of plant toxins over time can lead to serious health problems.
Some of the problems caused by consuming high-oxalate foods include
- Inflammation and oxidative stress
- Impaired absorption of important nutrients, including iron, calcium, and magnesium. Oxalates are behind the surprising fact that virtually none of the iron in spinach is absorbed by your body.
- Suppressed immune function and reduced mitochondrial activity.
- Kidney stone formation.
- Fungal infections in the intestine
How do You Eliminate Oxalate from the Body?
The most straightforward and effective approach to eliminate oxalate is to cut out high oxalate foods. Once the source of oxalate is eliminated, your body will naturally metabolize oxalate and excrete it through the stool and urine.
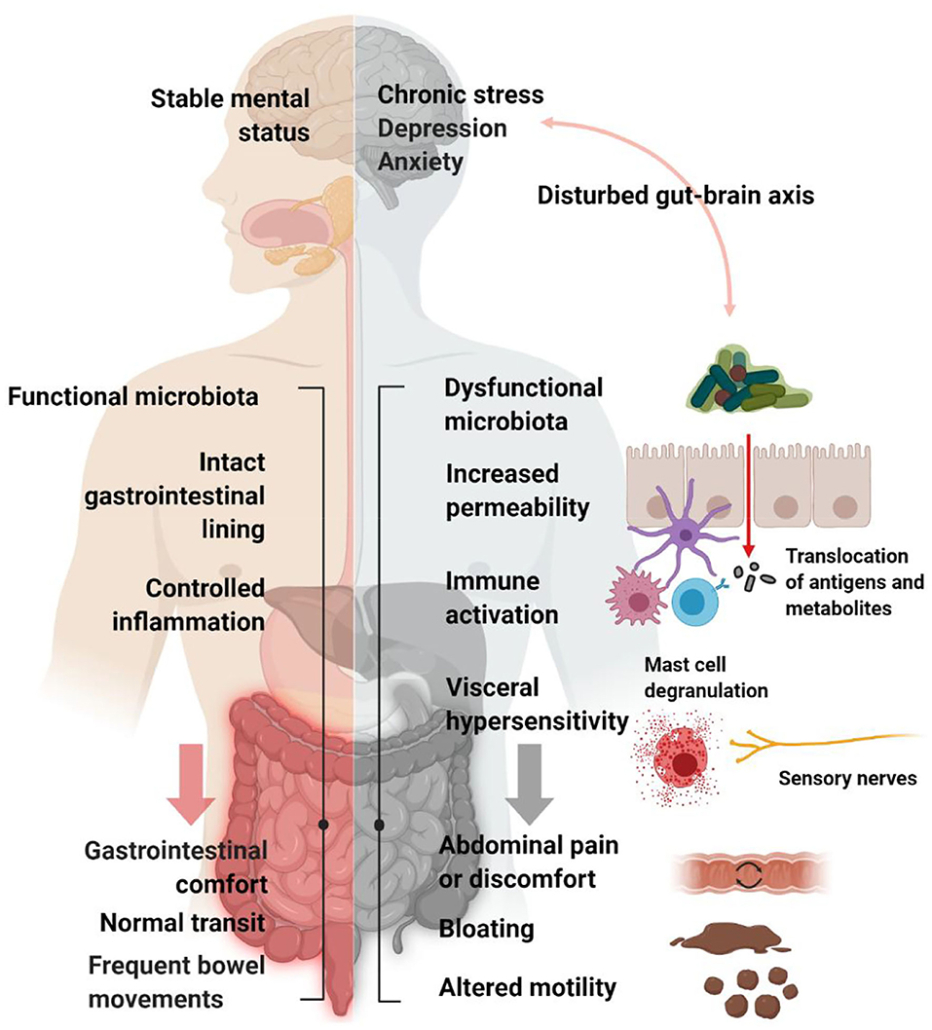
What is Oxalate Dumping?
“Oxalate dumping” is the term given to the metabolic process of expelling oxalate.
It is thought to occur when you significantly reduce oxalate intake.
Though oxalate dumping is not a medical term, thousands of people report the phenomenon, especially all meat carnivore dieters. This detox process can come with some uncomfortable side effects, including
- Body and joint pain
- sore throat
- burning tongue
- bladder pain.
- Cloudy urine and frequent urination for the body to expel oxalates.
