We include products in articles we think are useful for our readers. If you buy products or services through links on our website, we may earn a small commission.
Top 10 Glutamine Foods and Benefits

Glutamine is a vital amino acid that plays many beneficial roles in the body. The best way to get glutamine is from high glutamine whole foods like steak, pork, eggs, dairy, and seafood.
As an amino acid, glutamine is a building block for proteins. It is also a powerful factor in promoting intestinal health and immune function.
Let’s take a closer look at the best l-glutamine foods and the benefits of this important amino acid.
Table of Contents
What is Glutamine?
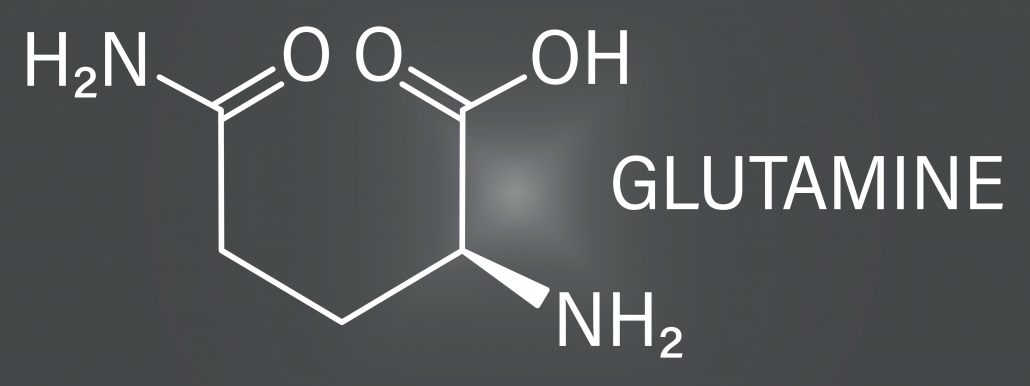
Glutamine comes in two forms, L-glutamine and D-glutamine. Though molecularly similar, the type found in foods is L-glutamine, and D-glutamine isn’t remotely as important [1].
As an amino acid, L-glutamine factors in a number of critical bodily functions, including [2][3]:
- creating proteins
- Immunity
- gut health
- transporting substances through the blood
- supporting organ health
L-glutamine is the most abundant amino acid circulating in your body, and our bodies can produce most of the glutamine it needs [3][4][5].
Though there are times when we’re stressed, healing from injuries, and when fighting disease and infection when our bodies cannot produce enough glutamine and we have to get it from our food [6]. This means that l-glutamine is a ‘conditionally essential amino acid.
Top 10 Glutamine Foods
A typical standard American diet provides between 3-6 grams of glutamine per day [6], But some of this comes from inferior plant sources like soy and corn that are high in unhealthy plant toxins and antinutrients like phytohormones and phytic acid.
Since glutamine is an amino acid, the best glutamine foods will be animal products high in protein. But as Dr. Kiltz and researchers like Amber O’Hearn point out, humans evolved on a diet of fatty meats.
So the best glutamine foods will have a combination of both high levels of glutamine and high levels of healthy fats.
Let’s take a look at the top l-glutamine foods.
1. Ribeye Steak-6916mg in 1 270 gram filet
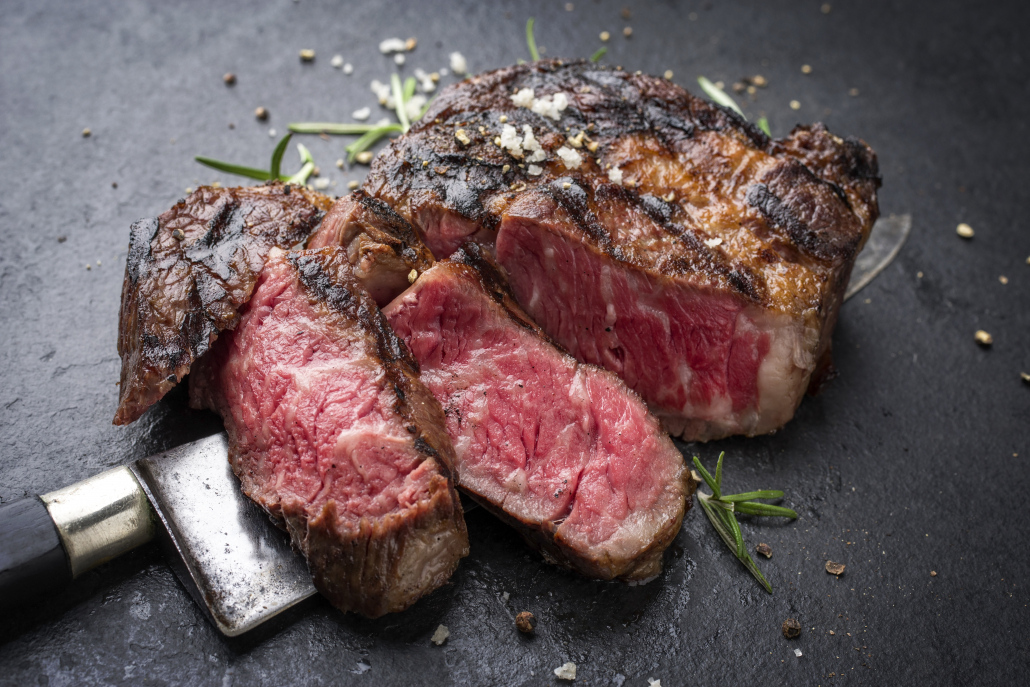

Ribeye is not only the tastiest but the most nutritionally replete cut of steak.
