We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Paleo vs Keto: Which is Healthier

The paleo diet and keto diet are two of the most popular wellness trends in the world. And both claim to be inspired by how our caveman ancestors ate. However, when it comes to keto vs paleo, there are major differences to be aware of, both in terms of accurately recreating the diets of ancient humans and health outcomes.
In this article we’ll compare paleo vs keto, looking at the similarities and differences, along with the pros and cons of each.
Table of Contents
What is Paleo?
The paleo diet focuses on eating the types of foods presumed to have been eaten by early humans during the paleolithic era.
These foods include meat, fish, vegetables, and fruit. Paleo eliminates dairy, grains, legumes, processed foods, and sweeteners.
The philosophy behind paleo is that after eons of evolution our bodies are genetically designed to consume the foods of our paleolithic ancestors.
This approach is based on the fact that for most of human evolution, foods that arose with agriculture and dairy did not exist. A full 70% of modern foods are products of the agricultural revolution which began only 10,000 years ago [1]. By contrast, the paleolithic periods lasted nearly two million years.
The foods allowed on a paleo diet include:
- Meat and fish (often lean)
- Eggs
- Nuts and seeds
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Specific fats and oils including coconut oil, olive oil, avocado oil, lard, tallow, ghee/butter
- Some raw sweeteners including raw honey, maple syrup, coconut sugar, raw stevia
Critique of Paleo
Critics point out that the term ‘paleo’ is merely a marketing term and does not accurately represent the diet of ancient humans.
Most of the vegetables, fruit, and oils permitted on the paleo diet did not exist in the paleolithic period.
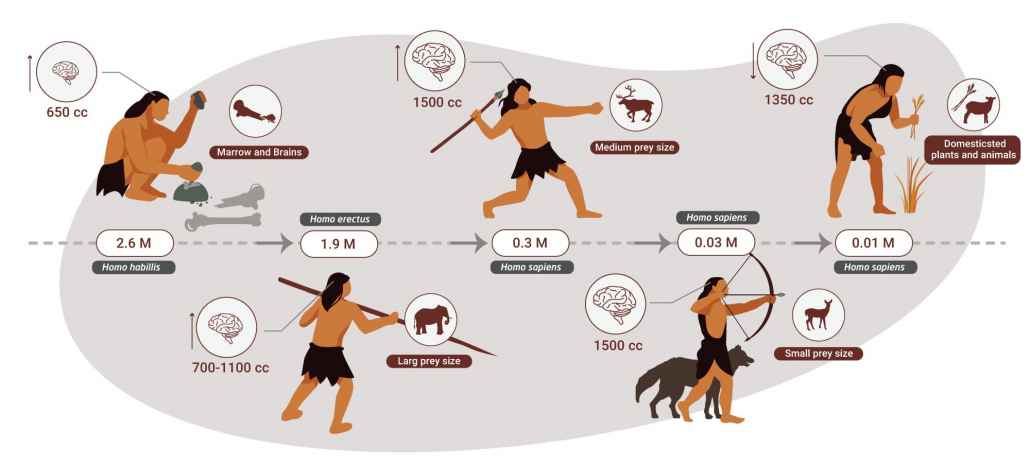
For our ancestors, nuts and seeds were few and far between and required a lot of processing to remove poisons. Meat on the other hand was abundantly harvested from large animals (megafauna) that roamed the globe for most of the paleolithic period. So it’s likely that nearly all paleolithic humans got 55-95% of their calories from meat.