- painful bowel movements
- skin rashes
- mood swings
- fatigue
- dizziness
- painful urination
- brain fog
- Panic and overwhelm
- depression
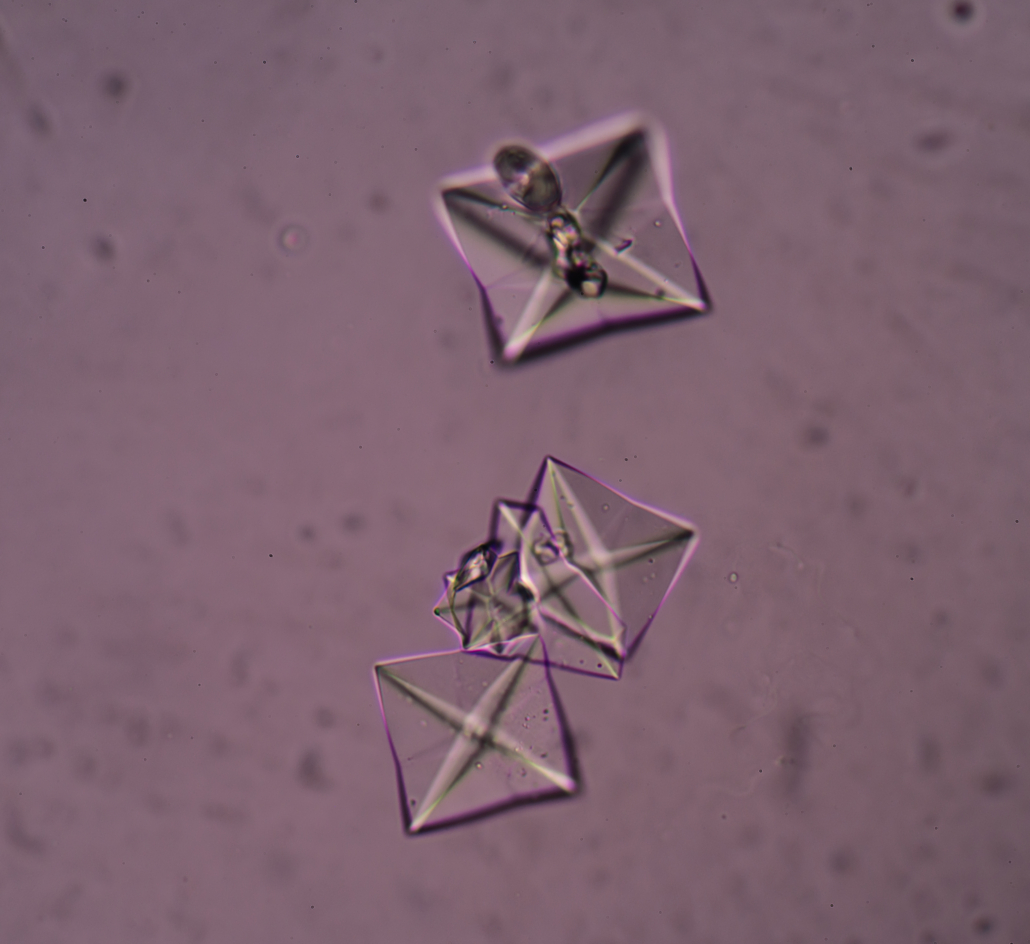
These symptoms are remarkably similar to the detox process known as the Jarisch–Herxheimer reaction that takes place when candida yeast die off in the intestines. These similarities suggest a link between resolving fungal infections associated with oxalate crystals.
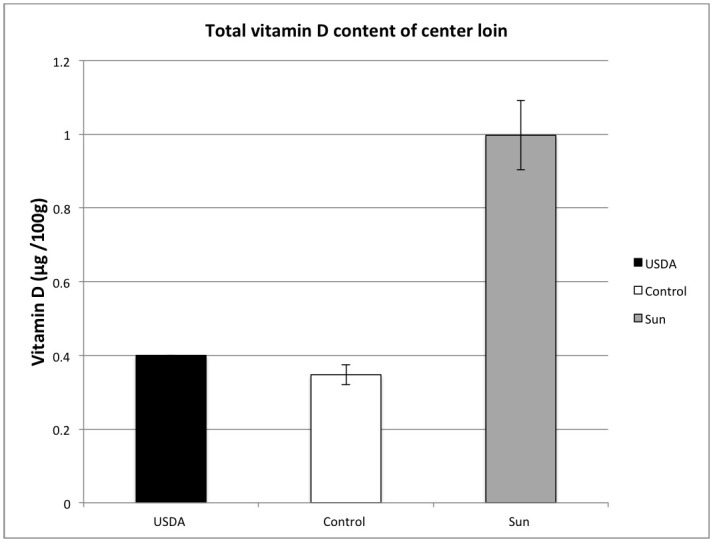
20 High Oxalate Foods
Foods are considered to be high oxalate when they contain more than 50 mg per 100-g serving.
This list of high oxalate foods will help you avoid the worst offenders.
1. Beet Greens 1,200-2,300 mg of oxalate per 100 grams
Beet greens aren’t crunchy because they’re just dirty–it’s all that oxalate. That’s right, the crunchy or sandy texture of many leafy greens is actually the abundance of poisonous oxalate crystals.
Beetroot has less, but is still considered a high oxalate food with 125 mg per 100-gram serving.
2. Swiss Chard 500-900 mg per ½ cup
Swiss chard is loaded with a natural toxin called oxalate. Just one half-cup of steamed white-stalked swiss chard has about 500 mg of oxalate and ½ cup of steamed red swiss chard has over 900 mg of oxalate
3. Spinach: 755 mg per ½ cup
Spinach and many other leafy greens are high in oxalate. Though they’re often heralded for their supposed mineral content, oxalates impair binding to these minerals, rendering them useless. 4
4. Rhubarb: 541 mg per ½ cup
Bye-bye, rhubarb tarts. Granted, most of the rhubarb oxalate is in the leaves, so if you stick with the stalks, you’ll be in better shape. But it’s probably not worth the risk.\
5. Cacao (Cocoa powder) 360 to 567 mg per 100 g
Though cocoa is delicious and high in magnesium, it’s not a good choice for people trying to reduce their oxalate intake.
