We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Meat Based Diet: Approaches and Health Benefits

In recent years, there has been a surge of interest and experimentation with the meat-based dietary wisdom of our ancestors. Numerous meat-based diets, ranging from restrictive carnivore elimination diets to more relaxed meat based diets that include dairy, greens, and fruit, have had their time in the limelight.
In this article, we’ll explore the various modern approaches to meat based diets, along with their rationale and health benefits.
Table of Contents
What are Meat Based Diets?
Meat-based diets are approaches to eating in which you get the vast majority of your calories from meat and animal products.
These diets are typically centered around red meat, especially from ruminant animals like cows, bison, lamb, elk, and goat. Ruminant meats have the most favorable fatty acids, fat-to-protein ratios, and the most abundance of the widest array of micronutrients.
Many approaches to a meat based diet prize organ meats, which are the most nutrient-dense foods on earth. While other popular meat based diet foods include poultry, pork, fish, shellfish, and full-fat dairy.
Since meat is essentially a zero carb food, most meat based diets are ketogenic, meaning that they require high-fat and moderate protein intake.
Because of the fat requirements most meat based meals are augmented with nourishing animal fats like butter, ghee, and tallow.
Origins of Meat Based Eating
Meat based diets aren’t a newfangled diet trend; they’re a return to ancestral eating patterns.
The philosophy supporting meat based eating is based on significant research revealing that our hunter-gatherer ancestors evolved on a hypercarnivorous diet for nearly 2 million years.
The dietary reasoning follows that in a world teaming with huge animals (called “megafauna”) it would be a waste of energy/calories to collect/gather far less nutritious plant foods.
Our species only began turning to agriculture 10,000 years ago, in large part because we had become so skilled at hunting large land animals that their populations collapsed.
A study of the 229 remaining hunter-gatherer groups found that on average, animal foods provided over two-thirds of calories, with a range of 26 to 99 percent.
It’s important to keep in mind that these are modern hunter-gatherers in a world that has far fewer large animals than our ancestors had access to. This strongly suggests that when given the chance, humans seek and eat meat above all other food sources.
![Intro In recent years there has been a surge of interest and experimentation with the meat-based dietary wisdom of our ancestors. Numerous meat-based diets ranging from restrictive carnivore elimination diets, to more relaxed meat based diets that include dairy, greens, and fruit, have had their time in the limelight. In this article, we’ll explore the various modern approaches to meat based diets, along with their rationale and health benefits. What are Meat Based Diets? Meat-based diets are approaches to eating in which you get the vast majority of your calories from meat and animal products. These diets are typically centered around red meat, especially from ruminant animals like cows, bison, lamb, elk, and goat. Ruminant meats have the most favorable fatty acids, fat-to-protein ratios, and the most abundance of the widest array of micronutrients. Many approaches to a meat based diet prize organ meats, which are the most nutrient-dense foods on earth. While other popular meat based diet foods include poultry, pork, fish, shellfish, and full-fat dairy. Since meat is essentially a zero carb food, most meat based diets are ketogenic, meaning that they require high-fat and moderate protein intake. Because of the fat requirements most meat based meals are augmented with nourishing animal fats like butter, ghee, and tallow. Origins of Meat Based Eating Meat based diets aren’t a newfangled diet trend, they’re a return to ancestral eating patterns. The philosophy supporting meat based eating is based on significant researching revealing that our hunter gatherer ancestors evolved on a hypercarnivorous diet for nearly 2 million years. The dietary reasoning follows that in a world teaming with huge animals (called “megafauna”) it would be a waste of energy/calories to collect/gather far less nutritious plant foods. [6] Our species only began turning to agriculture 10,000 years ago, in large part because we had become so skilled at hunting large land animals that their populations collapsed. [9] A study of the 229 remaining hunter-gatherer groups found that on average, animal foods provided over two-thirds of calories, with a range of 26 to 99 percent. [7] [8] It’s important to keep in mind that these are modern hunter gatherers in a world that has far fewer large animals than our ancestors had access to. This strongly suggests that when given the chance, humans seek and eat meat above all other food sources. Nutrients in a Meat Based Diet Much is made by meat based enthusiasts about how “nutrient dense” animal products are. And the research supports their excitement. Meat and animal products are far and away the best source of proteins, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Below we’ll summarize some of the nutrients that are found exclusively, or in appreciable quantities, in meat. Vitamin B12 B12 is an essential nutrient that your body needs for proper neurological function and the formation of red blood cells. Found only in meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. [13] [14] Omega-3 fatty acids An essential fatty acid–which means you can only get it from food. Omega-3s play a critical role in heart health, brain function, controlling inflammatory responses, and overall well-being. Vitamin D3 In the right conditions, your body can get most of its vitamin D from sunshine. Yet most people don’t get enough sun and are vitamin D deficient. Your body needs vitamin D to regulate calcium and phosphorus absorption, support bone health, proper immune function, and inflammation control. Creatine Found almost exclusively in animal products, particularly in meat, creatine is important for muscle growth and maintenance. Vitamin A (retinol) One of the most important vitamins, A is essential to maintaining vision,immune function, and reproduction, and physical development. [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] You may have heard of plants like carrots containing vitamin A, but this is in a carotene form which is only a precursor to vitamin A. 45% of people have a genetic variation that makes it impossible to convert and use vitamin A from plants, while everyone else can convert only a very small amount. This makes vitamin A (retinol) from plant foods extremely important. [9][10] [11] Heme iron Heme iron is needed for the transport oxygen throughout your body, and it’s a component of hemoglobin in red blood cells and myoglobin in muscle cells. Though you can get some iron from plants, your body has a hard time using it. While heme iron from animals is easily used by the body. This is why vegans and vegetarians are often iron deficient.18 19 20 Other Essential Nutrients There are various other nutrients that exist to some degree in plants, yet are far more abundant and useable when sourced from animal products. These nutrients include zinc, vitamin K, choline, and selenium. [6] Benefits of a Meat Based Diet The most important study on the benefits of the meat based diet came out of Harvard university and was published in 2021. This massive study gathered self-reported data from 2,029 people who had been eating a carnivore diet for at least 6 months. [41] Lead researchers Dr. Belinda Lennerz and Dr. David Ludwig concluded: “Contrary to common expectations, adults consuming a carnivore diet experienced few adverse effects and instead reported health benefits and high satisfaction.” [1] Significant of the remarkable benefits reported by meat-based eaters included 93% improved or resolved obesity and excess weight 93% improved hypertension 98% improved conditions related to diabetes 97% improved gastrointestinal symptoms 96% improved psychiatric symptoms Now let’s compare the different types of all meat diets. Standard Carnivore Diet The standard carnivore diet means eating only animals products and eliminating all plant foods including fruits, veggies, grains, nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils. Like most most meat based diets, the standard carnivore diet is centered