We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Is Goat Meat Healthy? Nutrition and Benefits

With the rise in ancestral meat-based eating approaches like nose-to-tail and carnivore, there has been growing interest in alternative meats. As a result, goat meat, also called “mutton” and “chevon,” has found its way back into the limelight.
In many cultures of the Mediterranean, north African, and Middle Eastern regions, goat meat is far more popular than beef, chicken, and pork and has been a central part of traditional diets for millennia.
With the growing popularity of goat meat come questions surrounding its nutritional value and health benefits.
In this article, we’ll explore the advantages of incorporating goat meat into your diet, including its potential impact on various health markers, including heart health and weight management.
Table of Contents
Goat Meat 101
Goats were first domesticated around 11,000 years ago, making them the oldest domesticated animal on earth.
Goat, like the meat of sheep, has two main classifications.
- Capretto or kid, is from young milk-fed goats aged 4 months or less. It is leaner and more tender than meat from adult goats.
- Chevon is goat meat that comes from an animal between 4 and 14 months old. Tougher than meat from young goats, it is best slow-cooked with moist heat as with stews and curries.
Not all goats are raised for meat. Some goat breeds are raised specifically for milk. Popular meat breeds include the Spanish, Brush, and Boer types.
Where Do People Eat the Most Goat Meat?
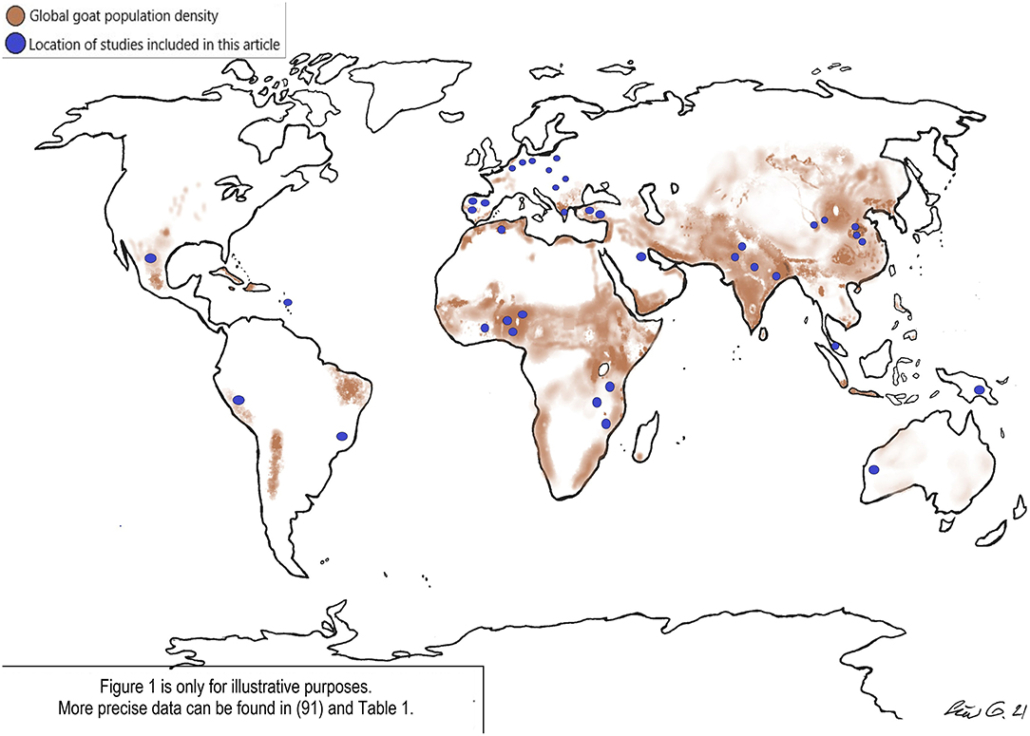
Source: Frontiers in Veterinary Science
Unlike many other types of meat, goat meat is not culinarily constrained by culture and religious taboos. This allows it to be integral to a wide swatch of global diets, including in Africa, the Caribbean, the Middle East, the Mediterranean, and many parts of South and East Asia.
Interestingly, goat is less common in countries with more recent European settlements, including Australia, America, and Canada.
Part of the reason for this is a combination of convenience and economics. Cattle require much more forage than goats. For example, the same pasture that sustains 25 goats can only sustain five steers. A the same time, you can harvest much more meat from cattle than goats. So where there is more foraging land, cattle abound.
However, one place in America with an abundance of goats is Texas, which is home to 44% of the U.S.’s three million-plus goats. In Texas and in other states, ranchers are raising goats as a less energy intensive and more environmentally friendly red meat.