In addition to robust amounts of glutamine, ribeye offers an abundance of healthy fats, B vitamins, zinc, and numerous meat-specific nutrients like carnosine and carnitine.
The zinc provided by ribeye steak is 400% more bioavailable than the kind you find in breakfast cereals [7]. Zinc is cardioprotective and essential to our immune system, thereby enhancing the immune-boosting properties of this high glutamine food.
In men, zinc deficiency is associated with lower sperm count and erectile dysfunction [8].
Ribeye is so healthy in fact, that it is possible to thrive on a carnivore diet of mostly ribeye, salt, and water
2. Skirt Steak- 9428mg in 6oz
Skirt steak is another nutrient-dense ruminant meat that provides a complete matrix of macro and micronutrients.
However, when consuming skirt steak on keto, it may be somewhat lean when considering your keto macro percentages. Consider boosting your fat content with tallow or ghee.
3. Lamb Shoulder Roast- 8767mg in 6oz
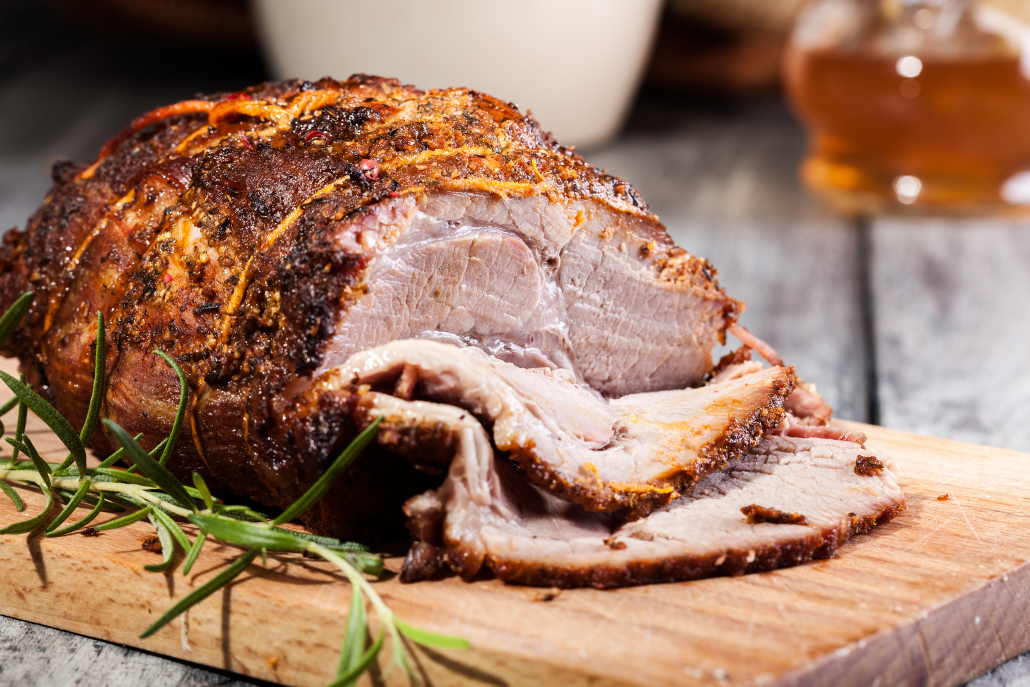

In addition to high levels of glutamine, lamb shoulder is also high in a beneficial fatty acid called Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)
CLA may have powerful anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties [9][10].
4. Pork Chops (With Fat)- 8353mg in 1 chop
. Pork chops are also high in a micronutrient called Choline. Though flying under most people’s nutritional radar, choline plays a key role in balancing your nervous system, regulating mood, boosting memory, and the formation of cell membranes [11].
Choline also provides more powerful antioxidant effects than Vitamin E [12].