around fatty ruminant meats, augmented with pork, eggs, seafood, poultry, and dairy if tolerated. Most carnivore dieters experiment with some organ meats, especially beef liver. Nose-to-Tail Meat Based Diet Nose-to-tail meat based eating means consuming a variety of meats, including organ meats like liver, spleen, marrow, heart, pancreas, and brains. This is likely the closest to a truly ancestral meat based diet that modern humans will get. Many nose-to-tail dieters also allow for full fat dairy products. Lion “Elimination Diet” The lion diet was popularized by Michaela and Jordan Peterson. It entails eliminating all foods but meat, salt, and water. The meat in this diet is only from ruminant animals, and requires the fattiest cuts. As an elimination protocol, the lion diet makes you the subject of your own nutritional study. In the short term, this approach is aimed at eliminating all variables–especially toxic plant compounds–that may be contributing to metabolic issues, chronic inflammation, and digestive problems. Carnivore Adjacent Diet The “carnivore adjacent” meat based diet entails getting 80-90% of your calories from animal products, and the remainder from low-carb and low toxin plants, fruits, nuts, and seeds. It still requires cutting out all processed foods, added sugars, grains, and vegetable oils. Many people use this approach as “training wheels” on the path to a full carnivore diet. Meat and Greens Diet The meat and greens diet means eating only fatty meat, greens, water, and salt. Some people allow grass-fed butter, while other insist on cooking only in animal fats like tallow. This is another version of a meat based elimination diet. After 30-90 days of dieters often explore adding full-fat dairy, eggs, pork, poultry, and seafood. Like the other meat based diets on this list, meat and greens diet eliminates all industrial foods, including toxic seed “vegetable” oils, grains, and sugars. It’s worth noting that greens are high in a particularly plant toxin called oxalic acid that can cause intestinal issues and block the absorption of various nutrients. Meat and Fruit Diet The meat and fruit approach to a meat-based diet was popularized by “Carnivore, M.D.” Paul Saladino. After years of consuming and promoting a meat-only diet, Saladino found that his electrolyte levels were unstable. When he moved to Costa Rica he began exploring the effects of eating fruit and found that his insulin was lower when eating fruit and meat and when on a fully ketogenic diet. Saladino then discovered that having more stable insulin levels helped with electrolyte balance. Podcast host Joe Rogan is another meat based enthusiast who claims that meat and fruit make up 90% of his diet. Some people doing the meat and fruit approach focus only on fruits high in vitamin C and keep their carb contributions to less than 50 grams per day. While others, like Saladino, jettison carb counting and eat up to 200 or 300 grams of fruit carbs per day. The meat and fruit diet may be a good approach for hard-training athletes who deplete glycogen stores and need to reload to maintain athletic performance. Meat Based Diets: The Bottom Line Meat based diets offer a way to realign our modern dietary habits with the way our hunter gatherer ancestors ate for the vast majority of our time on earth. Meat based diets provide an abundance of the most nutrient dense foods on earth, while eliminating all processed industrial foods, added sugars, and vegetable oils. This way of eating can help regulate blood sugar, eliminate harmful plant toxins and antinutrients, reduce inflammation and autoimmune disorders, increase testosterone and libido, improve mental clarity, increase energy, and support overall wellbeing. time line of human carnivory](https://www.doctorkiltz.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Figure-1-Human-brain-Dr.-Miki-Ben-Dor-1536x689-2-1440x646-2-1030x462.jpg)
Source: Dr Miki Ben Dor
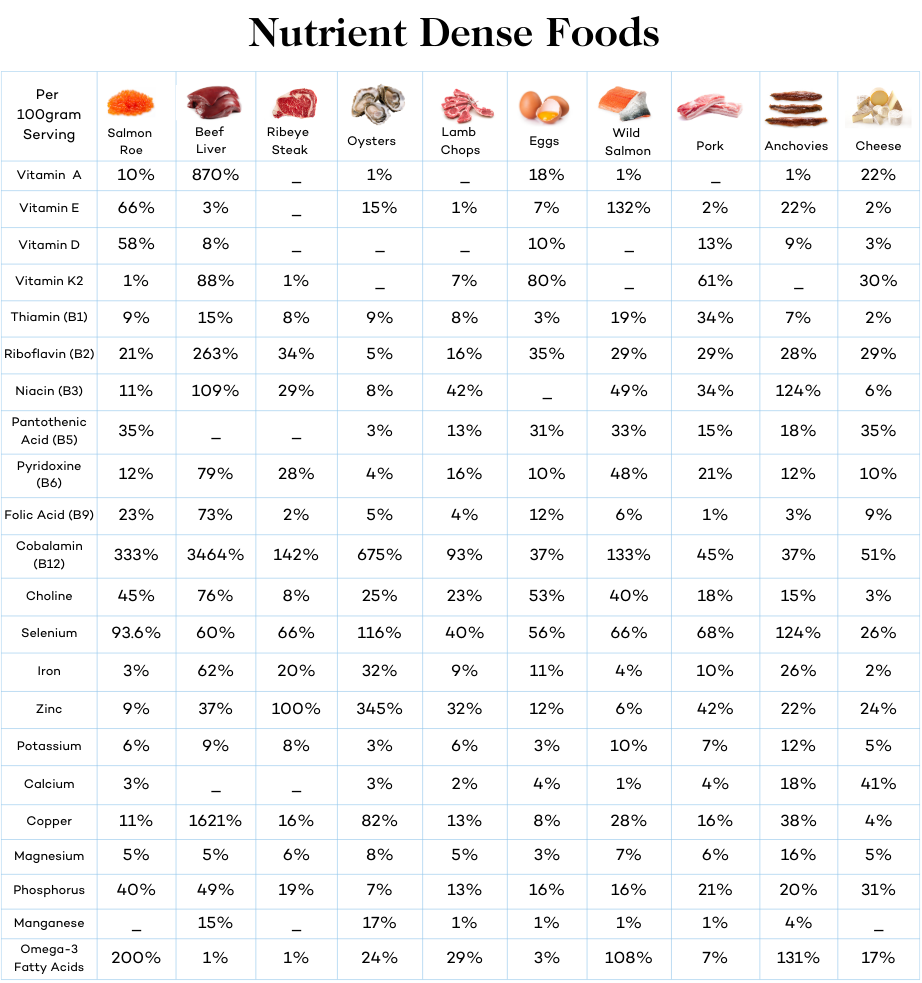
Nutrients in a Meat Based Diet
Much is made by meat based enthusiasts about how “nutrient-dense” animal products are. And the research supports their excitement. Meat and animal products are far and away the best sources of proteins, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals.
