We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Top 8 Benefits of Ghee (Clarified Butter)
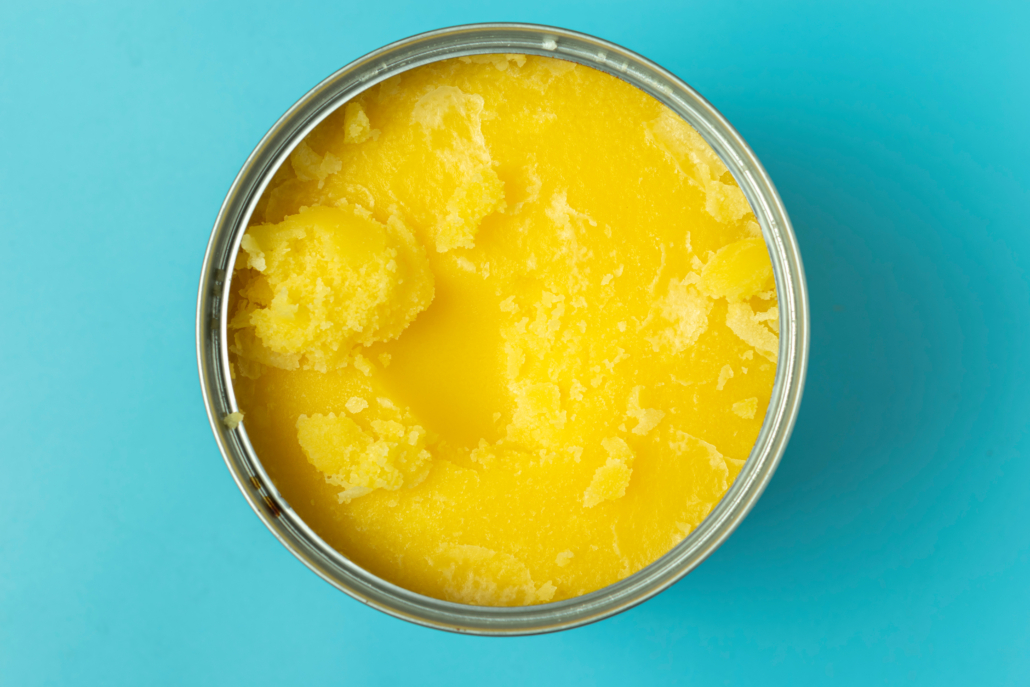

Ghee is a type of butter that has been “clarified” to remove dairy proteins. The result is a delicious, remarkably nutritious fat with numerous health benefits.
In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of ghee as they’re revealed and understood by modern nutritional science.
Table of Contents
What is Ghee?
Ghee is clarified butter. This means it has been simmered to evaporate water content, skimmed of milk solids, and strained to remove any additional impurities.
The glassy, nutty, golden substance that remains in ghee. It’s pure butterfat, with essentially no lactose (dairy sugar), casein (dairy protein) or water content.
Ghee has been the core fat of South Asian cultures for millennia. The traditional Hindu religious scriptures, called the Vedas, refer to ghee as the “first and the most essential of all foods.”
The Mahabharata says, “From ghee flows the sustenance of all the worlds.” It’s believed to increase Dhi (intelligence) refine Buddhi (intellect) and strengthen Smrti (memory).
The literal deification of ghee speaks to the primal centrality of fat in the human diet. Our brains and bodies need healthy fats to thrive.
More recently, ghee has made a deserving splash in the nutritional health and wellness communities worldwide.
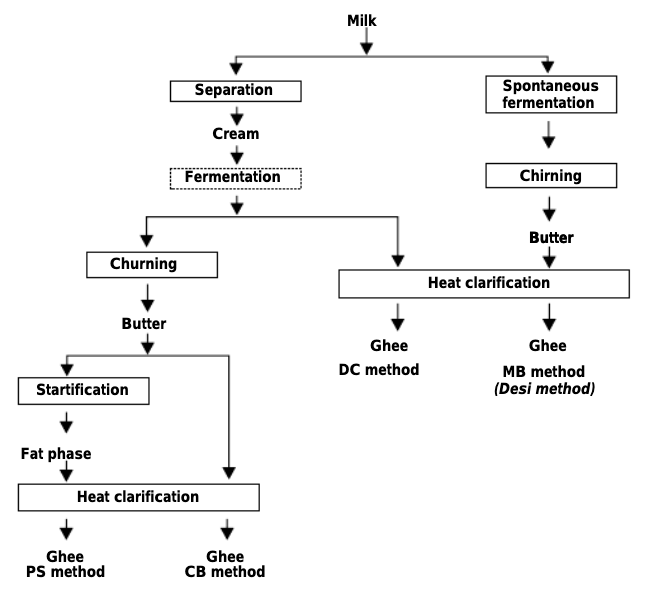
Source: Indian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Life Sciences 2016. www.cibtech.org/sp.ed/jls/2016/02/jls.htm 2016
What Does Ghee Taste Like?
High-quality ghee smells and tastes nutty, with a hint of caramel. Imagine taking the root flavor of butter and turning it up a few notches.