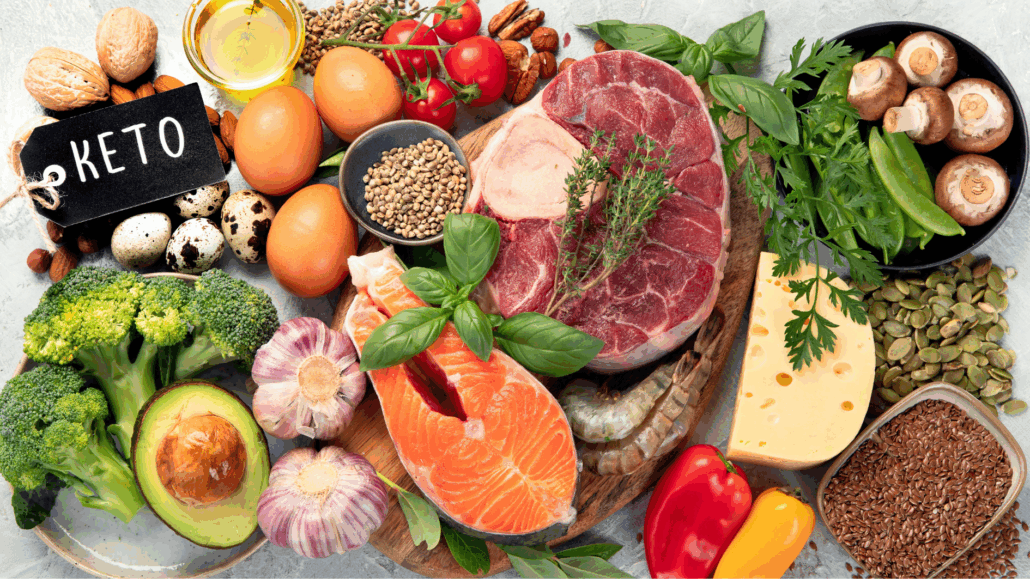
What is Keto?
The ketogenic diet (keto) is a high-fat low-carb, moderate-protein diet.
Drastically reducing carbohydrate intake triggers your metabolism to break down fat stored on the body, and to use fat from food as the primary energy source. Some of this fat gets converted into energy molecules called ketones.
When your body is producing high levels of ketones, you are in ketosis.
In contrast, the standard American diet is high in starch and sugar. The average American consumes 50%-60% of calories from carbohydrates, 20% of which come from added sugars. [6]
Paleolithic Keto
Many people who practice keto, view it as an ancestral way of eating that more accurately represents the eating patterns of paleolithic people than the paleo diet. In this way, keto can be viewed as a correction or update upon the paleo diet.
Keto Macros
There are various types of ketogenic diets, but they all call for macronutrient ratios within these ranges:
- 70-80% of calories from fat
- 15-30% calories from protein
- 0-10% calories from carbohydrate
People practice keto for various possible benefits, many of which have been supported by research including [2][3][4][5]:
- Protection against diabetes
- Supporting cancer treatment
- Reduced risk of Alzheimer’s
- Reduced epileptic symptoms
- Weight loss
- Reset gut microbiome
What Paleo and Keto Have in Common
Though paleo and keto have their own specific rules, they do share some important things in common.
Whole Foods
Both keto and paleo emphasize whole foods. These are foods that haven’t been processed through modern industrial techniques and are generally fresh (not preserved) before they are cooked or reach your plate.
Common whole foods include:
- Meat
- Fish
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Nuts
For both of keto and pale the elimination of processed foods loaded with industrial fats, processed grains, and added sugars is a key factor in their health benefits [6].
It’s worth noting that there are many packaged and processed foods labeled as ‘paleo-friendly’ and ‘keto-friendly’. In the case of paleo, these foods may meet paleo standards of ingredients, but not of freshness. While ‘keto-friendly’ processed foods often meet macronutrient ratios but contain various unhealthy industrial ingredients.
For a rundown of whole foods, keto snacks click here.
Eliminate Refined Sugars
Keto calls for dramatically cutting carbs, and paleo calls for eliminating processed foods. These two rules mean that both diets cut out essentially all added sugars.
One exception on keto is the small amount of sugar in some keto ice cream recipes.
When it comes to paleo, no refined sugars does not necessarily mean a low sugar diet. Honey, maple syrup, and fruit are all sources of sugar that are not restricted.
Eliminate Grains and Legumes
Both paleo and keto eliminate grains and legumes. The reasoning overlaps and diverges in interesting ways.
For paleo dieters, legumes and grains are eliminated because they were not part of the diet humans evolved on.
Central to the reasoning behind their elimination is that they contain plant toxins and antinutrients. These naturally occurring compounds including phytoalexins, lectins, phytates, phytohormones are part of a plant’s defense mechanisms [7][8][9].