Below, we’ll summarize some of the nutrients that are found exclusively, or in appreciable quantities, in meat.
Vitamin B12
B12 is an essential nutrient that your body needs for proper neurological function and the formation of red blood cells. Found only in meat, fish, eggs, and dairy.
Omega-3 fatty acids
An essential fatty acid–which means you can only get it from food. Omega-3s play a critical role in heart health, brain function, controlling inflammatory responses, and overall well-being.
Vitamin D3
In the right conditions, your body can get most of its vitamin D from sunshine. Yet most people don’t get enough sun and are vitamin D deficient. Your body needs vitamin D to regulate calcium and phosphorus absorption, support bone health, proper immune function, and inflammation control.
Creatine
Found almost exclusively in animal products, particularly in meat, creatine is important for muscle growth and maintenance.
Vitamin A (retinol)
One of the most important vitamins, A is essential to maintaining vision, immune function, reproduction, and physical development. You may have heard of plants like carrots containing vitamin A, but this is in a carotene form which is only a precursor to vitamin A. 45% of people have a genetic variation that makes it impossible to convert and use vitamin A from plants, while everyone else can convert only a very small amount. This makes vitamin A (retinol) from plant foods extremely important.
Heme iron
Heme iron is needed for the transport of oxygen throughout your body, and it’s a component of hemoglobin in red blood cells and myoglobin in muscle cells. Though you can get some iron from plants, your body has a hard time using it. While heme iron from animals is easily used by the body. This is why vegans and vegetarians are often iron deficient.
Other Essential Nutrients
There are various other nutrients that exist to some degree in plants, yet are far more abundant and useable when sourced from animal products. These nutrients include zinc, vitamin K, choline, and selenium.
Benefits of a Meat Based Diet
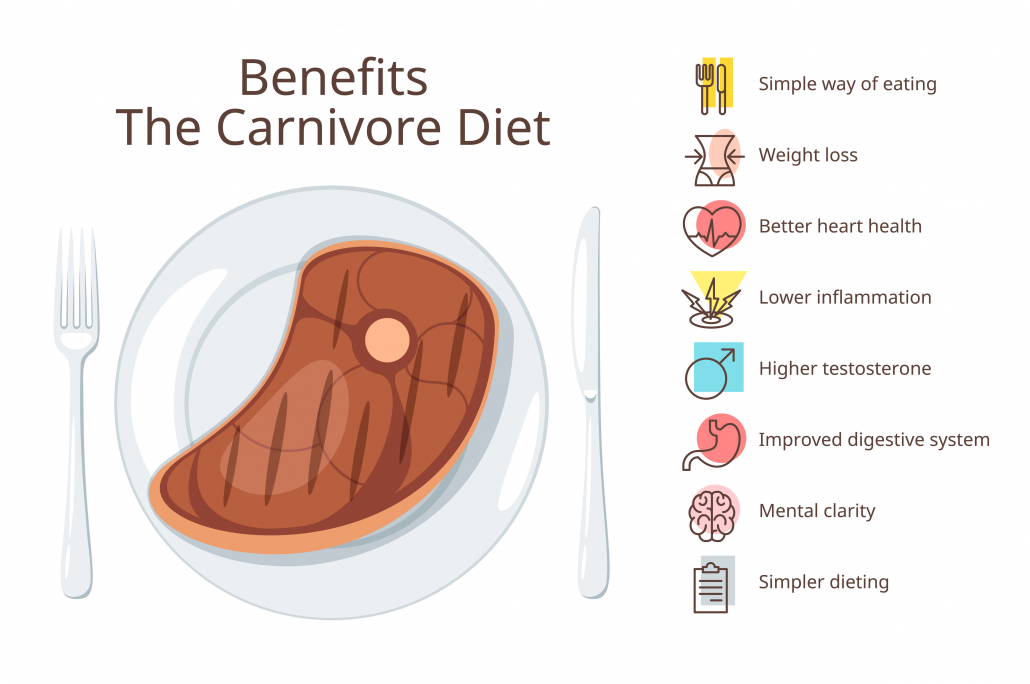
The most important study on the benefits of the meat based diet came out of Harvard university and was published in 2021.