Goat Meat Nutrition
Like other red meats, goat is a nutrient-dense whole food that provides a complex of healthy fats, proteins, essential vitamins, and vital minerals.
| Nutrient | Per 150 grams (⅓ lb) serving | % RDV |
| Fat | 3.5g | |
| Saturated Fat | 1.1g | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 1550mg | |
| Cholesterol | 85.8mg | |
| Protein | 31g | |
| VITAMINS | ||
| Thiamin (B1) | .2mg | 14% |
| Riboflavin (B2) | .7mg | 57% |
| Niacin (B3) | 5.6mg | 35% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.7mcg | 71% |
| MINERALS | ||
| Iron | 4.3mg | 24% |
| Potassium | 579.5mg | 12% |
| Phosphorus | 270.9mg | 22% |
| Zinc | 6mg | 55% |
| Copper | .4mg | 30% |
| Selenium | 13.2mcg | 24% |
Health Benefits of Goat Meat
When asking, “Is goat meat healthy” we have to consider how rich it is in essential and important macro and micronutrients. Let’s take a look at some of the heavy hitters and how they can contribute to your health goals.
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)
Goat meat is among the world’s richest sources of Conjugated linoleic acid, or CLA.
CLA is a type of fatty acid mainly found in grass-fed ruminant animals and provides numerous studies benefits, including
- Significant protection against various cancers. . Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2013 Jan 1″/] A 2016 study out of Finland found that women who consumed adequate CLA experienced a 60% reduction in incidences of breast cancer compared with women who consumed lower levels of CLA.
- Reduces the risk of various metabolic diseases, including type 2, cardiovascular disease, and obesity.
- Profound anti-inflammatory effects
- Boosts immune function
Vitamin B12
Goat meat is a rich source of vitamin B12. B12 is essential to the proper function of numerous physiological processes, including
- Red blood cell production
- Turning the food we consume into useable energy
- DNA synthesis
- Neurological function
- Overall health and vitality
Vitamin B12 found in goat and other red meat is a key factor in the numerous studies that show that meat eaters experience significantly lower incidences of depression and psychiatric disorders than vegetarians and vegans.
Heme Iron
Goat meat is a good source of heme iron, which vital to
- Oxygen transport
- Energy production
- Red blood cell formation
If you don’t get enough iron you’ll suffer from anemia.
The type of iron in goat meat, called heme iron, is far more absorbable than iron found in plant foods, which is why anemia is prevalent among vegans and vegetarians.
Selenium
Goat is a good source of selenium. This essential trace mineral provides antioxidant properties and is part of enzymes and proteins called selenoproteins.
Selenium is a mineral that is an essential part of various enzymes and proteins called selenoproteins. These proteins play an essential role in important physiological processes, including :
- Thyroid function
- Immune function and infection resistance
- Reproductive health
- DNA synthesis
- Reducing oxidative stress
- Increases glutathione–considered the “master” antioxidant
- Protects against various cancers
- Protection against neurodegenerative disease, including Alzheimer’s
- Supports lung health
Zinc
Goat meat provides 55% of your RDV of zinc per ⅓ lb serving.
Zinc is one of the most important yet underrated nutrients that your body needs to complete numerous vital functions, including
- Growth and development
- Blood sugar regulation
- increase testosterone levels and improve sperm quality
- Immune function
- Bone health
- Wound healing
- Control inflammation and oxidative stress
Potassium
Goat meat is high in potassium, making it a great addition to an all-meat carnivore diet.
Potassium is an essential nutrient that teams up with sodium to maintain normal fluid levels inside your cells.
Potassium plays key roles in an array of bodily functions, including
- muscle contractions
- nerve impulses
- Digestion
- Blood pressure
- heart rhythm
- pH balance
Drawbacks to Goat Meat?
The only nutritional drawback of goat meat is that it is a very lean meat. This makes it unsuitable on its own for people consuming low-carb high-fat diets like keto and carnivore.
Of course, you can always add a couple of tablespoons of tallow to your stewed goat and meet your macro ratios just fine.
The other drawback to goat is mainly its texture. As a lean meat, goat can taste gamey and tough if not cooked with moist heat. Goat dishes are also prepared with lots of spices to “compliment” the often gamey flavor.
Is Goat Meat Healthy? The Bottom Line
Is goat meat healthy? Certainly! Goat meat is replete with essential nutrients, including complete proteins, healthy fats, B vitamins, iron, zinc, selenium, and potassium.
It’s no wonder that goats were the first domesticated animals and have remained the most popular meat in many parts of the world.