When consumed by humans, these plant toxins can contribute to numerous health problems stemming from digestive issues, nutrient deficiencies, and leaky gut.
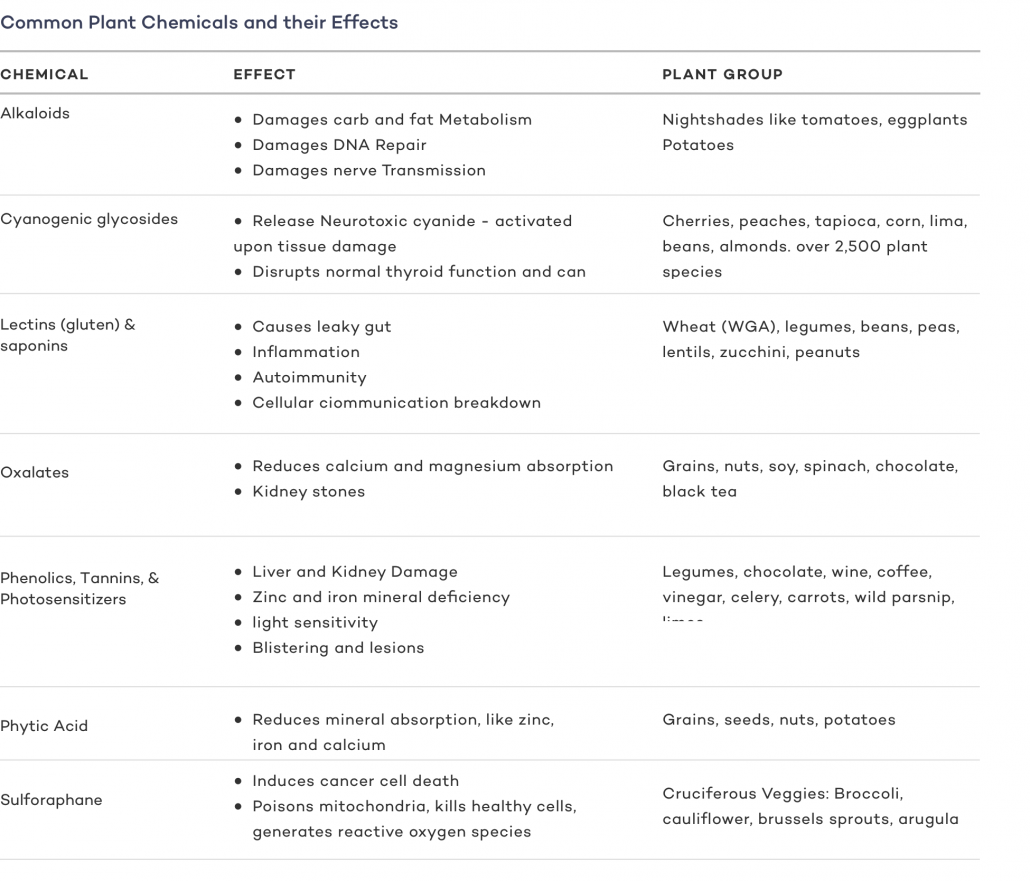
A standard keto diet eliminates legumes and grains because they are very high in carbs. However, many keto dieters, especially those practicing the carnivore diet, take an evolutionary perspective by eliminating or greatly reducing all plant foods to avoid plant toxins.
This approach is supported by recent research suggesting that for most of human history our caveman ancestors were apex predators that ate mostly meat [10].
Focus on Healthy Fats
Both keto and paleo call for consuming healthy fats while eliminating processed fats, especially from vegetable oils.
Keto puts much greater emphasis on fats in general since they account for 70-80% of daily caloric intake.
Butter and ghee, are featured on keto but eliminated on paleo.
Some Shared Health Benefits
Both paleo and keto have been shown consistent health benefits that overlap when it comes to weight loss.
One study looking at the effectiveness of paleo for weight loss in a population of postmenopausal obese women found 12.6% weight loss after 12 months [11].
Various other studies show that paleo can help reduce weight, waist circumference, blood sugar, and insulin levels while improving markers of heart health [12][13][14][15][16].