This massive study gathered self-reported data from 2,029 people who had been eating a carnivore diet for at least 6 months.
Lead researchers Dr. Belinda Lennerz and Dr. David Ludwig concluded: “Contrary to common expectations, adults consuming a carnivore diet experienced few adverse effects and instead reported health benefits and high satisfaction.”
Some of the remarkable benefits reported by meat-based eaters included
- 93% improved or resolved obesity and excess weight
- 93% improved hypertension
- 98% improved conditions related to diabetes
- 97% improved gastrointestinal symptoms
- 96% improved psychiatric symptoms

Now let’s compare the different types of all meat diets.
Standard Carnivore Diet
The standard carnivore diet means eating only animal products and eliminating all plant foods, including fruits, veggies, grains, nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
Like most meat based diets, the standard carnivore diet is centered around fatty ruminant meats, augmented with pork, eggs, seafood, poultry, and dairy if tolerated.
Most carnivore dieters experiment with some organ meats, especially beef liver.
Nose-to-Tail Meat Based Diet
Nose-to-tail meat based eating means consuming a variety of meats, including organ meats like liver, spleen, marrow, heart, pancreas, and brains.
This is likely the closest to a truly ancestral meat based diet that modern humans will get.
Many nose-to-tail dieters also allow for full-fat dairy products.
Lion “Elimination Diet”
The lion diet was popularized by Michaela and Jordan Peterson. It entails eliminating all foods but meat, salt, and water.
The meat in this diet is only from ruminant animals, and requires the fattiest cuts. As an elimination protocol, the lion diet makes you the subject of your own nutritional study.
In the short term, this approach is aimed at eliminating all variables–especially toxic plant compounds–that may be contributing to metabolic issues, chronic inflammation, and digestive problems.
Carnivore Adjacent Diet
The “carnivore adjacent” meat based diet entails getting 80-90% of your calories from animal products, and the remainder from low-carb and low toxin plants, fruits, nuts, and seeds.
It still requires cutting out all processed foods, added sugars, grains, and vegetable oils. Many people use this approach as “training wheels” on the path to a full carnivore diet.
Meat and Greens Diet
The meat and greens diet means eating only fatty meat, greens, water, and salt. Some people allow grass-fed butter, while others insist on cooking only in animal fats like tallow.
This is another version of a meat based elimination diet. After 30-90 days of dieters often explore adding full-fat dairy, eggs, pork, poultry, and seafood.
Like the other meat based diets on this list, meat and greens diet eliminates all industrial foods, including toxic seed “vegetable” oils, grains, and sugars.
It’s worth noting that greens are high in a particular plant toxin called oxalic acid that can cause intestinal issues and block the absorption of various nutrients.
Meat and Fruit Diet
The meat and fruit approach to a meat-based diet was popularized by “Carnivore, M.D.” Paul Saladino.
After years of consuming and promoting a meat-only diet, Saladino found that his electrolyte levels were unstable. When he moved to Costa Rica he began exploring the effects of eating fruit and found that his insulin was lower when eating fruit and meat and when on a fully ketogenic diet. Saladino then discovered that having more stable insulin levels helped with electrolyte balance.
Podcast host Joe Rogan is another meat based enthusiast who claims that meat and fruit make up 90% of his diet.
Some people doing the meat and fruit approach focus only on fruits high in vitamin C and keep their carb contributions to less than 50 grams per day.
While others, like Saladino, jettison carb counting and eat up to 200 or 300 grams of fruit carbs per day.
The meat and fruit diet may be a good approach for hard-training athletes who deplete glycogen stores and need to reload to maintain athletic performance.
Meat Based Diets: The Bottom Line
Meat based diets offer a way to realign our modern dietary habits with the way our hunter-gatherer ancestors ate for the vast majority of our time on earth.
Meat based diets provide an abundance of the most nutrient-dense foods on earth, while eliminating all processed industrial foods, added sugars, and vegetable oils.
This way of eating can help regulate blood sugar, eliminate harmful plant toxins and antinutrients, reduce inflammation and autoimmune disorders, increase testosterone and libido, improve mental clarity, increase energy, and support overall well-being.