Ghee Nutrition
| Ghee (1 tbsp, 14.8 grams) | |
| Calories | 123 calories |
| Total fat | 14 grams |
| Saturated fat | 8.7 grams |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4 grams |
| Cholesterol | 36 mg |
| Sodium | 0.3 mg |
| Carbohydrates | 0 grams |
| Protein | 0 grams |
| Vitamin A | 117 mcg |
| Vitamin E | 0.39 mg |
| Vitamin K | 1.2 mcg |
| Calcium | 0.56 mg |
| CLA (conjugated linoleic acid) | 148 mg |
8 Powerful Benefits of Ghee
Ghee is essentially 97% fat, so the benefits of ghee will be based primarily on its fatty acid profile.
Studies show that ghee is high in medium and short-chain saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, and Omega-3 fatty acids.
Now let’s explore the top 8 most potent benefits of ghee.
1. Rich in Conjugated Linoleic Acid
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is a highly beneficial fatty acid produced when cows ferment the grass they eat in their rumen stomach.
Ghee from grass-fed cows has been found to provide 10 mg of CLA per gram of fat. This makes ghee one of the most potent sources of CLA out there.
Studies show that consuming CLA is associated with powerful health benefits, including
- Reduction in body fat and increase in lean muscle mass
- Reduced risk of heart disease
- Supports immune response and reduces inflammation
- Combats diabetes
- Improves bone density
A 2021 study on mice with pancreatitis found that ghee effectively reduced inflammation.5
Since we humans don’t have a rumen stomach that ferments grass, we can’t produce CLA on our own. So we rely on the products of grass fed cow, sheep, buffalo, and goats.
It’s also worth noting that the CLA that you get in supplement form is made from toxic vegetable “seed” oils. Not surprisingly, supplemental CLA is associated with numerous adverse health effects, including increased inflammation, Insulin resistance, spiked HDL (bad cholesterol), and diarrhea.
The moral of the story is to get your CLA from natural sources like ghee.
2. High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
A tablespoon of ghee provides around 200 mg or 20% RDV of omega-3 fatty acids.
This essential polyunsaturated fatty acid has been found to help prevent heart disease and stroke, protect against various cancers, and relieve numerous autoimmune disorders, including lupus, eczema, and rheumatoid arthritis.
3. High in Monounsaturated Fatty Acids
Monounsaturated fatty acids and Conjugated Linoleic Acids found in ghee make up 20-30% of the fat content.
Monounsaturated fatty acids have been shown to
- Reduce inflammation
- reduce bad cholesterol
- increase good cholesterol
- Potentially reduce the risk of heart disease
4. Butyrate
Butyrate, one of the saturated fatty acids in ghee, has been shown to support insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and can reduce symptoms of IBS, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease.
5. Promotes Skin and Heart Health
In addition to healthy fats, ghee also provides antioxidants and vitamins that promote skin health when eaten and when applied topically.
A 2023 study found that “ghee possesses antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antiseptic properties, making it beneficial for treating skin-associated problems.”
In another study, patients consumed 60 ml of ghee daily for seven days. On average, the group experienced an 8.3% decrease in serum total cholesterol, a 26.6% reduction in serum triglycerides, a 17.8% decrease in serum phospholipids, and a 15.8% decrease in serum cholesterol esters.
In addition to these positive effects on blood lipids, the patients also enjoyed a significant reduction in scaling, erythema, pruritis, and itching and striking improvements in overall skin appearance.
A 2018 study of 200 people in India found that participants who consumed more ghee and less vegetable oil had healthier serum lipid markers associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
6. High Smoke Point
At a smoke point of 450°F or 232°C, ghee is the best animal fat for high-heat cooking.
This high smoke point means that it’s suitable for frying and sauteing without degrading into potentially harmful compounds.
By comparison, the smoke point of butter is only 350°F.
7. Lactose and Casein-Free
Most people with lactose intolerance and/or dairy allergies tolerate ghee.
This is because the lactose (milk sugar), and casein (dairy protein) that account for most adverse reactions are removed during the process of clarification.
8. Increased Nutrient Absorption
Much has been made about the modest amounts of important fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K2 in ghee.
But ghee’s major nutritive effect is to aid in the absorption of these same fat-soluble vitamins from more vitamin-dense yet leaner foods like liver, steak, and lamb.
Ghee aids in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and phytonutrients from other foods, making your meals more nutritionally beneficial.
Increased intake and absorption of vitamin A retinol (the kind of vitamin A that you can only get from animal products), is critical for maintaining eye health, immune function, and skin health.
The Benefits of Ghee: The Takeaway
Ghee is a type of clarified butter. This means that it’s been filtered by heat and strained to remove lactose and dairy proteins. The result is a wonderfully fatty, golden substance that’s suitable for most people who are allergic to lactose and dairy proteins.
Since ghee is 97% pure fat, the benefits of ghee derive from its excellent fatty acid profile. These benefits include
- An abundance of beneficial conjugated linoleic acids, Omega-3 fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, and short and medium-chain saturated fatty acids
- Improved skin health
- Supports heart health due to anti-inflammatory and serum lipid improvements
- High smoke point for high-heat cooking
- Lactose and casein free (less allergenic)
- Increases absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.