Various studies on low-carb, high-fat diets like keto, showed consistent short-term weight loss, reduced blood sugar, and insulin regulation [17][18].
A study looking at a Mediterranean keto diet for 22 obese men, found that all the participants had lost at least 30 pounds and reversed all markers of metabolic syndrome [19].
Paleo vs Keto: How They Diverge
Though paleo and keto share some similarities, they diverge in important ways that can lead to very different health outcomes.
Macronutrients
Paleo does not call for any specific macronutrient ratios and does not restrict carbs, whereas carbs are restricted and fat intake is boosted on keto.
Carbs
For most people, a paleo diet will be a relatively low-carb diet due to the elimination of high-carb grains, legumes, and added sugars.
But if you eat a lot of fruit, honey, and starchy vegetables, a paleo diet can be quite high in carbs. The allowance of these sweet foods can make it difficult to curb carb addiction and make the diet less effective at combating features of metabolic syndrome.
Keto calls for a dramatic reduction in carbs since restricting carbs is the key to activating ketosis. It also calls for centering your diet around healthy keto fats, fatty fish and seafood, and fatty keto meats.
Keto allows for some low-carb fruits, and low-carb keto veggetables.
Though these fatty foods can, and probably should be the center of a paleo diet, the mainstream paleo directions call for a focus on lean meats with only supplemental use of fats.
Dairy and Soy
Full-fat dairy like many keto cheeses, keto yogurts, butter, and ghee are important staples for many keto dieters.
However, there is a growing movement in keto to substitute A1 dairy products–due to intolerance of specific dairy proteins–with A2 dairy from specialized cows, goats, sheep, and buffalo.
Keto also allows for soy products like tofu, tempe, and soybeans, which can be an important source of protein for vegan keto dieters.
On paleo all forms of dairy are off-limits, as is soy because it is a legume.
Paleo vs. Keto: Which is Healthier
When comparing paleo vs keto, the big question is which is healthier?
The answer to this question depends in large part on how well you formulate your meal plan.
If you do “dirty” keto by focusing only on macronutrient ratios and allowing for processed foods high in industrial oils and chemical sweeteners, a paleo diet of whole foods will be healthier.
On the other hand, a high sugar paleo diet with lots of fruits, honey, and starchy vegetables can result in hyperinsulinemia. This condition is associated with infertility, metabolic syndrome, type II diabetes, heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders [20][21][22]
If your goal is to activate the health benefits of a low-carb diet, keto is likely the best option. However it is possible to eat a low-carb paleo diet, but you’ll likely need to boost your fat intake to meat your energy needs, in which case you will essentially be going keto.
Side Effects
A standard paleo diet will have fewer side effects with transitioning from a Standard American Diet. Transitioning into ketosis can have unpleasant but temporary side effects.
These can be mitigated with simple strategies like staying well hydrated, adding more salt to meals, consuming more fat, and supplementing electrolytes.
Convenience
Paleo is less restrictive than a standard ketogenic diet because you don’t have to worry about limiting carbs. For this reason, it may be more convenient and easier to stick with.
In the long term, many people practice a hybrid version of keto and paleo. This entails focusing on whole foods like fatty meats and low-carb fruits and veggies while elminiating grains and legumes, but without being very strict about macronutrient ratios.
This flexible approach allows people to cycle in and out of ketosis and is a version of what’s called a cyclical keto diet.
Keto vs Paleo: The Bottomline
The ketogenic diet means dramatically cutting carbs and increasing fat intake. It’s been shown effective for weight loss, controlling blood sugar, protection against neurological and metabolic disorders, and can reset the gut microbiome.
The paleo diet calls for eating whole foods and eliminating dairy, grains, and legumes. Though the paleo diet purports to include only foods that were eaten by paleolithic humans, it’s more of a marketing tactic.
Paleolithic humans did not have access to the vast majority of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds that modern paleo dieters eat. It’s also likely that our ancestors prized animal fats and organ meats over the lean meats championed by paleo dieters.
For most people, the healthiest most sustainable option will be a hybrid diet centered on fatty animal foods, supplemented with low-carb fruits and veggies, while eliminating grains, legumes, added sugars, and all processed foods.