6. Soy products 235-336 mg per 3 oz.
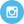
At 235 milligrams of oxalate per 3 oz. serving, there are certainly better options for getting your protein. How about a zero oxalate ribeye steak?
At 336 mg per serving, soymilk and yogurt are even greater contributors to your oxalate load.
And oxalate is only one of the numerous plant toxins contained in soy products.
Soy has high concentrations of phytohormones that can disrupt hormone levels in the human body, distorting the male androgen to female estrogen balance, and leading to disruptions in egg formation and sperm production.
7. Peanuts 187 mg per 100 grams
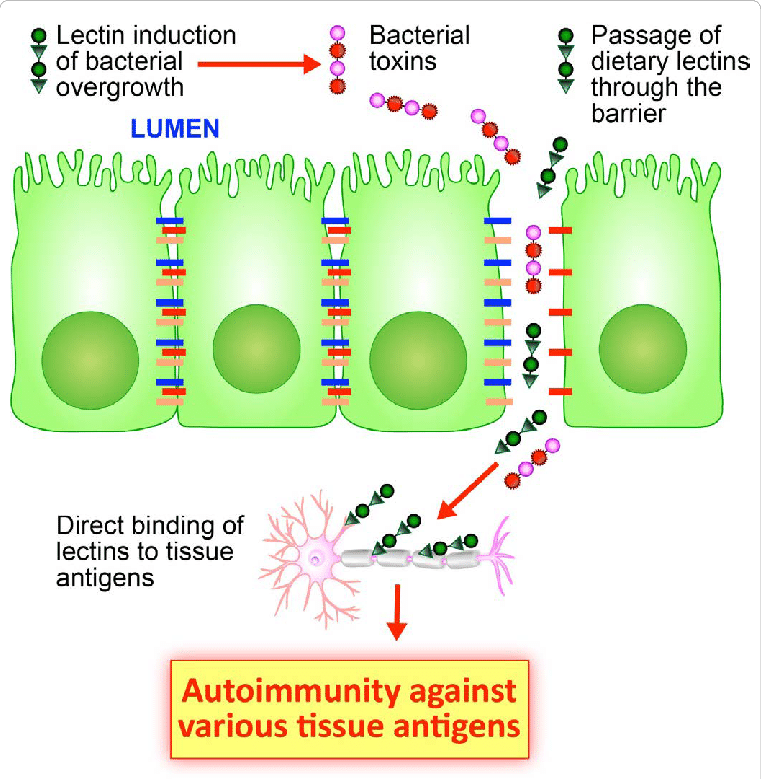
As a legume, peanuts contain another plant toxin called lectin. These sticky proteins can team up with oxalate to damage the lining of your gut leading to intestinal permeability.
When your gut barrier is compromised, lectin can enter your bloodstream, where they bind with bacteria and viruses making it easier for them to reach their targets in your body.
8. Almonds 366 mg per 100 grams
This works out to 122 mg of oxalate per 22 nuts–about a handful.
Recent studies also suggest that alternative plant-based milk, including almond milk, are underappreciated sources of oxalate that can lead to kidney stones.
9. Buckwheat Groats: 133 mg per ½ cup
Buckwheat groats are like nuttier rice, but they don’t have a place on a low oxalate diet.
And if you’re lamenting the loss of fiber, don’t. Consuming fiber and oxalate together can amplify the ways that both compounds impede mineral absorption.
In addition to fiber and oxalate, buckwheat also contains another antinutrient called phytic acid. This compound blocks the absorption of zinc, magnesium, and calcium. And studies show that calcium is needed to reduce oxalate damage.
10. Potatoes 97 mg per medium baked potato
Since much of the oxalate is in the skin of potatoes, occasionally consuming peeled potatoes won’t add much to your oxalate load. Good news for those of you who enjoy the occasional tallow-friend french fries carnivore “treat” day special.
11. Navy beans 76 mg per ½ cup
Like peanuts, navy beans are another legume with a potentially harmful combination of oxalate and lectin.
Other High Oxalt Foods to Avoid
The following foods round out the bottom of the list.
12. Bulgar: 86 mg per cup
13. Raspberries: 48 mg per cup
14. Dates: 24 mg per date
15. Okra: 57 mg per 1/2 cup
16. Cashews: 49 mg per 1 oz
17. Lentil soup: 39 mg per cup
18. sweet potatoes: 28 mg per cup
19. Bran flakes: 57 mg per cup
20. tar fruit juice: 800 mg per 4 oz.
High Oxalate Foods: The Bottom Line
Oxalates are compounds that occur naturally in many popular plant foods.
Consuming too much oxalate (oxalic acid) has been linked to various health issues, including kidney problems, intestinal fungal infections, and inflammation.
The good news is that by reducing high-oxalate foods, your body will naturally metabolize and expel oxalate.