5. Chicken Leg- 9979mg in 1 leg, with skin
Chicken legs with skin contain the most glutamine of any food on this list, but they are lower in other essential nutrients like vitamin B. So if you’re just looking to boost glutamine, chicken legs are a solid choice. Wrap it in bacon for a boost of both flavor and glutamine!
6. Pork Tenderloin- 7902mg in 6oz
In addition to high levels of glutamine, pasture-raised pork is also a rare dietary source of vitamin D. Both vitamin D and glutamine have powerful immune-supporting functions.
7. Cooked Coho Salmon (Wild)- 6945mg in 6oz fillet
Wild coho salmon is a fatty keto fish with a robust amount of glutamine and vitamin B.
8. Ground Beef – 6715mg in 6oz
Ground beef is so common that it’s easy to forget how nutritious it is, especially from pasture-raised cows. It’s high in glutamine, B vitamins, zinc, and selenium.
9. Snapper- 6673mg in 1 fillet
Snapper is one of the highest glutamine sources among seafood. It is also one of the most robust dietary sources of vitamin D, with 138% RDV per 200 grams.
Add in the 138% of selenium and numerous B vitamins and the only thing that’s missing is fat. Drizzle generously with butter or olive oil to make snapper the centerpiece of a Mediterranean keto or pescatarian keto dinner.
10. Atlantic Mackerel- 6050mg in 6oz fillet
Atlantic mackerel is also a great source of vitamin D, which has been shown to be effective in reducing the severity of viral infections, including COVID-19 [13].
As one of the world’s most fatty fish, a single 3 oz serving provides a robust 2990 mg of omega-3.
Glutamine Supports the Immune System
Glutamine plays a vital role in supporting the immune system by fueling white blood cells and intestinal cells [14]
Getting sufficient glutamine from food can become critically important when levels decrease due to burns, injuries, chronic stress, and surgeries [15][16].
If you don’t get enough glutamine, your immune system becomes compromised. Doctors often prescribe high glutamine foods and supplementation when recovering from injuries and surgery [17][18][19].
If you don’t get enough glutamine from food, your body will turn to break down muscle to synthesize it [20][21].
Studies show that glutamine supplements can reduce infection and lead to shorter hospital stays after surgeries [22].
In critically ill patients, glutamine supplementation has been shown to increase survival rates and reduce medical costs [23][24].
In studies of animals infected with bacteria or viruses, supplementation with glutamine has been shown to improve immune function [25][26].
In healthy adults, getting l-glutamine through high glutamine foods in your diet is enough to receive its immune-boosting benefits without the need for supplementation [27].
Glutamine Supports Intestinal Health
A key to the immune-supporting benefits of l-glutamine is how it supports intestinal health.
In fact, the intestines and digestive system are the largest physical components of the immune system in the human body.
Intestinal cells serve critical immune functions, the health of your microbiome–the community of bacteria in your intestines–plays a major role in immune response, and the integrity of our gut lining protects us from pathogens, sugars, and plant toxins from crossing the intestinal barrier and entering our bloodstream [28][29][30].
By fueling intestinal cells, glutamine helps maintain tight joints in the intestinal walls, which protects against leaky gut [31][32].
Dosage, Safety, and Side Effects
As the most common amino acid produced naturally in the body, there is no risk of harm when consuming it from food.
Studies have shown supplementation beyond what you get from food to be generally safe.
Studies on dosages from 5-45 grams per day for six weeks showed no negative side effects [33][34]. However, some experts are concerned about the sustained use of supplementation [35].
The safest and most sustainable way to ensure robust glutamine levels is to consume it the way nature intended as part of a complex nutritional matrix found in whole animal foods.
Glutamine and Cancer
Since some cancer cells use glutamine for fuel, there has been some concern that glutamine may fuel cancer. However, research tells us that this is not the case.
Researchers have concluded, “A large body of evidence in vivo suggests that supplemental glutamine does not make tumors grow but in fact, results in decreased growth through stimulation of the immune system. When given with radiation or chemotherapy, glutamine protects the host and actually increases the selectivity of therapy for the tumor” [36].
Glutamine Foods: The Takeaway
L-glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid, meaning that our body produces sufficient amounts on its own, but when stressed or injured, we need to get more of it from our food.
Glutamine plays key roles in fueling immune cells and intestinal cells, which support our immune system and protect our bodies from infection by viruses and bacteria and from inflammation and autoimmune disorders due to plant toxins.
Consuming high glutamine whole foods from animal sources is an excellent way to nourish the body with this important amino acid while providing an abundance of essential macro and micronutrients, including complete proteins, healthy fats, B vitamins, zinc, choline, selenium, and numerous beneficial meat-specific compounds.